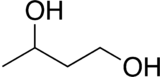
1,3-Butanediol
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Butane-1,3-diol | |||
| Other names
1,3-butylene glycol, butane-1,3-diol, or 1,3-dihydroxybutane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
| ||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
Beilstein Reference |
1731276 1718944 (R) | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.209 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E1502 (additional chemicals) | ||
Gmelin Reference |
2409 2493173 (R) | ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | 1,3-Butylene+glycol | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula |
C4H10O2 | ||
| Molar mass | 90.122 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.0053 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −50 °C (−58 °F; 223 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 204 to 210 °C; 399 to 410 °F; 477 to 483 K | ||
Solubility in water |
1 kg dm−3 | ||
| log P | −0.74 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 8 Pa (at 20 °C) | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.44 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std molar entropy (S |
227.2 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−501 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−2.5022 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
Pictograms |
 | ||
Signal word |
Warning | ||
Hazard statements |
H319, H413 | ||
Precautionary statements |
P305+P351+P338 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 108 °C (226 °F; 381 K) | ||
Autoignition temperature |
394 °C (741 °F; 667 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related butanediol |
1,2-Butanediol | ||
Related compounds |
2-Methylpentane | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
1,3-Butanediol is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2OH. With two alcohol functional groups, the molecule is classified as a diol. The compound is a colorless, water-soluble liquid. It is one of four common structural isomers of butanediol. It has no large scale uses.[1][2]
Production and uses
Hydrogenation of 3-hydroxybutanal gives 1,3-butanediol:[3]
- CH3CH(OH)CH2CHO + H2 → CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2OH
Dehydration of 1,3-butanediol gives 1,3-butadiene:
- CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2OH → CH2=CH-CH=CH2 + 2 H2O
Occurrence
In biology, 1,3-butanediol is used as a hypoglycaemic agent. 1,3-Butanediol can be converted into β-hydroxybutyrate and serve as a substrate for brain metabolism.[4]
References
- ↑ Gräfje, Heinz; Körnig, Wolfgang; Weitz, Hans-Martin; Reiß, Wolfgang; Steffan, Guido; Diehl, Herbert; Bosche, Horst; Schneider, Kurt; Kieczka (2000). "Butanediols, Butenediol, and Butynediol". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a04_455.
- ↑ Parchem, fine & specialty chemicals. "1,3 Butylene Glycol".
- ↑ Kohlpaintner, Christian; Schulte, Markus; Falbe, Jürgen; Lappe, Peter; Weber, Jürgen (2008). "Aldehydes, Aliphatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_321.pub2.
- ↑ Marie, Christine; Bralet, Anne-Marie; Bralet, Jean (1987). "Protective Action of 1,3-Butanediol in Cerebral Ischemia. A Neurologic, Histologic, and Metabolic Study". Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 7 (6): 794–800. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1987.136. PMID 3693436.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.