Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Knee Posterior Cruciate Ligament
- Article Author:
- Chandler Cox
- Article Author:
- Steven Graefe
- Article Editor:
- Bruno Bordoni
- Updated:
- 7/31/2020 5:35:00 PM
- For CME on this topic:
- Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Knee Posterior Cruciate Ligament CME
- PubMed Link:
- Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Knee Posterior Cruciate Ligament
Introduction
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) derives its name for its attachment to the posterior aspect of the tibia and the 'cross' structure formed with the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) inside the joint capsule of the knee. Similar to the other ligaments in the knee, the function of the PCL is to provide stabilization of the knee joint. It is one of two cruciate ligaments of the knee that acts primarily to restrict posterior tibial translation relative to the femur. The PCL is the functional counterpart of the ACL, which prevents excessive anterior tibial translation relative to the femur. Together, the cruciate ligaments act as static stabilizers that hold the knee joint together throughout its full range of motion.[1]
The PCL is the largest and strongest ligament in the knee and consists of two bundles: the anterolateral bundle and the posteromedial bundle. The PCL is susceptible to injury by a posterior force to the proximal tibia when the knee is in the flexed position. For example, in motor vehicle collisions with anterior impact, the driver's knee hits the dashboard causing posterior displacement of the proximal tibia and injuring the PCL. PCL injuries rarely occur in isolation and most commonly involve damage to other ligaments of the knee as well. The posterior drawer test is useful to assess the stability of the PCL clinically, and magnetic resonance imaging can confirm a PCL injury or tear.[2][3][4]
Structure and Function
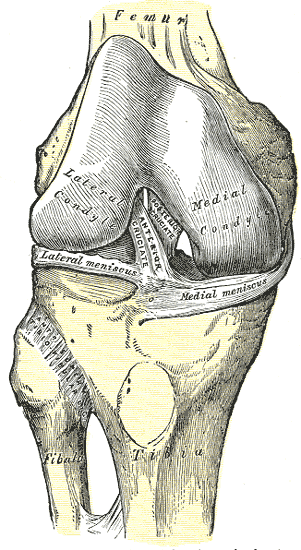
The PCL is one of four major ligaments of the knee involved in the stabilization of the femur and tibia at the knee joint. The other ligaments are the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), the medial collateral ligament (MCL), and the lateral collateral ligament (LCL). The PCL is an intra-articular, extra-synovial structure, as it is inside the joint capsule, but separated from the synovial cavity. The PCL, with a thickness nearly twice that of the ACL, is stronger and has more of a direct path than the ACL. The PCL originates along the posterior aspect of the tibial plateau, specifically at the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia, and passes superiorly, anteriorly, and laterally to insert at the anterolateral margin of the medial condyle of the femur. The PCL's primary function is to prevent posterior translation of the tibia when flexing the knee. It also resists varus, valgus, and internal and external rotational forces on the knee joint. Generally, the PCL is lax when the knee is fully extended and taut when the knee is in flexion.[1][5]
The PCL, like other ligaments in the body, is composed of dense regular connective tissue organized in parallel fashion containing mostly type 1 collagen fibers.
The PCL is comprised of two ligamentous bundles: the anterolateral bundle (ALB) and the posteromedial bundle (PMB). The insertions of these attachments on the femur are used to identify these bundles as the tibial attachments are compact and difficult to differentiate. The anterolateral bundle is larger compared to the posteromedial bundle. The femoral attachment of the ALB, estimated to range from 112 to 118 mm in area, is much larger than the size of its tibial attachment, estimated at around 88 mm. The tibial attachment of the ALB is bordered medially and posteriorly by the PMB, with a horizontal bony prominence known as the 'bundle ridge' separating the two. Overall, the PMB is smaller than the ALB. The femoral attachment of the PMB is estimated to range from 60 to 90 mm in area, while the tibial attachment measures approximately 105 mm along the posteromedial aspect of the ALB.[1][5]
Previously researchers thought that the ALB and the PMB had independent functions: the ALB primarily functioning in knee flexion and the PMB in knee extension. However, recent biomechanical studies have found that changes in orientation during knee flexion and extension prevent either bundle from exhibiting a complete dominance in the overall function of the PCL in restraining posterior tibial motion. Recent studies have also identified the PCL as a secondary restraint to both internal and external rotation, particularly between 90 and 120 degrees of flexion.[1][5]
Posterior Cruciate Ligament:
- Origin: the posterior intercondylar region of the tibia
- Insertion: the anterolateral margin of the medial condyle of the femur
- Function: prevention of posterior translation of the tibia relative to the femur; generalized knee stability
- Blood Supply: middle geniculate artery
- Sensory Innervation: posterior articular nerve
The PCL is composed of two bundles: the anterolateral bundle and the posteromedial bundle
Anterolateral Bundle of the PCL:
- Taut in knee flexion
- Lax in knee extension
Posteromedial bundle of the PCL:
- Taut in knee extension
- Lax in knee flexion
Embryology
Blood Supply and Lymphatics
The blood supply of the PCL primarily comes from the middle geniculate artery, a branch of the popliteal artery. The terminal branches of the middle geniculate artery ultimately form a peri-ligamentous network with the synovial fold covering the PCL. The blood vessels in this peri-ligamentous network penetrate the PCL in a horizontal direction and anastomose with a longitudinally oriented intraligamentous network. The blood vessels within the ligament are in the loose connective tissue situated between the dense connective tissue of the longitudinal ligament fiber bundles. The blood supply within the PCL is not homogeneous. Both fibrocartilaginous entheses at each attachment site of the PCL are devoid of blood vessels. Additionally, the middle third of the PCL is relatively avascular, with the central portion having the least amount of blood supply. The lymphatic drainage of the PCL follows a similar distribution as the blood supply since lymphatics accompany most of the smaller vessels.[8]
Nerves
The PCL receives sensory innervation from the posterior articular nerve, a branch of the tibial nerve. The posterior articular nerve penetrates the posterior capsule of the knee to innervate the PCL. Four types of receptors exist in the PCL: Ruffini slow adapting M-receptors, Pacinian fast adapting M-receptors, Golgi-like tendon receptors, and pain receptors. The afferent feedback to the central nervous system appears to assist in the proprioception and, ultimately, stabilization of the knee.[9]
Muscles
The mechanoreceptors of the posterior ligament influence the musculature that acts on the knee. This mechanoreceptor activity contributes to better neuromuscular coordination during the phases of the gait cycle.
Surgical Considerations
In isolated PCL injuries, the recommendation for surgery is only for acute injuries with severe posterior tibial subluxation and instability. Surgical reconstruction is also the recommended approach when there is damage to other structures in the knee in addition to the PCL. Such cases require surgery within two weeks of the injury to allow for the best anatomical ligament repair of the PCL and to reduce capsular scarring. There is no gold standard approach to PCL reconstruction, and debate exists on the best graft source, placement of tibial and femoral tunnels, the number of graft bundles, and the amount of graft tension. There are several allografts and autologous tissues used for PCL reconstruction. The most common allograft tissue is the Achilles tendon. With allograft reconstruction, surgical time decreases, and there exists a small risk of iatrogenic trauma to the harvest site. As far as autologous tissue grafts are concerned, bone-patellar tendon-bone is most common. The bone plugs allow for sufficient fixation of the tissue, but there is the risk of harvest site morbidity.[10]
Recent literature has investigated whether a single or double-bundle approach to PCL reconstruction using either a tibial inlay or tunnel method results in better outcomes. A double-bundle procedure allows for the reconstruction of both the anterolateral and posteromedial bundles of the PCL, which restores normal knee kinematics across a full range of motion. Comparatively, a single bundle approach only focuses on reconstructing the bigger and stronger anterolateral bundle and has been shown to primarily restore normal knee kinematics through 0 to 60 degrees of knee flexion. However, there has been no literature proving superior functional outcomes of one surgical approach over the other.[10]
There are two methods used by orthopedic surgeons to place the graft with the goal being to recreate the optimal biomechanical restraint of the PCL. The tunnel method is an arthroscopic procedure in which graft placement is in an acute angular turn. The placement of the graft in this method can potentially elongate and thin the graft over time. The tibial inlay approach places the graft near the trough at the tibial insertion of the PCL and avoids having to place the graft in the acute angular turn used in the tunnel method, however, the tibial inlay approach is an open procedure. Additional research may determine if there are better functional, long-term outcomes for one approach over the other.[10]
Like any surgery, PCL reconstruction carries potential complications, including fracture, neurovascular injury to the popliteal artery, deep vein thrombosis, residual laxity, and loss of range of motion. Although reduction of posterior tibial laxity associated with PCL injury is the goal of surgery, residual laxity is the most common problem following surgery; this can be due to an additional undiagnosed PLC or soft tissue injury. Range of motion limitations following surgery typically result from the restriction of knee flexion that is addressable with physical therapy. In more serious cases, the range of motion limitations could be due to improper placement of the graft or excessive tension placed on the graft.[10]
Clinical Significance
Injury to the PCL rarely occurs independently of other knee injuries. ACL, medial collateral ligament (MCL), and posterolateral corner (PLC) injuries are all commonly seen with PCL injuries. While not as common as ACL injuries, there is a 2 to 3% prevalence of PCL injuries in athletic knee injuries and up to a 40% incidence in trauma patients with knee effusions. Mechanisms of PCL injury include hyperextension, posteriorly directed force to the proximal tibia on a flexed knee, forced hyperflexion of the knee, rotation combined with varus or valgus force, and knee dislocation. The mechanism of injury can also often give clues as to whether there is damage to related structures. ACL rupture is common in hyperextension injuries, and rotational injuries with varus or valgus stress typically involve multiple ligaments and meniscal or chondral injury. Classically, the PCL suffers injury by a "dashboard injury." Dashboard injuries occur when a driver collides into another car or another object, and the car's dashboard hits the driver's proximal tibia. This force displaces the tibia posteriorly and injures the PCL.[5][10]
Patients who suffer an isolated PCL injury seldom report a popping or tearing sound or sensation that is common with ACL and MCL injuries. More frequently, patients will complain of vague, non-specific symptoms, such as generalized knee discomfort. Unless there is a concomitant injury to other supporting structures of the knee, patients with PCL injuries rarely report feeling gross instability. Acutely after the injury, patients may complain of knee swelling, stiffness, pain in the posterior aspect of the knee, or pain with deep knee flexion. Patients with a chronic PCL injury may present with vague anterior knee pain, difficulty going up or downstairs, or pain with sprinting or deceleration.[5][10][11]
The physical exam is essential in diagnosing and determining the severity of a PCL injury. The clinician should assess the range of motion in the affected knee, and patients with a PCL tear may present with a 10 to 20-degree loss of knee flexion compared to the uninvolved side. This motion loss is commonly attributed to the tibia shifting posteriorly earlier during knee flexion and thus reaching a range of motion endpoint sooner due to the loss of normal restraint to posterior displacement that the PCL provides. The range of motion is also potentially limited by knee effusion and pain. The posterior drawer test is the most common clinical exam used to assess PCL function. The test is performed with the patient supine while flexing the hip 45 degrees and the knee 90 degrees. It is essential to keep the tibia held in a neutral position with the foot flat on the exam table as this decreases the likelihood of a false-negative test for PCL injury by minimizing the tension through the PLC and allowing maximal posterior tibial subluxation. A posteriorly directed force should be applied to the tibia with the examiner's thumbs while their fingers are wrapped around the tibia assessing for hamstring muscle activation. The goal of the posterior drawer test is to evaluate the amount of posterior translation or step off at the medial joint line. On a normal resting knee, the tibia lies approximately 0-2 mm anterior to femoral condyles. Any posterior tibial translation that is 3 mm or greater is indicative of a positive posterior drawer test and PCL injury. Recent studies have also found that posterior tibial translation greater than 10 mm is suggestive of additional trauma to the PLC. The sensitivity and specificity of the posterior drawer test is reportedly 90% and 99%, respectively.[5][10][11]
In patients with an isolated PCL injury, non-operative management is often the recommended course. Surgery should be considered immediately over non-operative management if other ligamentous structures are damaged, and there is increased rotation instability of the knee. Surgical intervention can also be an option with PCL injuries when conservative, non-operative management has failed or there increased osteoarthritic changes in the PCL-deficient knee present. During acute management of an isolated PCL injury, rehabilitation should focus on reducing knee joint effusion, restoring range of motion, and regaining muscle strength, especially of the quadriceps. Mild tears generally have a rapid recovery, with patients able to return to full activity within two to four weeks of injury. More severe ligamentous tears may require a period of immobilization and partial weight-bearing before beginning physical therapy. These patients should be able to return to full activity within three months of injury. Those that continue to have pain and are unable to resume a pre-injury level of function may require surgical intervention.[5][10][11][12]
(Click Image to Enlarge)
(Click Image to Enlarge)
(Click Image to Enlarge)