Study of Health in Pomerania
The Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP) is a population-based epidemiological study consisting of two independent cohorts (SHIP and SHIP-TREND). The SHIP investigates common risk factors, subclinical disorders and manifest diseases with highly innovative non-invasive methods in the high-risk population of northeast Germany. The study is not interested in one specific disease. The SHIP study´s main aims include the investigation of health in all its aspects and complexity involving the collection and assessment of data relevant to the prevalence and incidence of common, population-relevant diseases and their risk factors.
Design

The aims of both studies are: (i) investigation of the long-term progression of subclinical findings, their determinants and prognostic values (SHIP-2); (ii) analysis of the secular trend of subclinical and overt diseases and their determinants in a high-risk population (SHIP-TREND vs SHIP-0); and (iii) assessment of the prevalence of subclinical findings (SHIP-TREND).
For SHIP-0, a sample of 7008 women and men aged 20 to 79 years was drawn in the cities of Greifswald, Stralsund and Anklam and 29 communities in the surrounding region which is part of West Pomerania, a region in the northeast of Germany, adjacent to the Baltic Sea in the north and to the Polish border in the east. West Pomerania is the north-eastern part of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, one of the 16 federal German states.
A separate stratified random sample of 8016 adults aged 20–79 years was drawn for SHIP-TREND in the same area.
Currently, data are collected for the second examination follow-up of the first SHIP cohort (SHIP-2) and baseline examinations of the second SHIP cohort (SHIP-TREND).
SHIP-0: Data collection was conducted between October 1997 and May 2001.
SHIP-1 follow-up examination: SHIP-0 participants were invited again. The first 5-year-follow-up was conducted between October 2002 and September 2006.
SHIP-2 follow-up examination: The 11-year follow-up has started in June 2008 and was completed in autumn 2012.
SHIP-Trend-0: A new sample was drawn for a new cohort, which was examined between September 2008 and summer 2012.
Data collection
The following table shows all the instruments which are integrated in the SHIP examination.
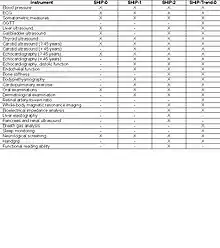

Previous results
The West Pomeranian population indicate a high prevalence of common risk factors and diseases. Especially overweight and obesity are more prevalent than in other German regions. Gallstone diseases are very common and 30% of all adults suffer from hepatic steatosis. The prevalence of arterial hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy is much higher in the West Pomeranian adult population. In the Northeast of Germany nearly 50% - 60% indicate these diseases.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
SHIP is the first population based cohort study worldwide which includes whole-body MRI. The aims of the following main whole body-MRI study are:

(1)To provide prevalence estimates for different MR findings in a general adult population.
(2)To establish population-based MRI reference parameters for various organs and organ parts such as left and right ventricular size or volume of liver, spleen, kidney, prostate,[1] and brain structures . Clinical MR reference parameters currently in use were derived from small, nonrepresentative samples and are thus prone to selection bias.
(3)To correlate MR findings with clinical examination results, metabolomic and genome-wide analysis in order to help elucidate the complex associations that exist between risk factors and diseases.
MRI Protocol
Additionally to the standard whole-body MRI protocol (right figure) men have the option to undergo contrast-enhanced cardiac MRI and MR angiography and women cardiac MRI and MR mammography. Participants with a drug allergy or allergy to any kind of contrast agent are excluded from the contrast-enhanced modules and only undergo standard protocol.
Assessment of Pathological Findings and Management
Two trained radiologists review all scans independently to evaluated images for presence or absence of pathological findings. In case of a difference between the two observer a third reading is performed to reach a consensus on the discrepant finding.
Pathological findings are categorized using the method chosen by Bryan et al. for the Cardiovascular Health Study. This method classifies all findings into 4 basic categories. The management of pathological findings and communication with study participants are defined in a standardized protocol accepted by the local ethics committee. Participants with category IV findings are immediately transferred to a clinical specialist. Cases with positive findings of category II and III are referred to an Advisory Board established when the study began. and having as permanent members specialists from medical, surgical, neurological, epidemiological and radiological departments. Upon presentation of cases they reach a consensus about whether to recommend further clinical work-up or not. Participants in whom relevant findings are made get informed about the abnormality and recommendation of the Advisory Board.
Ship-Legende
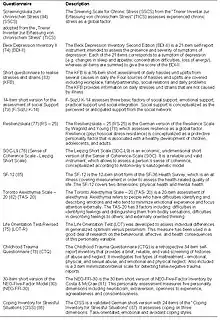
SHIP-LEGEND stands for Life-Events and Gene-Environment interaction in Depression; its main aim is the identification of genetic factors which interact with stress and traumatic events to increase the risk of major depressive disorders. SHIP is the basis for this research. Between July 2007 and August 2010 n=2393 probands were interviewed. The interviewer assessed stress, traumas and strains in childhood and adulthood of the probands. Additionally diagnostic interviews were performed to diagnose current and lifetime mental disorders (DSM-IV). A broad range of questionnaires were administered to assess e.g. alexithymia (Toronto Alexithymia Scale 20), aversive childhood conditions (Childhood Trauma Questionnaire), depression (Beck Depression Inventory-2), resilience (RS-25) and personality traits (NEO-FFI).
Funding
SHIP is funded by following institutions: Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Ministry of Cultural Affairs as well as the Social Ministry of the Federal State of Mecklenburg-West Pomerania, Federal Ministry of Nutrition, Agriculture and Consumer’s Safety, German Research Foundation, Competence Network Heart Failure, Competence Network Diabetes, German Asthma and COPD Network, Genopathomik, Alfried Krupp von Bohlen und Halbach Foundation, Alexander v. Humboldt Foundation, Leibniz Society, Siemens AG, Health Care Sector (Erlangen, Germany), Pfizer Pharma GmbH (SBU Endocrinology and Ophthalmology; Berlin Germany), Novo Nordisk (Mainz, Germany), Data Input GmbH (Darmstadt, Germany), GABA International AG (Therwil, Switzerland), Imedos Systems (Jena, Germany) and Heinen and Löwenstein (Bad Ems, Germany).
Publications
- Buch S, Schafmeyer C, Völzke H, Becker C, Franke A, von Eberstein H, Kluck C, Bäßmann I, Brosch M, Lammert F, Miquel JF, Nervi F, Wittig M, Rosskopf D, Timm B, Höll C, Seeger M, ElSharawy A, Fändrich F, Fölsch UR, Krawczak M, Schreiber S, Nürnberg P, Tepel J, Hampe J. A genome-wide association scan identifies the hepatic cholesterol transporter ABCG5/ABCG8 as a susceptibility factor for human gallstone disease. Nat Genetics 2007;39:995-999
- Baumeister SE, Völzke H, Marschall P, John U, Schmidt CO, Alte D. Impact of fatty liver disease on health care utilization and costs in the general population: a 5-year observation. Gastroenterology 2008;134:85-94
- Desvarieux M, Schwahn C, Völzke H, Demmer RT, Lüdemann J, Kessler C, Jacobs DR, John U, Kocher T. Gender differences in the relationship between periodontal disease, tooth loss and atherosclerosis. Stroke 2004;35:2029-2035
- Döring A, Gieger C, Mehta D, Gohlke H, Prokisch H, Coassin S, Fischer G, Henke K, Klopp N, Kronenberg F, Paulweber B, Pfeufer A, Rosskopf D, Völzke H, Illig T, Meitinger T, Wichmann HE, Meisinger C. SLC2A9 influences uric acid concentrations with pronounced gender-specific effects. Nat Genetics 2008;40:430-436
