Human brain development timeline
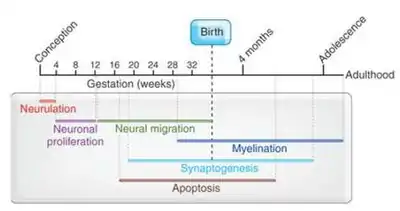
Conception
| Day | Event | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 33 | posterior commissure appears | Ashwell et al. (1996)[2] |
| 33 | medial forebrain bundle appears | Ashwell et al. (1996)[2] |
| 44 | mammillothalamic tract appears | Ashwell et al. (1996)[2] |
| 44 | stria medullaris thalami appears | Ashwell et al. (1996)[2] |
| 51 | axons in optic stalk | Dunlop et al. (1997)[3] |
| 56 | external capsule appears | Ashwell et al. (1996)[2] |
| 56 | stria terminalis appears | Ashwell et al. (1996)[2] |
| 60 | optic axons invade visual centers | Dunlop et al. (1997)[3] |
| 63 | internal capsule appears | Ashwell et al. (1996)[2] |
| 63 | fornix appears | Ashwell et al. (1996)[2] |
| 70 | anterior commissure appears | Ashwell et al. (1996)[2] |
| 77 | hippocampal commissure appears | Ashwell et al. (1996)[2] |
| 87.5 | corpus callosum appears | Ashwell et al. (1996)[2] |
| 157.5 | eye opening | Clancy et al. (2007)[4] |
| 175 | ipsi/contra segregation in LGN and SC | Robinson & Dreher (1990)[5] |
Studies report that three primary structures are formed in the sixth gestational week. These are the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain, also known as the prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and the rhombencephalon respectively. Five secondary structures originate from these in the seventh gestational week. These are the telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon, and myelencephalon; the lateral ventricles, third ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, and upper and lower parts of the fourth ventricle in adulthood originated from these structures.[6] The appearance of cortical folds first takes place during 24 and 32 weeks of gestation.[7]
Childhood and adolescence
Cortical white matter increases from childhood (~9 years) to adolescence (~14 years), most notably in the frontal and parietal cortices.[8] Cortical grey matter development peaks at ~12 years of age in the frontal and parietal cortices, and 17 years in the temporal lobes (with the superior temporal cortex being last to mature) for women and they have reached full maturity at age 16-17. For men, they become fully mature at age 18. In terms of grey matter loss, the sensory and motor regions mature first, followed by other cortical regions.[8] Human brain maturation continues to around 20[9] to 25[10] years of age.
See also
- Brain development timelines
- Development of the nervous system in humans
- Evolution of the brain
- Practopoiesis
References
- ↑ Tau, G. Z.; Peterson, B. S. (2010). "Normal Development of Brain Circuits". Neuropsychopharmacology. 35 (1): 147–168. doi:10.1038/npp.2009.115. PMC 3055433. PMID 19794405.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Ashwell, K. W.; Waite, P. M.; Marotte, L (1996). "Ontogeny of the projection tracts and commissural fibres in the forebrain of the tammar wallaby (Macropus eugenii): timing in comparison with other mammals". Brain, Behavior and Evolution. 47 (1): 8–22. doi:10.1159/000113225. PMID 8834781.
- 1 2 Dunlop, S. A.; Tee, L. B.; Lund, R. D.; Beazley, L. D. (1997). "Development of primary visual projections occurs entirely postnatally in the fat-tailed dunnart, a marsupial mouse, Sminthopsis crassicaudata". The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 384 (1): 26–40. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19970721)384:1<26::AID-CNE2>3.0.CO;2-N. PMID 9214538.
- ↑ Clancy, B; Kersh, B; Hyde, J; Darlington, R. B.; Anand, K. J.; Finlay, B. L. (2007). "Web-based method for translating neurodevelopment from laboratory species to humans". Neuroinformatics. 5 (1): 79–94. doi:10.1385/ni:5:1:79. PMID 17426354.
- ↑ Robinson, S. R.; Dreher, B (1990). "The visual pathways of eutherian mammals and marsupials develop according to a common timetable". Brain, Behavior and Evolution. 36 (4): 177–195. doi:10.1159/000115306. PMID 2279233.
- ↑ Kim MS, Jeanty P, Turner C, Benoit B (January 2008). "Three-dimensional sonographic evaluations of embryonic brain development". J Ultrasound Med. 27 (1): 119–24. doi:10.7863/jum.2008.27.1.119. PMID 18096737.
- ↑ Budday, Silvia; Raybaud, Charles; Kuhl, Ellen (2014-01-01). "A mechanical model predicts morphological abnormalities in the developing human brain". Scientific Reports. 4: 5644. doi:10.1038/srep05644. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 4090617. PMID 25008163.
- 1 2 Blakemore, S.J. (June 2012). "Imaging brain development: the adolescent brain". NeuroImage. 61 (2): 397–406. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.11.080. PMID 22178817.
- ↑ Johnson SB, Blum RW, Giedd JN (2009). "Adolescent maturity and the brain: the promise and pitfalls of neuroscience research in adolescent health policy". J Adolesc Health. 45 (3): 216–21. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2009.05.016. PMC 2892678. PMID 19699416.
- ↑ Arain M, Haque M, Johal L, Mathur P, Nel W, Rais A, Sandhu R, Sharma S (2013). "Maturation of the adolescent brain". Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 9: 449–61. doi:10.2147/NDT.S39776. PMC 3621648. PMID 23579318.
External links
- Translating Time — a website providing translation of brain developmental times among different species