Salicylate poisoning
| Salicylate poisoning | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Salicylism, salicylate toxicity, aspirin poisoning, aspirin toxicity, aspirin overdose | |
 | |
| A skeletal structural formula for aspirin. | |
| Specialty | Emergency medicine |
| Symptoms | Ringing in the ears, nausea, abdominal pain, fast breathing rate[1] |
| Complications | Swelling of the brain or lungs, seizures, low blood sugar, cardiac arrest[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Early: Slightly elevated blood aspirin levels ~ 2.2 mmol/L (30 mg/dL, 300 mg/L), respiratory alkalosis[1] Late: Metabolic acidosis[1] |
| Differential diagnosis | Sepsis, heart attack, agitation[1] |
| Prevention | Child-resistant packaging, low number of pills per package[1] |
| Treatment | Activated charcoal, intravenous sodium bicarbonate with dextrose and potassium chloride, dialysis[2] |
| Prognosis | ~1% risk of death[3] |
| Frequency | > 20,000 per year (US)[1] |
Salicylate poisoning, also known as aspirin poisoning, is the acute or chronic poisoning with a salicylate such as aspirin.[1] The classic symptoms are ringing in the ears, nausea, abdominal pain, and a fast breathing rate.[1] Early on, these may be subtle, while larger doses may result in fever.[1][4] Complications can include swelling of the brain or lungs, seizures, low blood sugar, or cardiac arrest.[1]
While usually due to aspirin, other possible causes include oil of wintergreen and bismuth subsalicylate.[2] Excess doses can be either on purpose or accidental.[1] Small amounts of oil of wintergreen can be toxic.[2] Diagnosis is generally based on repeated blood tests measuring aspirin levels and blood gases.[1] While a type of graph has been created to try to assist with diagnosis, its general use is not recommended.[1] In overdose maximum blood levels may not occur for more than 12 hours.[2]
Efforts to prevent poisoning include child-resistant packaging and a lower number of pills per package.[1] Treatment may include activated charcoal, intravenous sodium bicarbonate with dextrose and potassium chloride, and dialysis.[2] Giving dextrose may be useful even if the blood sugar is normal.[2] Dialysis is recommended in those with kidney failure, decreased level of consciousness, blood pH less than 7.2, or high blood salicylate levels.[2] If a person requires intubation, a fast respiratory rate may be required.[1]
The toxic effects of salicylates have been described since at least 1877.[5] In 2004, more than 20,000 cases with 43 deaths were reported in the United States.[1] About 1% of those with an acute overdose die, while chronic overdoses may have worse outcomes.[3] Older people are at higher risks of toxicity for any given dose.[5]
Signs and symptoms

Aspirin overdose has potentially serious consequences, sometimes leading to significant morbidity and death. Patients with mild intoxication frequently have nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, lethargy, ringing in the ears, and dizziness. More significant signs and symptoms occur in more severe poisonings and include high body temperature, fast breathing rate, respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis, low blood potassium, low blood glucose, hallucinations, confusion, seizure, cerebral edema, and coma. The most common cause of death following an aspirin overdose is cardiopulmonary arrest usually due to pulmonary edema.[7]
Severity
The severity of toxicity depends on the amount of aspirin taken.
| Severity | Mild (150 mg/kg) | Moderate (150–300 mg/kg) | Severe (300–500 mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toxicity | No toxicity expected | Mild to moderate toxicity expected | Life-threatening toxicity expected |
| Symptoms | Nausea, vomiting, dizziness | Nausea, vomiting, ringing in the ears, headache, confusion, hyperventilation, tachycardia, fever | Delirium, hallucinations, seizures, coma, respiratory arrest |
Pathophysiology
Salicylate toxicity works by uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation. It inhibits Kreb's cycle, meaning the body is unable to produce ATP, leading to anaerobic metabolism with consequent raised lactate and ketone bodies.
Acute aspirin or salicylates overdose or poisoning can cause initial respiratory alkalosis though metabolic acidosis ensues thereafter. The acid-base, fluid, and electrolyte abnormalities observed in salicylate toxicity can be grouped into three broad phases:
- Phase I is characterized by hyperventilation resulting from direct respiratory center stimulation, leading to respiratory alkalosis and compensatory alkaluria. Potassium and sodium bicarbonate are excreted in the urine. This phase may last as long as 12 hours.[8]
- Phase II is characterized by paradoxic aciduria in the presence of continued respiratory alkalosis occurs when sufficient potassium has been lost from the kidneys. This phase may begin within hours and may last 12–24 hours.[8]
- Phase III is characterized by dehydration, hypokalemia, and progressive metabolic acidosis. This phase may begin 4–6 hours after ingestion in a young infant[9] or 24 hours or more after ingestion in an adolescent or adult.[8]
Diagnosis
The acutely toxic dose of aspirin is generally considered greater than 150 mg per kg of body mass.[10] Moderate toxicity occurs at doses up to 300 mg/kg, severe toxicity occurs between 300 and 500 mg/kg, and a potentially lethal dose is greater than 500 mg/kg.[11] Chronic toxicity may occur following doses of 100 mg/kg per day for two or more days.[11]
Monitoring of biochemical parameters such as electrolytes and solutes, liver and kidney function, urinalysis, and complete blood count is undertaken along with frequent checking of salicylate and blood sugar levels. Arterial blood gas assessments typically find respiratory alkalosis early in the course of the overdose due to hyperstimulation of the respiratory center, and may be the only finding in a mild overdose. An anion-gap metabolic acidosis occurs later in the course of the overdose, especially if it is a moderate to severe overdose, due to the increase in protons (acidic contents) in the blood.
The diagnosis of poisoning usually involves measurement of plasma salicylate, the active metabolite of aspirin, by automated spectrophotometric methods. Plasma salicylate levels generally range from 30–100 mg/l (3–10 mg/dl) after usual therapeutic doses, 50–300 mg/l in patients taking high doses, and 700–1400 mg/l following acute overdose.[12] Patients may undergo repeated testing until their peak plasma salicylate level can be estimated.[13] Optimally, plasma levels should be assessed four hours after ingestion and then every two hours after that to allow calculation of the maximum level, which can then be used as a guide to the degree of toxicity expected.[14] Patients may also be treated according to their individual symptoms.
Prevention
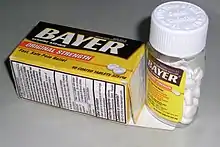
Efforts to prevent poisoning include child-resistant packaging and a lower number of pills per package.[1]
Treatment
Initial treatment of an acute overdose involves resuscitation followed by gastric decontamination by administering activated charcoal, which adsorbs the aspirin in the gastrointestinal tract. Stomach pumping is no longer routinely used in the treatment of poisonings, but is sometimes considered if the patient has ingested a potentially lethal amount less than one hour before presentation.[15] Inducing vomiting with syrup of ipecac is not recommended.[10] Repeated doses of charcoal have been proposed to be beneficial in cases of aspirin overdosing,[16] although one study found that they might not be of significant value.[17] Regardless, most clinical toxicologists administer additional charcoal if serum salicylate levels are increasing.
Intravenous fluids
Intravenous fluids containing dextrose such as dextrose 5% in water (D5W) are recommended to keep a urinary output between 2 and 3 ml/kg/h.[18]
Sodium bicarbonate is given in a significant aspirin overdose (salicylate level greater than 35 mg/dl 6 hours after ingestion) regardless of the serum pH, as it enhances elimination of aspirin in the urine. It is given until a urine pH between 7.5 and 8.0 is achieved.[19]
Dialysis
Hemodialysis can be used to enhance the removal of salicylate from the blood, usually in those who are severely poisoned. Examples of severe poisoning include people with high salicylate blood levels: 7.25 mmol/l (100 mg/dl) in acute ingestions or 40 mg/dl in chronic ingestions,[19] significant neurotoxicity (agitation, coma, convulsions), kidney failure, pulmonary edema, or cardiovascular instability.[13] Hemodialysis also has the advantage of restoring electrolyte and acid-base abnormalities while removing salicylate.[20]
Indication for dialysis
- Salicylate level high than 100 mg/dl (acute), > 59 mg/dl (chronic)
- Severe acid base imbalance
- Severe cardiac toxicity - ARDS
- Cerebral involvement/ neurological signs and symptoms
- Rising serum salicylate level despite arlkalinization / multidose activated charcoal
- Unable to tolerate fluids with fluid overload
Epidemiology
During the latter part of the 20th century, the number of poisonings from salicylates declined, mainly because of the increased popularity of other over-the-counter analgesics such as paracetamol (acetaminophen). Fifty-two deaths involving single-ingredient aspirin were reported in the United States in 2000; however, in all but three of these cases, the reason for the ingestion of lethal doses was intentional—predominantly suicidal.[21]
History
Aspirin poisoning has controversially been cited as a possible cause of the high mortality rate during the 1918 flu pandemic, which killed 50 to 100 million people.[22]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 O'Malley, GF (May 2007). "Emergency department management of the salicylate-poisoned patient". Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. 25 (2): 333–46, abstract viii. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2007.02.012. PMID 17482023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Walls, Ron (2017). Rosens Emergency Medicine Concepts and Clinical Practice (9th ed.). Elsevier. p. X. ISBN 978-0323354790.
- 1 2 McNeil Consumer & Specialty Pharmaceuticals (2002). "Assessment of Safety of aspirin and other Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)". FDA. Archived from the original on 14 May 2017. Retrieved 27 June 2017.