- Dörr M, Wolff B, Robinson DM, John U, Lüdemann J, Meng W, Felix SB, Völzke H. The association of thyroid function with cardiac mass and left ventricular hypertrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:673-677
- Dörr M, Vogelgesang D, Robinson DM, Kors JA, Felix SB, Völzke H. Thyroid function is associated with short rate-adjusted QT intervals. Results from a population-based study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91:4938-494
- Dörr M, Robinson DM, Wallaschofski H, Schwahn C, John U, Felix SB, Völzke H. Low serum thyrotropin is associated with high plasma fibrinogen. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91: 530-534
- Friedrich N, Völzke H, Hampe J, Lerch M, Jorgensen T. Known risk factors do not explain disparities in gallstone prevalence between Denmark and Northeast Germany. Am J Gastroenterol 2009; 104: 89 - 95
- Friedrich N, Haring R, Nauck M, Lüdemann J, Spilcke-Liss E, Felix SB, Dörr M, Brabant G, Völzke H, Wallaschofski H. Serum insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and mortality: results of the Study of Health in Pomerania. J Clin Endocrinol Metab; in press
- Gläser S, Friedrich N, Ewert R, Schäper C, Nauck M, Dörr M, Völzke H, Felix SB, Wallaschofski H, Koch B. Association between IGF-1 and IGFBP3 and lung function: results of the Study of Health in Pomerania. J Clin Endocrinol Metab; in press
- Grabe HJ, Lange M, Wolff B, Völzke H, Alte D, Lucht M, Freyberger HJ, John U, Cascorbi I. Mental and physical distress is modulated by a polymorphism in the 5-HT transporter gene interacting with social stressors and chronic disease burden. Mol Psychiatr 2005;10:220-224
- Grabe HJ, Spitzer C, Schwahn C, Barnow S, Lucht M, Freyberger HJ, John U, Wallaschofski H, Völzke H, Rosskopf D. The serotonin transporter gene promoter polymorphism (SLC6A4) and the susceptibility to posttraumatic stress disorder in the general population. Am J Psychiatr; in press
- Haring R, Wallaschofski H, Nauck M, Dörr M, Baumeister SE, Völzke H. Ultrasonographic hepatic steatosis increased prediction of mortality risk from elevated serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase levels. Hepatology; in press
- Haring R, Völzke H, Felix SB, Schipf S, Dörr M, Rosskopf D, Nauck M, Schöfl C, Wallaschofski H. Prediction of metabolic syndrome by low serum testosterone levels in men: Results from the Study of Health in Pomerania. Diabetes; in press
- Hegenscheid K, Kühn JP, Völzke H, Biffar R, Hosten N, Puls R. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging of healthy volunteers: pilot study results from the population-based SHIP study. Rofo. 2009;181(8):748-59.
- Houlston RS, Webb E, Broderick P, Pittman MA, Di Bernardo MC, Lubbe S, Chandler I, Vijayakrishnan j, Sullivan K, Penegar S, Carvajal-Carmona L, Howarth K, Jäger E, Spain S, Walther A, Barclay E, Martin L, Gorman M, Domingo E, Teixeira A, Kerr D, Cazier JB, Niittymäki I, Tuupanene S, Karhu A, Aaltonen L, Tomlinson IP, Farrington SM, Tenesa A, Prendergast JGD, Barnetson RA, Cetnarskyj R, Porteous ME, Pharoah PD, Kössler T, Hampe J, Buch S, Schafmayer C, Tepel J, Schreiber S, Völzke H, Chang-Claude J, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H, Zanke BW, Montpetit A, Hudson TJ, Gallinger S, Campbell H, Dunlop MG. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies 4 novel susceptibility loci for colorectal cancer. Nat Genetics 2008; 40: 1426 - 1435
- Koch B, Schäper C, Ittermann T, Spielhagen T, Völzke H, Ewert R, Gläser S. Reference values and ranges for cardiopulmonary exercise testing in a general adult population- results of the Study of Health in Pomerania. Eur Resp J 2009; 33: 389 - 397
- Kolz M, Johnson T, Sanna S, Teumer A, Vitart V, Perola M, Mangino M, Albrecht E, Wallace C, Farrall M, Johansson A, Nyholt DR, Aulchenko Y, Beckmann JS, Bergmann S, Bochud M, Brown M, Campbell H, Connell J, Dominiczak A, Homuth G, Lamina C, McCarthy MI, Meitinger T, Mooser V, Munroe P, Nauck M, Peden J, Prokisch H, Salo P, Salomaa V, Samani N, Schlessinger D, Uda M, Völker U, Wäber G, Waterwoth D, Wang-Sattler R, Writh AF, Adamski J, Whitfield JB, Gyllensten U, Wilson JF, Rudan I, Pramstaller P, Watkins H, Döring A, Wichmann HE, Spector TD, Peltonen L, Völzke H, Nagaraja R, Vollenweider P, Caulfield M, Illig T, Gieger C. Meta-analysis of 28,141 individuals identifies common variants within five new loci that influence uric acid concentrations. PLOS Genetics; in press
- Meisinger C, Heier M, Völzke H, Löwel H, Mitusch R, Lüdemann J, Hense HW. Regional disparities of hypertension prevalence and management within Germany. J Hypertens 2006; 24: 293-299
- Meisinger C, Gieger C, Prokisch H, Soranzo Z, Mehta D, Rosskopf D, Lichtner P, Klopp N, Stephens J, Watkins NA, Ouwehand WH, Deloukas P, Greinacher A, Koenig W, Nauck M, Rimmbach C, Völzke H, Peters A, Illig T, Meitinger T, Wichmann HE, Döring A. A genome-wide association study identifies three loci associated with mean platelet volume. Am J Hum Genet 2009; 84: 66 - 71
- Newton-Cheh, C.; Johnson, T.; Gateva, V.; Tobin, M. D.; Bochud, M.; Coin, L.; Najjar, S. S.; Zhao, J. H.; Heath, S. C.; Eyheramendy, S.; Papadakis, K.; Voight, B. F.; Scott, L. J.; Zhang, F.; Farrall, M.; Tanaka, T.; Wallace, C.; Chambers, J. C.; Khaw, K. T.; Nilsson, P.; Van Der Harst, P.; Polidoro, S.; Grobbee, D. E.; Onland-Moret, N. C.; Bots, M. L.; Wain, L. V.; Elliott, K. S.; Teumer, A.; Luan, J. A.; et al. (2009). "Genome-wide association study identifies eight loci associated with blood pressure". Nature Genetics. 41 (6): 666–676. doi:10.1038/ng.361. PMC 2891673. PMID 19430483.
- Puls R, Hosten N. (Hrgs.) Zufallsbefunde in der Ganzkörper-MRT. ABW Wissenschaftsverlag Berlin 2010, ISBN 978-3-940615-08-4
- Puls R, Hamm B, Hosten N. MRT ohne Radiologen - Ethische Aspekte bei bevölkerungsbasierten Studien mit MR-Untersuchungen. Rofo. 2010; 182:469-471
- Schmidt CO, Alte D, Sauer S, Völzke H, Friedrich N, Valliant R. (in press) Partial misspecification of survey design features sufficed to severely bias estimates of health related outcomes. J Clin Epidemiology.
- Soranzo N, Spector TD, Mangino M, Kühnel B, Rendon A, Teumer A, Willenborg C, Wright B, Chen L, Li M, Salo P, Voight BF, Burns P, Laskowski RA, Xue Y, Menzel S, Altshuler D, Bradley JR, Bumpstead S, Burnett MS, Devaney J, Döring A, Elosua R, Epstein S, Erber W, Falchi M, Garner SF, Ghori MJ, Goodall AH, Gwilliam R, Hall AS, Hammond N, Hengstenberg C, Illig T, König IR, Knouff CR, McPherson R, Melander O, Mooser V, Nauck M, Nieminen MS, O’Donnell CJ, Peltonen L, Potter SC, Prokisch H, Rader DJ, Rice CM, Roberts R, Salomaa V, Sambrook J, Schreiber S, Schunkert H, Schwartz SM, Serbanovic-Canic J, Sinisalo J, Siscovick DS, Stark K, Stephens J, Thompson JR, Völker U, Völzke H, Watkins NA, Wells GA, Wichmann HE, Heel DV, Tyler-Smith C, Thein SL, Kathiresan S, Perola M, Reilly MP, Stewart AF, Erdmann J, Samani NJ, Meisinger C, Greinacher A, Deloukas P, Ouwehand WH, Gieger C. A meta-analysis of eight haematological parameters identifies 22 associated loci and extensive disease pleiotropy on chromosome 12q24. Nat Genetics, in press
- Spitzer C, Barnow S, Völzke H, John U, Freyberger HJ, Grabe HJ. Trauma and Postraumatic Stress Disorder in an elderly community sample. J Clin Psychiatr 2008;69:693-700
- Tenesa A, Farrington SM, Prendergast JGD, Porteous ME, Walker M, Haq N, Barnetson RA, Theodoratou E, Cetnarskyj R, Cartwright N, Wilson R, Semple C, Clarke AJ, Reid FJL, Smith LA, Kavoussanakis K, Kossler T, Pharoah PDP, Buch S, Schafmayer C, Tepel J, Schreiber S, Völzke H, Schmidt CO, Hampe J, Wilkening S, Canzian F, Chang-Claude J, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H, Capella G, Moreno V, Deary IJ, Starr JM, Tomlinson IPM, Webb E, Houlston RS, Rennert G, Ballinger D, Rozek L, Gruber SB, Matsuda K, Kidokoro T, Nakamura Y, Zanke BW, Greenwood CMT, Rangrej J, Kustra R, Montpetit A, Hudson TJ, Gallinger S, Campbell H, Dunlop MG. A genome-wide association scan identifies three colorectal cancer susceptibility loci. Nat Genetics 2008;40:631-637
- Tomlinson IPM, Webb E, Carvajal-Carmona L, Broderick P, Howarth K, Pittman AM, Spain S, Lubbe S, Walther A, Sullivan K, Jaeger E, Fielding S, Rowan A, Vijayakrishnan J, Domingo E, Chandler I, Kemp Z, Qureshi M, Farrington SM, Tenesa A, Prendergast JGD, Bametson RA, Penegar S, Barclay E, Wood W, Martin L, Gorman M, Thomas H, Peto J, Bishop DT, Gray R, Maher ER, Lucassen A, Kerr D, Evans DGR, The CORGI Consortium, Schafmeyer C, Buch S, Völzke H, Hampe J, Schreiber S, John U, Kössler T, Pharoah P, van Wezel T, Morreau H, Wijnen JT, Hopper JL, Southey MC, Giles GG, Severi G, Catellvi-Bel S, Ruiz-Ponte C, Carracedo A, Castells A, The EPICOLON Consortium, Foersti A, Hemminki K, Vodicka P, Naccarati A, Lipton L, Ho JWC, Cheng KK, Sham PC, Luk J, Agundez JAG, Ladero JM, de la Hoya M, Caldés T, Niittymäki I, Tuupanene S, Karhu A, Aaltonen L, Cazier JB, Campbell H, Dunlop MG, Houlston RS. A genome-wide association study identifies novel colorectal cancer susceptibility loci on chromosomes 10p14 and 8q23.3. Nat Genetics 2008;40:623-630
- Vasan RS, Glazer NL, Felix JF, Lieb W, Wild PS, Felix SB, Watzinger N, Larson MG, Smith NL, Dehghan A, Großhennig A, Schillert A, Teumer A, Schmidt R, Kathiresan S, Lumley T, Aulchenko YS, König IR, Zeller T, Homuth G, Struchalin M, Aragam J, Bis JC, Rivadeneira J, Erdmann J, Dörr M, Greiser KH, Levy D, Haritunians T, Deckers JW, Stritzke J, Lackner KJ, Völker U, Ingelsson E, Iftikhar K, Härting J, O’Donnell CJ, Heckbert SR, Stricker BH, Ziegler A, Reffelmann T, Redfield MM, Werdan K, Mitchell GF, Rice K, Arnett D, Hofman A, Gottdiener JS, Uitterlinden AG, Meitinger T, Blettner M, Friedrich N, Wang TJ, Psaty BM, van Duijn CM, Wichmann HE, Munzel TF, Kroemer HK, Benjamin EJ, Rotter JI, Witteman JC, Schunkert H, Schmidt H, Völzke H, Blankenberg S. Novel genetic variants associated with cardiac structure and function: Genome-wide association findings of a prospective meta-analysis from the EchoGen Consortium. JAMA; in press
- Völzke H, Robinson DM, Schminke U, Lüdemann J, Rettig R, Felix SB, Kessler C, John U, Meng W. Thyroid function and carotid wall thickness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89:2145-2149
- Völzke H, Werner A, Wallaschofski H, Friedrich N, Robinson DM, Kindler S, Kraft M, John U, Hoffmann W. Occupational exposure to ionizing radiation is associated with autoimmune thyroid disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:4587-4592
- Völzke H, Warnke C, Dörr M, Kramer A, Gürtler L, Hoffmann W, Kors JA, John U, Felix SB. Prior history of diphtheria and current cardiac disorders. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2006; 25: 651-656
- Völzke H, Schwahn C, Dörr M, Schwarz S, Robinson D, Dören M, Felix SB, John U, Kocher T. Gender differences in the relation between number of teeth and systolic blood pressure. J Hypertens 2006; 24: 1257-1263
- Völzke H, Hoffmann W. [scientific letter] Radiation exposure and thyroid disorders in Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bomb survivors. JAMA 2006;296:512-513
- Völzke H, Alte D, Dörr M, Wallaschofski H, John U, Felix SB, Rettig R. The association between subclinical hyperthyroidism and blood pressure in a population-based study. J Hypertens 2006;24:1947-1953
- Völzke H. Mortality in patients with hepatitis B or hepatitis C. Lancet 2006;368:1767 [scientific letter]
- Völzke H, Schwarz S, Baumeister SE, Wallaschofski H, Schwahn C, Grabe HJ, Kohlmann T, John U, Dören M. Menopausal status and hepatic steatosis in a general female population. Gut 2007; 56: 594-595
- Völzke H, Friedrich N, Schipf S, Haring R, Lüdemann J, Nauck M, Dörr M, Brabant G, Wallaschofski H. Association between serum IGF-1 levels and thyroid disorders in a population-based study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:4039-4045
- Völzke H. Hyperthyroidism and mortality. [Scientific letter]. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;49:2229-2230
- Völzke H, Robinson D, Spielhagen T, Nauck M, Obst A, Ewert A, Wolff B, Wallaschofski H, Felix SB, Dörr M. Serum thyrotropin levels within the reference range are associated with endothelial function. Eur Heart J 2009; 30: 217 – 224
- Wolff B, Völzke H, Lüdemann J, Robinson DM, Vogelgesang D, Staudt A, Kessler C, Dahm JB, John U, Felix SB. Association between high serum ferritin levels and carotid atherosclerosis in the Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP). Stroke 2004;35:453 - 457
- Wolff B, Völzke H, Robinson D, Schwahn C, Vogelgesang D, Dahm JB, Kessler C, John U, Felix SB. Relation of parity with common carotid intima-media thickness among women of the Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP). Stroke 2005;36:938-943
References
- ↑ Habes M, Schiller T, Rosenberg C, Burchardt M, Hoffmann W (2013). "Automated prostate segmentation in whole-body MRI scans for epidemiological studies". Physics in Medicine and Biology. 58 (17): 5899–5915. Bibcode:2013PMB....58.5899H. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/58/17/5899. PMID 23920310.
- Völzke H, Alte D, Schmidt CO et al. (2009). "Cohort Profile: The Study of Health in Pomerania". International Journal of Epidemiology;1–14. doi:10.1093/ije/dyp394
- John U et al. (2001). "Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP) - A health examination survey in an east German region: Objectives and design". Sozial- und Präventivmedizin 46(3): 186-194.
- Bryan RN, Manolio TA, Schertz LD et al.(1994). "A method for using MR to evaluate the effects of cardiovascular disease on the brain: the cardiovascular health study". AJNR Am J Neuroradiol;15:1625-1633.