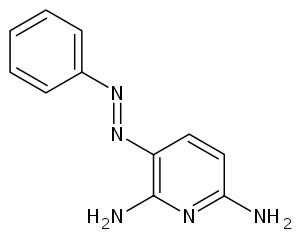
Phenazopyridine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Pyridium, others |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Azo dye[1] |
| Main uses | Urinary tract discomfort[1] |
| Side effects | Orange colored urine, yellowish skin, methemoglobinemia, hemolytic anemia[1][2] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682231 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H11N5 |
| Molar mass | 213.244 g·mol−1 |
Phenazopyridine, sold under the brand name Pyridium among others, is a medication used to help with the discomfort caused by urinary tract infection, surgery, or injury to the urinary tract.[1] For urinary tract infection it may be used together with antibiotics for the first two days.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Side effects may include orange colored urine and other body fluids.[1][2] Other side effects may include yellowish skin, methemoglobinemia, sulfhemoglobinemia, and hemolytic anemia.[1][3] Use is not recommended in those with kidney or liver problems.[1] There is no evidence of harm with use during pregnancy.[4] Use during breastfeeding is not recommended.[4] Phenazopyridine is a azo dye and how it works is not entirely clear.[1]
Phenazopyridine came into medical use in the 1930s.[5] It maybe available as a generic medication and over the counter.[1][6] In the United States six doses of 200 mg costs about 8 USD as of 2020.[7] It is not easily available in Canada as of 2015, though some pharmacies will make it.[8]
Medical uses
Phenazopyridine used for its local analgesic effects on the urinary tract. It is often used with an antibiotic at the beginning of treatment to help provide immediate symptomatic relief. Phenazopyridine does not treat infections or injury; it is only used for symptom relief.[9][10] It is recommended that it be used for no longer than the first two days.[10][6] Long-term use of phenazopyridine can mask symptoms.[11] High quality evidence in urinary tract infections is lacking as of 2014.[12]
Phenazopyridine is also prescribed for other cases requiring relief from irritation or discomfort during urination. For example, it is often prescribed after the use of an in-dwelling Foley catheter, endoscopic (cystoscopy) procedures, or after urethral, prostate, or urinary bladder surgery which may result in irritation of the epithelial lining of the urinary tract.[9][10]
Dosage
In adults the typical dose is 200 mg three times per day.[1]
Side effects

Phenazopyridine produces a vivid color change in urine, typically to a dark orange to reddish color. This effect is common and harmless, and indeed a key indicator of the presence of the medication in the body. Users of phenazopyridine are warned not to wear contact lenses, as phenazopyridine has been known to permanently discolor contact lenses and fabrics.[9][13] Some may be mistakenly concerned that this indicated blood in the urine. Phenazopyridine can also result in a falsely positive nitrite test on the urine.[6]
Phenazopyridine can also cause headaches, upset stomach (especially when not taken with food), or dizziness. Less frequently it can cause a pigment change in the skin or eyes, to a noticeable yellowish color. This is due to a depressed excretion via the kidneys causing a buildup of the medication in the skin, and normally indicates a need to discontinue usage.[10] Other such side effects include fever, confusion, shortness of breath, skin rash, and swelling of the face, fingers, feet, or legs.[9][10] Long-term use may cause yellowing of nails.[14]
Phenazopyridine should be avoided by people with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency,[10][15][16][17] because it can cause hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells) due to oxidative stress.[18] It has been reported to cause methemoglobinemia after overdose and even normal doses.[19] In at least one case the patient had pre-existing low levels of methemoglobin reductase,[20] which likely predisposed her to the condition. It has also been reported to cause sulfhemoglobinemia.[10][21][22] [23]
Cancer
Phenazopyridine is an azo dye.[24] Other azo dyes, which were previously used in textiles, printing, and plastic manufacturing, have been implicated as carcinogens that can cause bladder cancer.[25] While phenazopyridine has never been shown to cause cancer in humans, evidence from animal models suggests that it is potentially carcinogenic.[10][26]
Pregnancy
This medication is pregnancy category B. This means that the medication has shown no adverse events in animal models, but no human trials have been conducted.[10] It is not known if phenazopyridine is excreted in breast milk.[10]
Pharmacokinetics
The full pharmacokinetic properties of phenazopyridine have not been determined. It has mostly been studied in animal models, but they may not be very representative of humans.[27] Rat models have shown its half-life to be 7.35 hours,[28] and 40% is metabolized hepatically (by the liver).[28]
Mechanism of action
Phenazopyridine's mechanism of action is not well known, and only basic information on its interaction with the body is available. It is known that the chemical has a direct topical analgesic effect on the mucosa lining of the urinary tract. It is rapidly excreted by the kidneys directly into the urine.[27] Hydroxylation is the major form of metabolism in humans,[27] and the azo bond is usually not cleaved.[27] On the order of 65% of an oral dose will be secreted directly into the urine chemically unchanged.[10]
History
It may have been discovered by Bernhard Joos, the founder of Cilag.
Brand names
In addition to its generic form, phenazopyridine is distributed under the following brand names:
- Azo-Maximum Strength
- Azo-Standard
- Baridium
- Nefrecil
- Phenazalgin
- Phenazodine
- Pyridiate
- Pyridium
- Pyridium Plus
- Sedural
- Uricalm
- Uristat
- Uropyrine
- Urodine
- Urogesic
- Urovit
Society and culture
Cost
In the United States six doses of 200 mg costs about 8 USD as of 2020.[7]
.svg.png.webp) Phenazopyridine costs (US)
Phenazopyridine costs (US).svg.png.webp) Phenazopyridine prescriptions (US)
Phenazopyridine prescriptions (US)
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "Phenazopyridine Hydrochloride Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 25 July 2019. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- 1 2 Moldwin, Robert M. (2017). Urological and Gynaecological Chronic Pelvic Pain: Current Therapies. Springer. p. 237. ISBN 978-3-319-48464-8. Archived from the original on 2021-08-28. Retrieved 2020-10-13.
- ↑ "Phenazopyridine". Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed). National Library of Medicine (US). October 31, 2018. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- 1 2 "Phenazopyridine Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 2021-01-24. Retrieved 2020-10-13.
- ↑ Sneader, Walter (2005). Drug Discovery: A History. John Wiley & Sons. p. 383. ISBN 978-0-471-89979-2. Archived from the original on 2021-08-28. Retrieved 2020-10-13.
- 1 2 3 Wang, A; Nizran, P; Malone, MA; Riley, T (September 2013). "Urinary tract infections". Primary care. 40 (3): 687–706. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2013.06.005. PMID 23958364.
- 1 2 "Phenazopyridine Prices and Phenazopyridine Coupons". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 17 June 2019. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ↑ "Calgary doctor answers 'burning' questions about bladder infections". CBC. Archived from the original on 29 August 2018. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 "Pyridium Plus® Tablets" (PDF). Warner Chilcott. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 April 2014. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "PYRIDIUM (phenazopyridine) tablet, film coated". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 21 April 2014. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- ↑ Wang, Alina; Nizran, Parminder; Malone, Michael; Riley, Timothy (September 2013). "Urinary Tract Infections". Primary Care - Clinics in Office Practice. 40 (3): 693. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2013.06.005. PMC 1983013. PMID 5776230.
- ↑ "BestBets: Pyridium (phenazopyridine) for relieving dysuria symptoms in urinary tract infection : useful or not ?". bestbets.org. Archived from the original on 15 August 2020. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ↑ "Phenazopyridine: MedlinePlus Drug Information". Medline plus. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. Archived from the original on 25 July 2019. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- ↑ Amit, G; Halkin, A (15 December 1997). "Lemon-yellow nails and long-term phenazopyridine use". Annals of Internal Medicine (letter). 127 (12): 1137. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-127-12-199712150-00040. PMID 9412335. S2CID 41928972.
- ↑ Tishler, M; Abramov, A (1983). "Phenazopyridine-induced hemolytic anemia in a patient with G6PD deficiency". Acta Haematol. 70 (3): 208–9. doi:10.1159/000206727. PMID 6410650.
- ↑ Galun E, Oren R, Glikson M, Friedlander M, Heyman A (November 1987). "Phenazopyridine-induced hemolytic anemia in G-6-PD deficiency". Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 21 (11): 921–2. doi:10.1177/106002808702101116. PMID 3678069. S2CID 7262697.
- ↑ Mercieca JE, Clarke MF, Phillips ME, Curtis JR (4 Sep 1982). "Acute hemolytic anaemia due to phenazopyridine hydrochloride in G-6-PD deficient subject". Lancet. 2 (8297): 564. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90651-1. PMID 6125724. S2CID 27340450.
- ↑ Frank JE (October 2005). "Diagnosis and management of G6PD deficiency". American Family Physician. 72 (7): 1277–82. PMID 16225031. Archived from the original on 2021-08-28. Retrieved 2009-07-06.
- ↑ Jeffery WH; Zelicoff AP; Hardy WR. (February 1982). "Acquired methemoglobinemia and hemolytic anemia after usual doses of phenazopyridine". Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 16 (2): 57–9. doi:10.1177/106002808201600212. PMID 7075467. S2CID 20968675.
- ↑ Daly JS, Hultquist DE, Rucknagel DL (August 1983). "Phenazopyridine induced methaemoglobinaemia associated with decreased activity of erythrocyte cytochrome b5 reductase". Journal of Medical Genetics. 20 (4): 307–9. doi:10.1136/jmg.20.4.307. PMC 1049126. PMID 6620333.
- ↑ Halvorsen, SM; Dull, WL (September 1991). "Phenazopyridine-induced sulfhemoglobinemia: inadvertent rechallenge". American Journal of Medicine. 91 (3): 315–7. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(91)90135-K. PMID 1892154.
- ↑ Kermani TA, Pislaru SV, Osborn TG (April 2009). "Acrocyanosis from phenazopyridine-induced sulfhemoglobinemia mistaken for Raynaud phenomenon". Journal of Clinical Rheumatology. 15 (3): 127–9. doi:10.1097/RHU.0b013e31819db6db. PMID 19300288.
- ↑ Gopalachar AS, Bowie VL, Bharadwaj P (June 2005). "Phenazopyridine-induced sulfhemoglobinemia". Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 39 (6): 1128–30. doi:10.1345/aph.1E557. PMID 15886294. S2CID 22812461.
- ↑ "Phenazopyridine Hydrochloride". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on July 25, 2019. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- ↑ Transitional Cell Carcinoma Imaging at eMedicine
- ↑ "Phenazopyridine Hydrochloride" (PDF). Report on Carcinogens, Twelfth Edition (2011). National Toxicology Program. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 February 2013. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- 1 2 3 4 Thomas BH, Whitehouse LW, Solomonraj G, Paul CJ (April 1990). "Excretion of phenazopyridine and its metabolites in the urine of humans, rats, mice, and guinea pigs". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 79 (4): 321–5. doi:10.1002/jps.2600790410. PMID 2352143.
- 1 2 Jurima-Romet M, Thomas BH, Solomonraj G, Paul CJ, Huang H (March 1993). "Metabolism of phenazopyridine by isolated rat hepatocytes". Biopharm Drug Dispos. 14 (2): 171–9. doi:10.1002/bdd.2510140208. PMID 8453026. S2CID 29419875.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- Information about phenazopyridine Archived 2016-06-10 at the Wayback Machine from the US National Library of Medicine