- ↑ Brenner, George M.; Stevens, Craig (2012). Pharmacology E-Book: with STUDENT CONSULT Online Access (4 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 319. ISBN 978-1455702787. Archived from the original on 2017-08-18.
- 1 2 Roland, Peter S.; Rutka, John A. (2004). Ototoxicity. PMPH-USA. p. 28. ISBN 9781550092639. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017. Retrieved 27 June 2017.
- ↑ MedlinePlus > Aspirin Archived 2009-07-20 at the Wayback Machine Last Reviewed - 02/01/2009.
- ↑ Thisted, B; Krantz, T; Strøom, J; Sørensen, MB (May 1987). "Acute salicylate self-poisoning in 177 consecutive patients treated in ICU". Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 31 (4): 312–6. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.1987.tb02574.x. ISSN 0001-5172. PMID 3591255.
- 1 2 3 Salicylate Toxicity at eMedicine
- ↑ "Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)". toxnet.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 Chyka PA, Erdman AR, Christianson G, Wax PM, Booze LL, Manoguerra AS, Caravati EM, Nelson LS, Olson KR, Cobaugh DJ, Scharman EJ, Woolf AD, Troutman WG (2007). "Salicylate poisoning: an evidence-based consensus guideline for out-of-hospital management". Clinical Toxicology. 45 (2): 95–131. doi:10.1080/15563650600907140. PMID 17364628.
- 1 2 Temple, AR (February 1981). "Acute and chronic effects of aspirin toxicity and their treatment". Archives of Internal Medicine. 141 (3 Spec No): 364–9. doi:10.1001/archinte.141.3.364. ISSN 0003-9926. PMID 7469627.
- ↑ R. Baselt, Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 9th edition, Biomedical Publications, Seal Beach, CA, 2011, pp. 20-23.
- 1 2 Dargan, PI; Wallace, CI; Jones, AL (May 2002). "An evidenced based flowchart to guide the management of acute salicylate (aspirin) overdose". Emergency Medicine Journal. 19 (3): 206–9. doi:10.1136/emj.19.3.206. ISSN 1472-0205. PMC 1725844. PMID 11971828.
- ↑ Meredith TJ, Vale JA (1986). "Non-narcotic analgesics. Problems of overdosage". Drugs. 32 (Suppl 4): 117–205. doi:10.2165/00003495-198600324-00013. ISSN 0012-6667. PMID 3552583.
- ↑ Vale JA, Kulig K (2004). "Position paper: gastric lavage". Journal of Toxicology: Clinical Toxicology. 42 (7): 933–43. doi:10.1081/CLT-200045006. PMID 15641639.
- ↑ Hillman, RJ; Prescott, LF (Nov 1985). "Treatment of salicylate poisoning with repeated oral charcoal". British Medical Journal (Clinical Research Ed.). 291 (6507): 1472. doi:10.1136/bmj.291.6507.1472. ISSN 0267-0623. PMC 1418067. PMID 3933714.
- ↑ Kirshenbaum LA, Mathews SC, Sitar DS, Tenenbein M (Jun 1990). "Does multiple-dose charcoal therapy enhance salicylate excretion?". Archives of Internal Medicine. 150 (6): 1281–3. doi:10.1001/archinte.150.6.1281. ISSN 0003-9926. PMID 2191636.
- ↑ Marx, John (2006). Rosen's emergency medicine: concepts and clinical practice. Mosby/Elsevier. p. 2341. ISBN 978-0-323-02845-5.
- 1 2 Marx, John (2006). Rosen's emergency medicine: concepts and clinical practice. Mosby/Elsevier. p. 2342. ISBN 978-0-323-02845-5.
- ↑ Gaudreault, P; Temple, AR; Lovejoy Fh, FH (October 1982). "The relative severity of acute versus chronic salicylate poisoning in children: a clinical comparison". Pediatrics. 70 (4): 566–9. ISSN 0031-4005. PMID 7122154.
- ↑ Litovitz, TL; Klein-Schwartz, W; White, S; Cobaugh, DJ; Youniss, J; Omslaer, JC; Drab, A; Benson, BE (Sep 2001). "2000 Annual report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers Toxic Exposure Surveillance System". The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 19 (5): 337–95. doi:10.1053/ajem.2001.25272. ISSN 0735-6757. PMID 11555795.
- ↑ Starko, KM (1 November 2009). "Salicylates and pandemic influenza mortality, 1918-1919 pharmacology, pathology, and historic evidence". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 49 (9): 1405–10. doi:10.1086/606060. PMID 19788357.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Reingardiene, D; Lazauskas, R (2006). "[Acute salicylate poisoning]". Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania). 42 (1): 79–83. PMID 16467617.