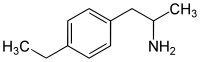
4-Ethylamphetamine
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H17N |
| Molar mass | 163.264 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
4-Ethylamphetamine (4-EA) is a substituted amphetamine derivative which has been sold as a designer drug. It is mainly known as a synthetic intermediate used as a building block to manufacture larger molecules,[1][2] but 4-EA is closely related in chemical structure to designer drugs such as 4-methylamphetamine and 4-ethylmethcathinone, and is both a synthetic precursor and a metabolite of the 25-NB derivative 4-EA-NBOMe.[3]
See also
- 25E-NBOMe
- 4-Et-PVP
- Amfepentorex
- DOET
- RTI-83
References
- ↑ Arnold MJ, Duriatti AD, Jung M, Katz RB, Liebeschuetz JW (1995). "Guanidinium and amidinium fungicides: A new class of carbocation mimetic ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitors". Pesticide Science. 44 (4): 341–355. doi:10.1002/ps.2780440406.
- ↑ Caspar AT, Meyer MR, Westphal F, Weber AA, Maurer HH (October 2018). "Nano liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry for the identification of metabolites of the two new psychoactive substances N-(ortho-methoxybenzyl)-3,4-dimethoxyamphetamine and N-(ortho-methoxybenzyl)-4-methylmethamphetamine". Talanta. 188: 111–123. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2018.05.064. PMID 30029353.
- ↑ Caspar AT, Westphal F, Meyer MR, Maurer HH (January 2018). "LC-high resolution-MS/MS for identification of 69 metabolites of the new psychoactive substance 1-(4-ethylphenyl-)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl] propane-2-amine (4-EA-NBOMe) in rat urine and human liver S9 incubates and comparison of its screening power with further MS techniques". Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 410 (3): 897–912. doi:10.1007/s00216-017-0526-0. PMID 28762065. S2CID 206923339.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.