Transversalis fascia
| Transversalis fascia | |
|---|---|
 The abdominal inguinal ring. ("Fascia transversalis" visible near center.) | |
 Femoral sheath laid open to show its three compartments. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fascia transversalis |
| TA98 | A04.5.02.011 |
| TA2 | 2389 |
| FMA | 12265 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The transversalis fascia (or transverse fascia) is a thin aponeurotic membrane of the abdomen. It lies between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle and the parietal peritoneum.
It forms part of the general layer of fascia lining the abdominal parietes. It is directly continuous with the iliac fascia, the internal spermatic fascia, and pelvic fasciae.
Structure
In the inguinal region, the transversalis fascia is thick and dense. It is joined by fibers from the aponeurosis of the transverse abdominal muscle. It becomes thin as it ascends to the diaphragm and blends with the fascia covering the under surface of this muscle. It is directly continuous with the iliac fascia, the internal spermatic fascia, and pelvic fasciae.
Borders
Behind, it is lost in the fat which covers the posterior surfaces of the kidneys.
Below, it has the following attachments: posteriorly, to the whole length of the iliac crest, between the attachments of the transverse abdominal and Iliacus; between the anterior superior iliac spine and the femoral vessels it is connected to the posterior margin of the inguinal ligament, and is there continuous with the iliac fascia.
Medial to the femoral vessels it is thin and attached to the pubis and pectineal line, behind the inguinal falx, with which it is united; it descends in front of the femoral vessels to form the anterior wall of the femoral sheath.
Beneath the inguinal ligament it is strengthened by a band of fibrous tissue, which is only loosely connected to the ligament, and is specialized as the iliopubic tract.
Opening
The spermatic cord in the male and the round ligament of the uterus in the female pass through the transversalis fascia at the deep inguinal ring, the entrance to the inguinal canal. This opening is not visible externally. In the male, the transverse fascia extends downwards as the internal spermatic fascia.[1]
Additional images
 Transversalis fascia
Transversalis fascia Diagram of sheath of Rectus.
Diagram of sheath of Rectus.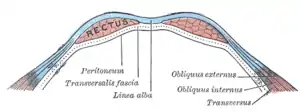 Diagram of a transverse section through the anterior abdominal wall, below the linea semicircularis.
Diagram of a transverse section through the anterior abdominal wall, below the linea semicircularis.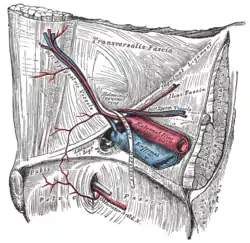 Gray547.png
Gray547.png
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 418 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 418 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ Jacob, S. (2008). "4 - Abdomen". Human Anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. pp. 71–123. doi:10.1016/B978-0-443-10373-5.50007-5. ISBN 978-0-443-10373-5.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 35:03-05 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Layers of the anterior wall."
- Anatomy photo:36:01-0202 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Inguinal Region, Scrotum and Testes: The Inguinal canal"
- Atlas image: abdo_wall49 at the University of Michigan Health System (look for #2)
- Cross section image: pembody/body12a—Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna