Voclosporin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lupkynis |
| Other names | VCS, ISA247 |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Calcineurin inhibitor[1] |
| Main uses | Lupus nephritis[1] |
| Side effects | High blood pressure, kidney dysfunction, diarrhea, headache, cough, abdominal pain, hair loss, tremor, mouth ulcers[1] |
| Interactions | Grapefruit[1] |
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| US NLM | Voclosporin |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
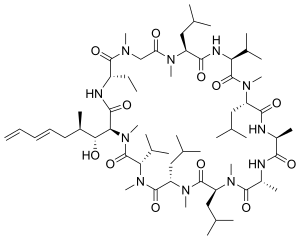
| Formula | C63H111N11O12 |
| Molar mass | 1214.646 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Voclosporin, sold under the brand name Lupkynis, is a medication used to treat lupus nephritis.[1] It is used in those with severe disease together with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and corticosteroids.[1][2] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include high blood pressure, kidney dysfunction, diarrhea, headache, cough, abdominal pain, hair loss, tremor, and mouth ulcers.[1] Other side effects may include high potassium and QT prolongation.[1] It is not typically used in people with long standing poor kidney function or significantly high blood pressure.[1] Use in pregnancy may harm the baby.[1] It interacts with grapefruit.[1] It is a calcineurin inhibitor.[1]
Voclosporin was approved for medical use in the United States in 2021 and Europe in 2022.[1][2] In the United States it costs about 13,400 USD per month.[3] It is not approved in the United Kingdom as of 2022.[4] It was previously studied for dry eyes.[4]
Medical uses
Lupus nephritis is a common form of glomerular nephritis occurring in patients with systemic lupus nephritis. Lupus nephritis commonly leads patients to chronic kidney failure and therefore places an emphasis on early intervention for improving treatment outcomes. Early intervention with voclosporin in combination with kidney response is believed to lead to more positive clinical outcomes for lupus nephritis patients.[5] Thus, voclosporin is used in combination with background immunosuppressive regimen for the treatment of lupus nephritis. Safety has not been established in combination with cyclophosphamide.[5]
It results in 41% of people having stable kidney function compared with 23% using a placebo.[2]
Dosage
It is generally started at 23.7 mg twice per day by mouth.[1] Lower doses may be used in those with slightly low kidney function.[1]
Side effects
Voclosporin has a boxed warning for malignancies and serious infections. Patients taking Voclosporin along with other immunosuppressants have an increased risk for developing malignancies and serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death.[1] The most common adverse reactions of voclosporin were (>3%), glomerular filtration rate decreased, hypertension, diarrhea, headache, anemia, cough, urinary tract infection, abdominal pain(upper), dyspepsia, alopecia, renal impairment, abdominal pain, mouth ulceration, fatigue. tremor, acute kidney injury, and decreased appetite.
People who are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed should not take this medication as it may cause fetal harm.[1] Voclosporin is not recomnended in a baseline eGFR less than or equal to 45 ml/min/1.73 m2 unless benefits exceeds risk. Dose should be reduced if the drug is used within this population as well as for patients who are hepatically impaired.[1] Avoid the use of live attenuated vaccines when patients are on this medication.[1] Avoid co-administration of voclosporin and other moderate to strong CYP3A4 inhibitors and if needed then reduce the dose of voclosporin. Dosages of PgP-substrate drugs should be reduced if co-administered with voclosporin.[5]
Pharmacology
Voclosporin is a cyclosporin A analog, similar to cyclosporin A with modifications on an amino acid within one region that allows the drug to bind to Calcineurin.[5] Voclosporin inhibits calcineurin, which then blocks the production of IL-2 and T-cell mediated immune responses. As a result of the calcineurin inhibition, podocytes (cells within the kidneys) are stabilized while inflammation is reduced. Reduction of inflammation within the kidneys prevents further renal damage.[5]
Pharmacokinetics
When administered on an empty stomach, the median Tmax of voclosporin is 1.5 hours.[5] The AUC is estimated to be 7693 ng/mL and the Cmax is estimated at 955 ng/mL.[5] The volume of distribution is approximately 2,154 L and distributes within the red blood cells. The distribution between the plasma and whole blood is affected by temperature and concentration.[5] The protein binding of voclosporin is 97%. The average terminal half-life of voclosporin is 63.6 L/h. The drug is mainly metabolized by the CYP3A4 hepatic cytochrome enzyme.[5] Pharmacologic activity is mainly attributed to the parent molecule itself, with the major metabolite being 8-fold less potent than the parent drug.[5]
History
Voclosporin was discovered by Isotechnika in the 1990s.[6] Isotechnika was founded in 1993 and merged with Aurinia Pharmaceuticals in 2013. In January 2021, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals received approval from the Food & Drug Administration to sell the drug Lupkynis.[7][8]
Society and culture
Legal status
On 21 July 2022, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for the medicinal product Lupkynis, intended for the treatment of lupus nephritis.[2][9] The applicant for this medicinal product is Otsuka Pharmaceutical Netherlands B.V.[9] Voclosporin was approved for medical use in the European Union in September 2022.[2]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 "Lupkynis- voclosporin capsule". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 30 July 2022. Retrieved 13 September 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Lupkynis EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 19 July 2022. Archived from the original on 22 September 2022. Retrieved 21 September 2022. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ "Lupkynis Prices, Coupons, Copay & Patient Assistance". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 25 May 2021. Retrieved 1 November 2022.
- 1 2 "Voclosporin". SPS - Specialist Pharmacy Service. 22 May 2018. Archived from the original on 3 March 2022. Retrieved 1 November 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Voclosporin". go.drugbank.com. Archived from the original on 16 April 2022. Retrieved 2022-04-16.
- ↑ U.S. Patent 6,605,593
- ↑ "Drug Trials Snapshot: Lupkynis". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 22 January 2021. Archived from the original on 11 February 2021. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Lupkynis". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 24 February 2021. Archived from the original on 15 September 2021. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- 1 2 "Lupkynis: Pending EC decision". European Medicines Agency. 21 July 2022. Archived from the original on 28 July 2022. Retrieved 30 July 2022. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |