Nasal fracture
| Nasal fracture | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Broken nose | |
 | |
| Plain X-ray showing a nasal fracture | |
| Specialty | Emergency medicine, otorhinolaryngology |
| Symptoms | Nose bleed, swelling, bruising[1][2] |
| Complications | Septal hematoma, other facial fractures, meningitis[1] |
| Usual onset | Young males[3] |
| Causes | Assault, trauma during sports, falls, motor vehicle collisions[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Typically based on symptoms, medical imaging not generally needed[1][4] |
| Treatment | Pain medication, cold compresses, possible reduction post resolution of swelling[1] |
| Prognosis | Generally good[5] |
| Frequency | Common[3] |
A nasal fracture, commonly referred to as a broken nose, is a fracture of one of the bones of the nose.[2] Symptoms may include bleeding, swelling, bruising, and an inability to breathe through the nose.[1][2] They may be complicated by other facial fractures or a septal hematoma.[1]
The most common causes include assault, trauma during sports, falls, and motor vehicle collisions.[1] Diagnosis is typically based on the signs and symptoms; with plain X-ray rarely of benefit.[1][6] CT scan may be useful if concerns of other fractures or complications are present.[6][4]
Treatment is typically with pain medication and cold compresses.[1] Reduction may be needed if there is new obstruction or obvious deformity, but can typically occur after the swelling has come down.[1][4] This can occur 5 to 14 days later.[6][4] Depending on the type of fracture, reduction may be closed or open.[2] Outcomes are generally good.[5]
Nasal fractures are common, comprising about 40% of facial fractures.[1][3] Males in their 20s are most commonly affected.[2]
Signs and symptoms

Symptoms of a broken nose include bruising, swelling, tenderness, pain, deformity, and/or bleeding of the nose and nasal region of the face. The patient may have difficulty breathing, or excessive nosebleeds (if the nasal mucosa are damaged). The patient may also have bruising around one or both eyes.
Cause
Nasal fractures are caused by physical trauma to the face. Common sources of nasal fractures include sports injuries, fighting, falls, and car accidents in the younger age groups, and falls from syncope or impaired balance in the elderly.[7]
Diagnosis
Nasal fractures are usually identified visually and through physical examination.[1] Medical imaging is generally not recommended.[1][2] A priority is to distinguish simple fractures limited to the nasal bones (Type 1) from fractures that also involve other facial bones and/or the nasal septum (Types 2 and 3). In simple Type 1 fractures X-Rays supply surprisingly little information beyond clinical examination. However, diagnosis may be confirmed with X-rays or CT scans, and these are required if other facial injuries are suspected.[2]
A fracture that runs horizontally across the septum is sometimes called a "Jarjavay fracture", and a vertical one, a "Chevallet fracture".[8]
Although treatment of an uncomplicated fracture of nasal bones is not urgent—a referral for specific treatment in five to seven days usually suffices—an associated injury, nasal septal hematoma, occurs in about 5% of cases and does require urgent treatment and should be looked for during the assessment of nasal injuries.[7]
.jpg.webp) Nasal bone fracture
Nasal bone fracture.jpg.webp) Nasal bone fracture
Nasal bone fracture.jpg.webp) Nasal bone fracture
Nasal bone fracture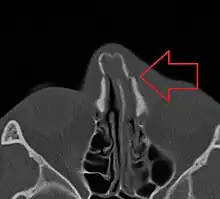 Bilateral nasal fracture as seen on CT scan
Bilateral nasal fracture as seen on CT scan
Treatment
Minor nasal fractures may be allowed to heal on their own provided there is not significant deformity. Ice and pain medication may be prescribed to ease discomfort during healing.[1] For fractures where the nose has been deformed, manual alignment may be attempted, usually with good results. A CT scan of the facial bones is recommended before this occur.[4] The reduction can take place within the next two weeks and potentially up to 5 weeks; though repair is recommended earlier in children (around 7 days).[4]
Reduction can take place with either local anesthetic or general anesthetic.[4] General anesthetic; however, is associated with better results as the nose can be manipulated more agressively.[4] Further surgery may still be desired at a later date.[4]
Injuries involving other structures (types 2 and 3) must be recognized and treated surgically.[9]
Prognosis
Bone stability after a fracture occurs between 3 and 4 weeks. Full bone fusion occurs between 4 and 8 weeks.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Das, D; Salazar, L (April 2017). "Maxillofacial Trauma: Managing Potentially Dangerous And Disfiguring Complex Injuries". Emergency Medicine Practice. 19 (4): 1–24. PMID 28362252.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Kühnel, TS; Reichert, TE (2015). "Trauma of the midface". GMS Current Topics in Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery. 14: Doc06. doi:10.3205/cto000121. PMC 4702055. PMID 26770280.
- 1 2 3 Fonseca, Raymond J. (2017). Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery - E-Book: 3-Volume Set (3 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 9780323444422. Archived from the original on 31 July 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Trujillo, Oscar; Lee, Clara (June 2023). "Nasal Fractures: Acute, Subacute, and Delayed Management". Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2023.05.004. PMID 37353368.
- 1 2 Marston, AP; O'Brien, EK; Hamilton GS, 3rd (April 2017). "Nasal Injuries in Sports". Clinics in Sports Medicine. 36 (2): 337–353. doi:10.1016/j.csm.2016.11.004. PMID 28314421.
- 1 2 3 Kucik, CJ; Clenney, T; Phelan, J (1 October 2004). "Management of acute nasal fractures". American family physician. 70 (7): 1315–20. PMID 15508543.
- 1 2 Bremke M, Gedeon H, Windfuhr JP, Werner JA, Sesterhenn AM (November 2009). "Nasal bone fracture: etiology, diagnostics, treatment and complications". Laryngorhinootologie. 88 (11): 711–6. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1224106. PMID 19562655.
- ↑ Sethi, Neeraj; Pearson, Amy; Bajaj, Yogesh (2016). Key Clinical Topics in Otolaryngology. 191: JP Medical Ltd. ISBN 9781909836358. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ↑ Mondin V, Rinaldo A, Ferlito A (May–June 2005). "Management of nasal bone fractures". Am J Otolaryngol. 26 (3): 181–5. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2004.11.006. PMID 15858774.
External links
| Classification |
|---|