Exploratory Data Analysis: Frequencies, Descriptive Statistics, Histograms, and Boxplots
- Article Author:
- Jacob Shreffler
- Article Editor:
- Martin Huecker
- Updated:
- 4/22/2020 12:26:25 PM
- For CME on this topic:
- Exploratory Data Analysis: Frequencies, Descriptive Statistics, Histograms, and Boxplots CME
- PubMed Link:
- Exploratory Data Analysis: Frequencies, Descriptive Statistics, Histograms, and Boxplots
Definition/Introduction
To clearly present findings to a target audience, researchers must utilize exploratory data techniques and create appropriate graphs and figures. By understanding data, researchers can determine if outliers exist, data are missing, and statistical assumptions will be upheld. Additionally, it is essential to comprehend these data when describing them in conclusions of a paper, in a meeting with colleagues invested in the findings, or while reading others’ work.
Issues of Concern
This comprehension begins with exploring these data through the outputs discussed in this article. Individuals who do not conduct research must still comprehend new studies, and knowledge of fundamentals in exploring data and interpretation of histograms and boxplots facilitates the ability to appraise new publications accurately. Without this familiarity, concerning decisions could be implemented based on inaccurate delivery or interpretation of medical studies.
Frequencies and Descriptive Statistics
Effective presentation of study results, in presentation or manuscript form, typically starts with frequencies and descriptive statistics (i.e., mean, medians, standard deviations). One can get a better sense of the variables in examining these data to determine the presence of a balanced and sufficient research design. Frequencies also inform on missing data and give a sense of outliers (will be discussed below).
Luckily, software programs are available to conduct exploratory data analysis. For this chapter, we will be examining the following research question.
RQ: Are there differences in drug life (length of effect) for Drug 23 based on the site of administration?
A more precise hypothesis could be: Is drug 23 longer-lasting when administered via site A compared to site B?
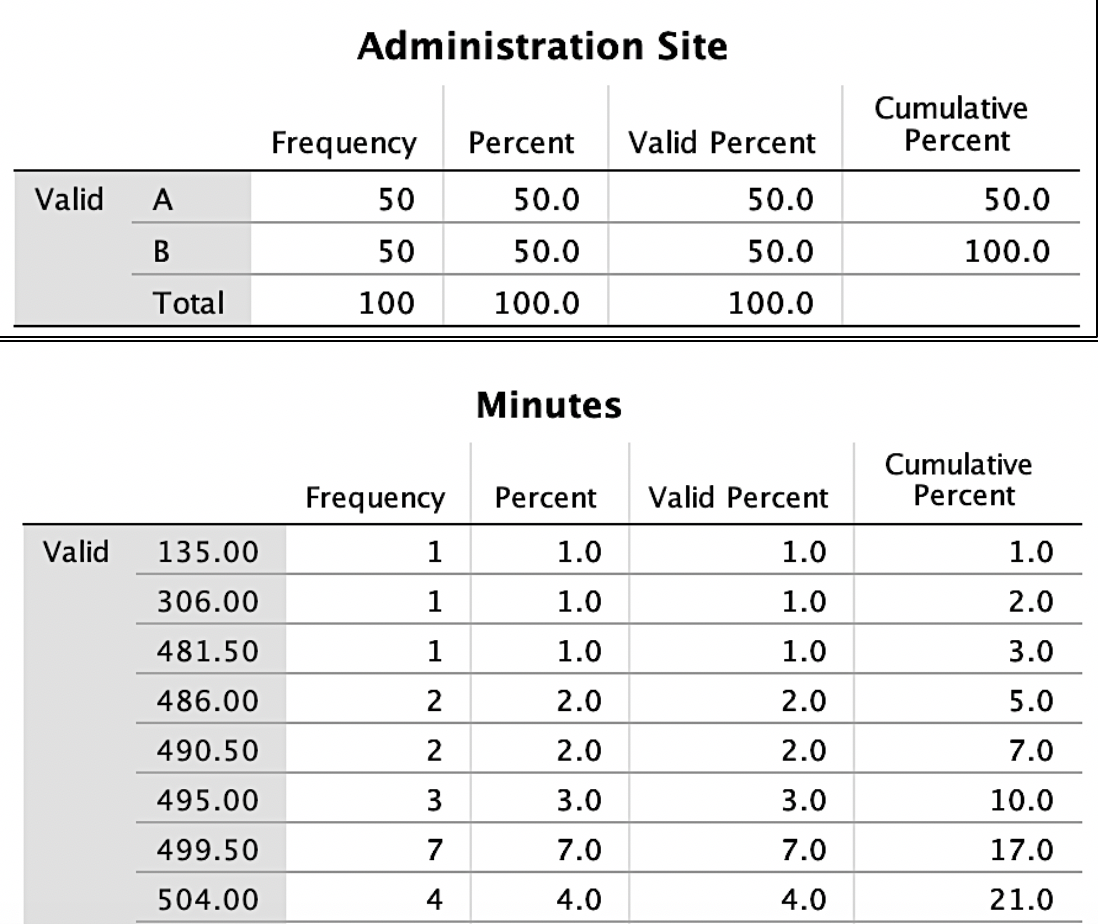
To address this research question, we will conduct exploratory data analysis. First, it is essential to start with the frequencies of the variables. To keep things simple, we will only include the variables of minutes (drug life effect) and administration site (A vs. B). Outputs for frequencies appear in Figure 1.
(See Exploratory Data Analysis Figure 1)
Figure 1 shows that the administration site appears to be a balanced design with 50 individuals in each group. The excerpt for minutes frequencies is the bottom portion of Figure 1 and shows how many cases fell into each time frame with the cumulative percent on the right-hand side. In examining Figure 1, we see one suspiciously low measurement (135), considering time variables. If a data point seems inaccurate, a researcher should find this case and confirm if this was an entry error. For the sake of this article, we will state that this was an entry error and should have been entered 535 and not 135. Had the analysis occurred without checking this, the data analysis and results and conclusions would be invalid. When conducting these frequencies, along with finding any entry errors and determining how groups are balanced, we look for potential missing data. If not responsibly evaluated, missing values can nullify results.
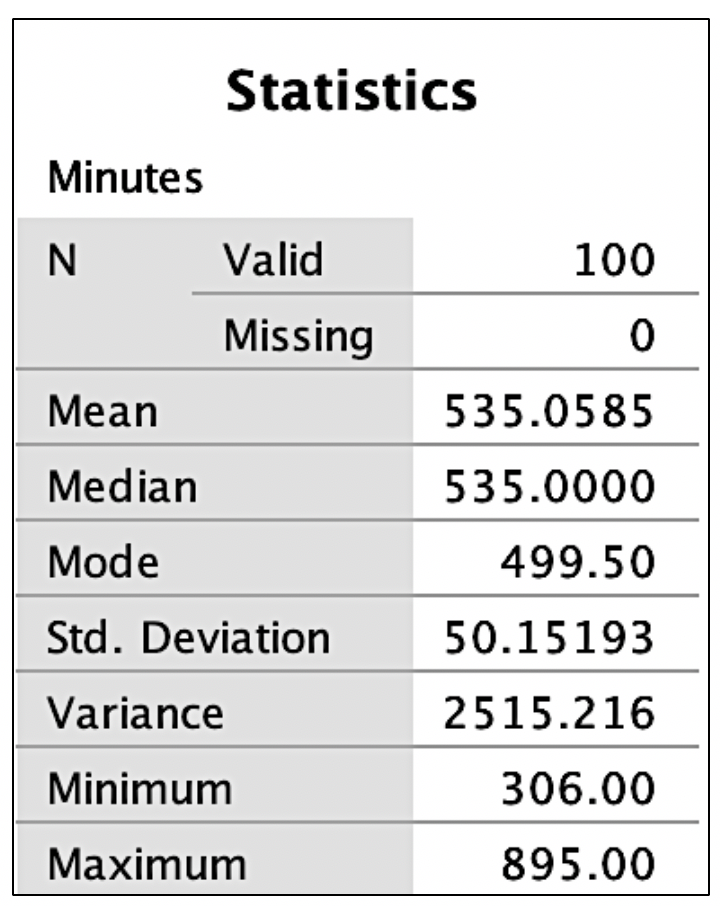
After replacing the incorrect 135 with 535, we can examine descriptive statistics, which include the mean, median, mode, minimum/maximum scores, and standard deviation. Output for the research example for the variable of minutes can be seen in figure 2. Observe each of these variables to ensure that the mean seems reasonable and that minimum and maximums are within an appropriate range based on medical competence or an available codebook. One assumption common in statistical analyses is a normal distribution. Figure 2 shows that the mode is different from both the mean and the median. We have visualization tools such as histograms to further examine these scores for normality and outliers before making any decisions.
(See Exploratory Data Analysis Figure 2)
Histograms
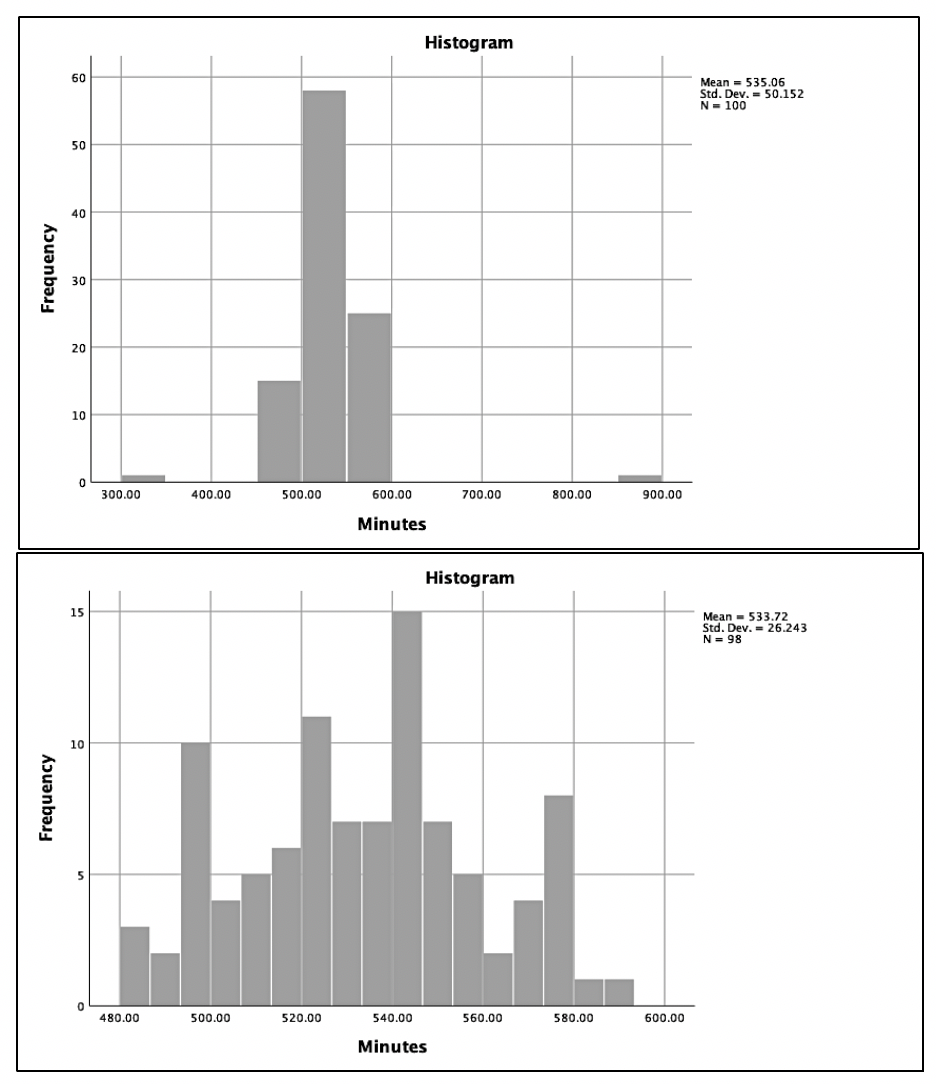
Histograms are useful in assessing normality, as many statistical tests (e.g., ANOVA and regression) assume that the data have a normal distribution. When data deviates from a normal distribution, it is quantified using skewness and kurtosis.[1] Skewness occurs when one tail of the curve is longer. If the tail is lengthier on the left side of the curve (there are many more cases on the higher values) than this would be negatively skewed, whereas if the tail is longer on the right side, it would be positively skewed. Kurtosis is another facet of normality. Positive kurtosis occurs when the center is more peaked (too many values fall in the middle), whereas negative kurtosis occurs when there are very heavy tails, and the center is not peaked enough.[2]
Additionally, histograms reveal outliers: data points either entered incorrectly or truly very different from the rest of the sample. When there are outliers, one must determine accuracy based on either random chance or the error in the experiment and provide strong justification if the decision made is to exclude them.[3] Outliers require attention to ensure the data analysis accurately reflects the majority of the data and are not influenced by any extreme values; therefore, cleaning these outliers up can result in better quality decision-making in clinical practice.[4] A common approach to determining if a variable is approximately normally distributed is converting values to z scores and determining if any scores are less than -3 or greater than 3. For a normal distribution, about 99% of scores should lie within three standard deviations of the mean.[5] Importantly, one should not automatically throw out any values outside of this range, but to consider it in corroboration with the other factors aforementioned. Outliers are relatively common, so when these are prevalent, one must make judgments to assess the risk and benefits of exclusion.[6]
Figures 3A and 3B provide examples of histograms. In figure 3A, we see two possible outliers causing kurtosis. If we only include values that fall within three standard deviations, we can see the result in figure 3B. This histogram appears much closer to an approximately normal distribution with the kurtosis being treated. Remember, consider all evidence before eliminating outliers. When reporting outliers in scientific paper outputs, account for the number of outliers excluded and justify why they were excluded.
(See Exploratory Data Analysis Figure 3)
Boxplots
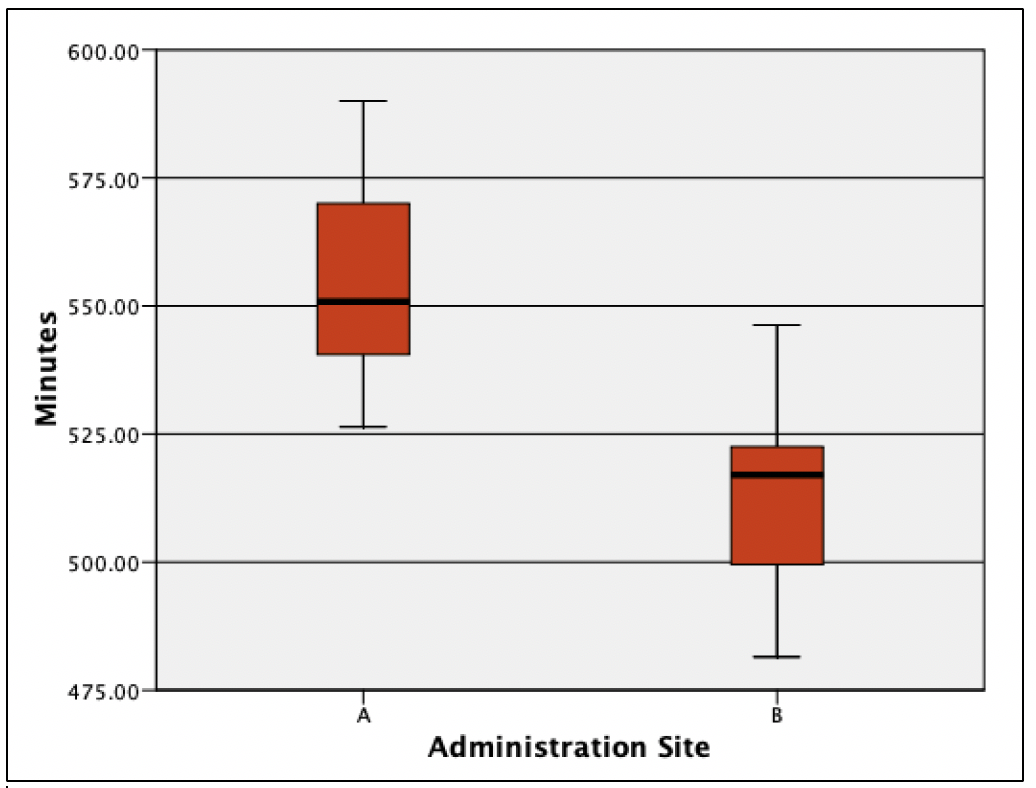
Boxplots can examine for outliers, assess the range of data, and show differences among groups. Boxplots provide a visual representation of ranges and medians, along with illustrating differences amongst groups and are useful in a variety of outlets, including evidence-based medicine.[7] Boxplots provide a picture of the distribution of data when there are numerous values, and all values cannot be clearly displayed (i.e., a scatterplot).[8] Figure 4 illustrates the differences between drug site administration and the length of drug life from the above example.
(See Exploratory Data Analysis Figure 4)
Figure 4 shows differences with potential clinical impact. Had any outliers existed (we already cleaned the data from the histogram), they would appear outside of the line endpoint. The red boxes represent the middle 50% of scores. The lines within each of the red boxes represent the median number of minutes within each administration site. The horizontal lines at the top and bottom of each line connected to the red box represent the 25th and 75th percentiles. In examining the difference boxplots, we see overlap in minutes between the two administration sites: the approximate top 25 percent from site B had the same time noted as the bottom 25 percent at site A. We can see that site B had a median minute amount under 525 whereas administration site A had a length greater than 550. Thus, if there were no difference in adverse reactions at site A, through analysis of this figure, provides evidence that healthcare providers should administer the drug via site A. Researchers could follow by testing a third administration site, site C. Figure 5 shows what would happen if site C led to a longer drug life compared to site A.
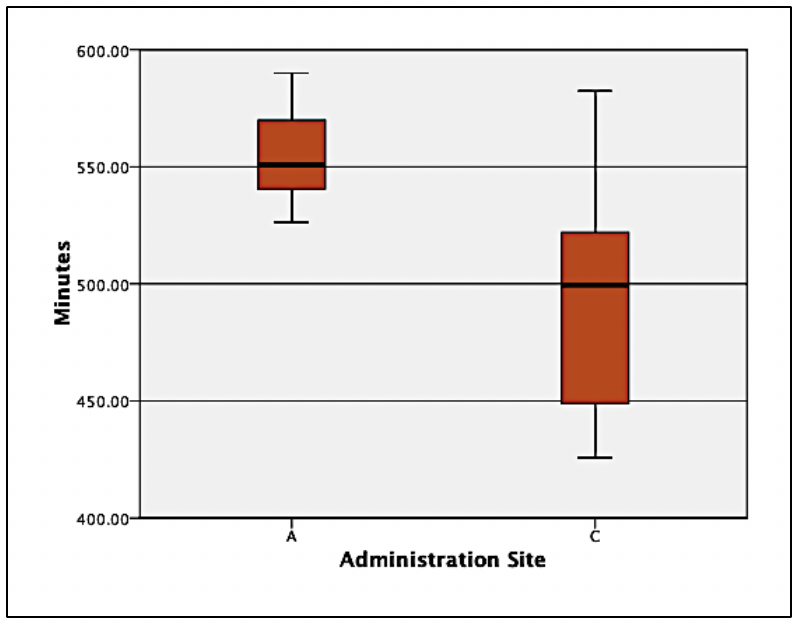
(See Exploratory Data Analysis Figure 5)
Figure 5 displays the same site A data as figure 4, but something looks different. The large variance at site C makes site A’s variance appear smaller. In order words, patients who were administered the drug via site C had a larger range of scores. Thus, some patients experience a longer half-life when the drug is administered via site C than the median of site A; however, the broad range (lack of accuracy) and lower median should be the focus. The precision of minutes is much more compacted in site A. Therefore, the median is higher, and the range is more precise. One may conclude that this makes site A a more desirable site.
Clinical Significance
Ultimately, by having an understanding of basic exploratory data methods, medical researchers and consumers of research can make quality and data-informed decisions. These data-informed decisions will result in the ability to appraise the clinical significance of research outputs. By overlooking these fundamentals in statistics, critical errors in judgment can be made.
(Click Image to Enlarge)
(Click Image to Enlarge)
(Click Image to Enlarge)
(Click Image to Enlarge)