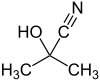
Acetone cyanohydrin
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile[1] | |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
|||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 3DMet | |||
Beilstein Reference |
605391 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.828 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | acetone+cyanohydrin | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1541 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula |
C4H7NO | ||
| Molar mass | 85.106 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 932 mg·mL−1 | ||
| Melting point | −21.2 °C; −6.3 °F; 251.9 K | ||
| Boiling point | 95 °C; 203 °F; 368 K | ||
| Vapor pressure | 2 kPa (at 20 °C) | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.399 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−121.7 to −120.1 kJ·mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−2.4514 to −2.4498 MJ·mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
Pictograms |
  | ||
Signal word |
Danger | ||
Hazard statements |
H300, H310, H330, H410 | ||
Precautionary statements |
P260, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 75 °C (167 °F; 348 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 2.25–11% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose) |
| ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible) |
None[2] | ||
REL (Recommended) |
C 1 ppm (4 mg·m−3) [15-minute][2] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[2] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | fishersci.com | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanenitriles |
| ||
Related compounds |
DBNPA | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Acetone cyanohydrin (ACH) is an organic compound used in the production of methyl methacrylate, the monomer of the transparent plastic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), also known as acrylic. It liberates hydrogen cyanide easily, so it is used as a source of such. For this reason, this cyanohydrin is also highly toxic.
Preparation
In the laboratory, this compound may be prepared by treating sodium cyanide with acetone, followed by acidification:[3]
Considering the high toxicity of acetone cyanohydrin, a lab scale production has been developed using a microreactor-scale flow chemistry[4] to avoid needing to manufacture and store large quantities of the reagent. Alternatively, a simplified procedure involves the action of sodium or potassium cyanide on the sodium bisulfite adduct of acetone prepared in situ. This gives a less pure product, one that is nonetheless suitable for most syntheses.[5]
Reactions
Acetone cyanohydrin is an intermediate en route to methyl methacrylate.[6] Treatment with sulfuric acid gives the sulfate ester of the methacrylamide, methanolysis of which gives ammonium bisulfate and methyl methacrylate.[7]
It is used as a surrogate in place of HCN, as illustrated by its use as a precursor to lithium cyanide:[8]
- (CH3)2C(OH)CN + LiH → (CH3)2CO + LiCN + H2
In transhydrocyanation, an equivalent of HCN is transferred from acetone cyanohydrin to another acceptor, with acetone as byproduct. The transfer is an equilibrium process, initiated by base. The reaction can be driven by trapping reactions or by the use of a superior HCN acceptor, such as an aldehyde.[9] In the hydrocyanation reaction of butadiene, the transfer is irreversible.[10]
Natural occurrence
Cassava tubers contain linamarin, a glucoside of acetohydrin, and the enzyme linamarase for hydrolysing the glucoside. Crushing the tubers releases these compounds and produces acetone cyanohydrin.
Safety
Acetone cyanohydrin is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the US Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act and carries an RCRA P069 waste code. The principal hazards of acetone cyanohydrin arise from its ready decomposition on contact with water, which releases highly toxic hydrogen cyanide.
References
- ↑ "acetone cyanohydrin - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification. Retrieved 8 June 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0005". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Cox, R. F. B.; Stormont, R. T. "Acetone Cyanohydrin". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, vol. 2, p. 7
- ↑ Heugebaert, Thomas S. A.; Roman, Bart I.; De Blieck, Ann; Stevens, Christian V. (2010-08-11). "A safe production method for acetone cyanohydrin". Tetrahedron Letters. 51 (32): 4189–4191. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2010.06.004.
- ↑ Wagner, E. C.; Baizer, Manuel. "5,5-Dimethylhydantoin". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, vol. 3, p. 323
- ↑ Wiley, Richard H.; Waddey, Walter E. (1949). "Methacrylamide". Organic Syntheses. 29: 61. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.029.0061.
- ↑ Bauer, William, Jr. "Methacrylic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_441..
- ↑ Tom Livinghouse (1981). "Trimethylsilyl Cyanide: Cyanosilylation of p-Benzoquinone". Org. Synth. 60: 126. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.060.0126.
- ↑ Haroutounian, Serkos A. (2001). "Acetone Cyanohydrin". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. eEROS. doi:10.1002/047084289X.ra014. ISBN 0471936235.
- ↑ Bini, L.; Müller, C.; Wilting, J.; von Chrzanowski, L.; Spek, A. L.; Vogt, D. (October 2007). "Highly selective hydrocyanation of butadiene toward 3-pentenenitrile". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129 (42): 12622–12623. doi:10.1021/ja074922e. hdl:1874/26892. PMID 17902667.
External links
- SIDS Initial Assessment Report for Acetone cyanohydrin from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
- CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards - Acetone Cyanohydrin