Zanubrutinib
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Brukinsa |
| Other names | BGB-3111 |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor[1] |
| Main uses | Mantle cell lymphoma,[1] lymphoplasmatic lymphoma[2] |
| Side effects | Low white blood cells, low platelets, rash, diarrhea, low hemoglobin[1] |
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| Typical dose | 320 mg per day[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| US NLM | Zanubrutinib |
| MedlinePlus | a620009 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
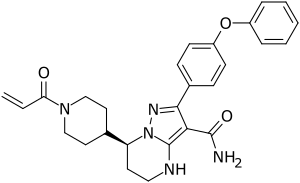
| Formula | C27H29N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 471.5509 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Zanubrutinib, sold under the brand name Brukinsa, is a medication used for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) which has received prior treatment.[1] It may also be used for lymphoplasmatic lymphoma.[2] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include low white blood cells, low platelets, rash, diarrhea, and low hemoglobin.[1] Other side effects may include bleeding, infection, atrial fibrillation, and another cancer.[1] Use during pregnancy may harm the baby.[1] It is a Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor and works by slowing tumor growth.[1]
Zanubrutinib was approved for medical use in the United States in 2019.[1] It received an orphan designation in Europe that year as well.[2] In the United States a month of treatment costs about 13,000 USD as of 2021.[4] This amount in China cost about 21,000 RMB (3,250 USD).[5]
Medical uses
Dosage
It is taken at a dose of 320 mg per day.[1]
History
Efficacy was evaluated in a phase II open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial of 86 patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who received at least one prior therapy.[6] Zanubrutinib was given orally at 160 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.[6] Efficacy was also assessed in BGB-3111-AU-003 (NCT 02343120), a phase I/II, open-label, dose-escalation, global, multicenter, single-arm trial of B‑cell malignancies, including 32 previously treated MCL patients treated with zanubrutinib administered orally at 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily.[6][7]
The primary efficacy outcome measure in both trials was overall response rate (ORR), as assessed by an independent review committee.[6] In trial BGB-3111-206, FDG-PET scans were required and the ORR was 84% (95% CI: 74, 91), with a complete response rate of 59% (95% CI 48, 70) and a median response duration of 19.5 months (95% CI: 16.6, not estimable).[6] In trial BGB-3111-AU-003, FDG-PET scans were not required and the ORR was 84% (95% CI: 67, 95), with a complete response rate of 22% (95% CI: 9, 40) and a median response duration of 18.5 months (95% CI: 12.6, not estimable).[6] Trial 1 was conducted at 13 sites in China, and Trial 2 was conducted at 25 sites in the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, Italy, and South Korea.[7]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted zanubrutinib priority review, accelerated approval, breakthrough therapy designation, and orphan drug designation.[8][6][9]
The FDA approved zanubrutinib in November 2019, and granted the application for Brukinsa to BeiGene USA Inc.[8][6][10]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "Zanubrutinib Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 16 January 2021. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- 1 2 3 "EU/3/19/2167". Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ↑ "Zanubrutinib". DrugBank. Archived from the original on 15 November 2019. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
- ↑ "Zanubrutinib Prices and Zanubrutinib Coupons - GoodRx". GoodRx. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ↑ "Application for the addition of Zanubrutinib on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines" (PDF). November 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "FDA grants accelerated approval to zanubrutinib for mantle cell lymphoma". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 15 November 2019. Archived from the original on 28 November 2019. Retrieved 27 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 "Drug Trials Snapshots Brukinsa". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 14 November 2019. Archived from the original on 23 January 2021. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 "FDA approves therapy to treat patients with relapsed and refractory mantle cell lymphoma supported by clinical trial results showing high response rate of tumor shrinkage". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 14 November 2019. Archived from the original on 15 November 2019. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ "Zanubrutinib Orphan Drug Designation and Approval". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 28 November 2019. Archived from the original on 28 November 2019. Retrieved 27 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Brukinsa". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 27 November 2019. Archived from the original on 28 November 2019. Retrieved 27 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |