Abductor hallucis muscle
| Abductor hallucis muscle | |
|---|---|
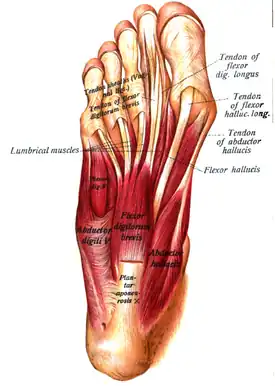 First layer of muscles of the sole of the foot (abductor hallucis visible at lower right) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Medial process of calcaneal tuberosity, Plantar aponeurosis, Flexor retinaculum |
| Insertion | Medial aspect of base of 1st phalanx of hallux |
| Artery | Medial plantar artery |
| Nerve | Medial plantar nerve |
| Actions | Abducts hallux |
| Antagonist | Adductor hallucis muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus abductor hallucis |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.056 |
| TA2 | 2672 |
| FMA | 37448 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The abductor hallucis muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the foot. It participates in the abduction and flexion of the great toe.
Structure
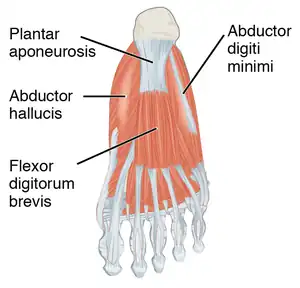
The abductor hallucis muscle is located in the medial border of the foot and contributes to form the prominence that is observed on the region. It is inserted behind on the tuberosity of the calcaneus, the flexor retinaculum, and the plantar aponeurosis.[1] Its muscle body, relatively thick behind, flattens as it goes forward. It ends in a common tendon with the medial head of the flexor hallucis brevis that inserts on the medial surface of the base of the first proximal phalanx and its related sesamoid bone. Its medial surface is superficial and covered with the muscle's fascia and the skin.[2]
Nerve supply
Abductor hallucis is supplied by the medial plantar nerve. The nerves that supply it enter the muscle from its upper border.
Additional images
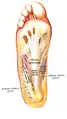 Superficial dissection of the sole of the foot, showing the medial eminence formed by abductor hallucis
Superficial dissection of the sole of the foot, showing the medial eminence formed by abductor hallucis.jpg.webp) Abductor hallucis muscle
Abductor hallucis muscle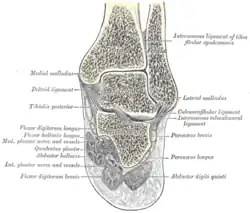 Coronal section through right talocrural and talocalcaneal joints
Coronal section through right talocrural and talocalcaneal joints
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 491 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 491 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ "Abductor Hallucis". Loyola University Medical Education Network. Retrieved 7 January 2015.
- ↑ Latarjet, Michel; Ruiz Liard, Alfredo (2005). Human Anatomy (Spanish ed.). Editorial Médica Panamericana. ISBN 978-950-06-1368-2.
External links
- Anatomy photo:16:st-0402 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- PTCentral