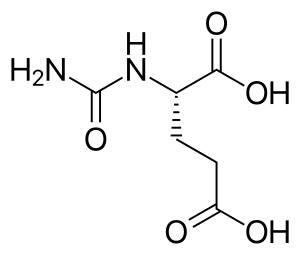
Carglumic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Carbaglu, Ucedane |
| Other names | (S)-2-ureidopentanedioic acid |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS 1) activator[1] |
| Main uses | High ammonia due to certain metabolic disorders[1] |
| Side effects | Vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, tonsillitis, low red blood cells, diarrhea, infections, low red blood cells, low blood sugar, pancreatitis, electrolyte abnormalities, headache[1] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| Typical dose | 10 to 250 mg/kg per day[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| US NLM | Carglumic acid |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | 30% |
| Protein binding | Undetermined |
| Metabolism | Partial |
| Elimination half-life | 4.3 to 9.5 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal (60%) and kidney (9%, unchanged) |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6H10N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 190.155 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Carglumic acid, sold under the brand name Carbaglu among others, is a medication used to treat high ammonia due to N-acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS) deficiency, propionic acidemia (PA) or methylmalonic acidemia (MMA).[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, tonsillitis, low red blood cells, diarrhea, infections, low red blood cells, low blood sugar, pancreatitis, electrolyte abnormalities, and headache.[1] Safety in pregnancy is unclear.[1] It is a carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS 1) activator, which works by activating an enzyme that breaks down ammonia.[1][2]
Carglumic acid was approved for medical use in Europe in 2003 and the United States in 2010.[1][2] It is available as a generic medication.[4] In the United Kingdom 60 tablets of 200 mg costs the NHS about £2,600 as of 2021.[4] This amount in the United States costs about 13,400 USD.[5] A generic version was approved in 2021 in the USA.[6]
Medical uses
Carglumic acid is indicated for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia and chronic hyperammonemia.[1][2][3]
Dosage
It is used at a dose of 10 to 250 mg/kg per day.[1] This is take as 2 to 4 doses.[1]
History
Carglumic acid is an orphan drug.[7][8]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 "Carbaglu- carglumic acid tablet". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 9 June 2021. Retrieved 9 June 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 "Carbaglu EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Archived from the original on 9 June 2021. Retrieved 9 June 2021.
- 1 2 "Ucedane EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Archived from the original on 9 June 2021. Retrieved 9 June 2021.
- 1 2 BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 1118. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ↑ "Carbaglu Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 20 April 2021. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ↑ Research, Center for Drug Evaluation and (10 February 2022). "2021 First Generic Drug Approvals". FDA. Archived from the original on 21 June 2022. Retrieved 22 October 2022.
- ↑ "Carglumic acid Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 17 June 2014. Archived from the original on 9 June 2021. Retrieved 9 June 2021.
- ↑ "Carglumic acid Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 20 January 1998. Archived from the original on 9 June 2021. Retrieved 9 June 2021.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- "Carglumic acid". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2021-06-09. Retrieved 2021-09-14.