Chiasmatic groove
| Chiasmatic groove | |
|---|---|
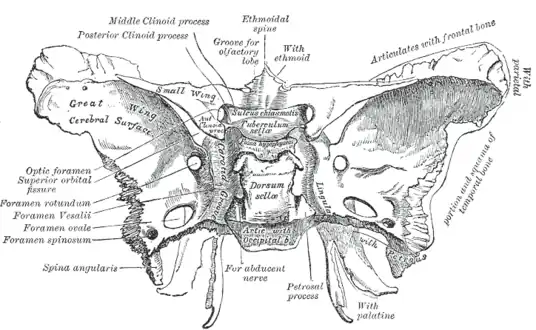 ethmoid bone. Upper surface. (Sulcus chiasmaticus labeled at center) | |
 Base of the skull. Upper surface. (Sphenoid bone is yellow; chiasmatic groove labeled at center left, fourth from the top of the labels near the yellow region.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Sulcus praechiasmaticus, sulcus chiasmaticus |
| TA98 | A02.1.05.005 |
| TA2 | 588 |
| FMA | 75760 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The superior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone is bounded behind by a ridge, which forms the anterior border of a narrow, transverse groove, the chiasmatic groove (optic groove, prechiasmatic sulcus), above and behind which lies the optic chiasma of cranial nerve 2 (the optic nerve).
The groove ends on either side in the optic foramen, which transmits the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery into the orbital cavity.
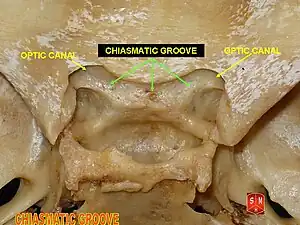
Chiasmatic groove
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 147 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 147 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- figures/chapter_42/42-18.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School
- Anatomy image: skel/internal2 at Human Anatomy Lecture (Biology 129), Pennsylvania State University (#7)
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.