Copanlisib
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Aliqopa /ˌælɪˈkoʊpə/ AL-ih-KOH-pah |
| Trade names | Aliqopa |
| Other names | BAY 80-6946 |
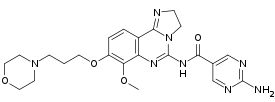
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | PI3-kinase inhibitor[1] |
| Main uses | Follicular lymphoma[2] |
| Side effects | High blood sugar, diarrhea, weakness, high blood pressure, low white blood cells, nausea, pneumonia, low platelets[2] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Routes of use | intravenous infusion only |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a617044 |
| Legal | |
| License data | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | 84.2%[3] |
| Metabolism | CYP3A4/5 (≈90%), CYP1A1 (≈10%)[3] |
| Elimination half-life | 39.1 hours (range: 14.6 to 82.4)[3] |
| Excretion | Feces (64%), Urine (22%); 14% were not recovered[3] |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H28N8O4 |
| Molar mass | 480.529 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Copanlisib, sold under the brand name Aliqopa, is a medication used to treat follicular lymphoma.[2] It is used in those who have failed other treatments.[2] It is given by injection into a vein.[2]
Common side effects include high blood sugar, diarrhea, weakness, high blood pressure, low white blood cells, nausea, pneumonia, and low platelets.[2] Other side effects may include infection and pneumonitis.[2] Use in pregnancy may harm the baby.[2] It is a PI3-kinase inhibitor.[1]
Copanlisib was approved for medical use in the United States in 2017.[2] As of 2022 it is not approved in either the United Kingdom or Europe.[4] In the United States it costs about 5,000 USD per dose as of 2022.[5]
Medical uses
Efficacy resulting in the approval of copanlisib was based on the subgroup of 104 patients with follicular lymphoma from a Phase 2 clinical trial.[6] Of these, 59 percent had a complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors that lasted about 12 months. To assess the safety of the drug, data from 168 adults with follicular lymphoma and other hematologic malignancies treated with copanlisib were evaluated.[7]
Copanlisib is administered as intravenous infusion on a weekly but intermittent schedule (three weeks on and one week off).
Dosage
It is given at a dose of 60 mg on day 1, 8, and 15 every 28 days.[2] A dose of 45 mg is used in those with moderate liver problems.[2]
Side effects
Data for safety and efficacy of copanlisib are described in the consumer-targeted FDA Drug Trial Snapshot.[7] Copanlisib can cause serious side effects including infections, hyperglycemia, hypertension, pneumonitis, neutropenia and skin rashes. The most common side effects of copanlisib are hyperglycemia, diarrhea, decreased general strength and energy, hypertension, leukopenia, neutropenia, nausea, lower respiratory tract infections and thrombocytopenia. Copanlisib can cause harm to unborn babies. Patients with reproductive potential are thus advised to use effective contraception. Lactating patients are advised to not breastfeed.
Mechanism of action
Copanlisib is an inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) with inhibitory activity predominantly against PI3K-α and PI3K-δ isoforms expressed in malignant B-cells. It has been shown to induce tumor cell death by apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation of primary malignant B cell lines.[3]
History
Follicular lymphoma
For follicular lymphoma, the FDA awarded copanlisib orphan drug status in February 2015 and fast track designation in February 2016.[8] The NDA for follicular lymphoma was granted priority review in May 2017.[9]
In September 2017, it received accelerated approval (FDA regulation 21 CFR Part 314 subpart H) for the treatment of adult patients experiencing relapsed follicular lymphoma who have received at least two prior systemic therapies. Further clinical trials are to be performed as a post-marketing requirement to verify the clinical benefit.[10]
Other
Copanlisib was granted orphan drug status for the treatment of splenic, nodal and extranodal subtypes of marginal zone lymphoma.[9]
Research
Phase II clinical trials are in progress for treatment of endometrial cancer,[11] diffuse large B-cell lymphoma,[12] cholangiocarcinoma,[13] and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.[6] Copanlisib in combination with R-CHOP or R-B (rituximab and bendamustine) is in a phase III trial for relapsed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).[14] Two separate phase III trials are investigating the use of copanlisib in combination with rituximab for indolent NHL[15] and the other using copanlisib alone in cases of rituximab-refractory indolent NHL.[16]
In a preclinical study, copanlisib was effective in inhibiting HER2+ breast cancer cells with acquired resistance to the HER2-inhibitors trastuzumab and/or lapatinib. This effect was increased when copanlisib was administered along with the aforementioned HER2-inhibitors.[17] Consequently, treatments of copanlisib with trastuzumab are being clinically trialled in HER2-positive breast cancer patients.[18]
References
- 1 2 "Copanlisib Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "DailyMed - ALIQOPA- copanlisib injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 18 March 2021. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "FDA Prescribing information for Aliqopa" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-04-06. Retrieved 2021-05-25.
- ↑ "Copanlisib". SPS - Specialist Pharmacy Service. 30 December 2015. Archived from the original on 3 October 2021. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- ↑ "Aliqopa Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 2019-04-12. Retrieved 2022-01-07.
- 1 2 Clinical trial number NCT01660451 for "Open-label, Uncontrolled Phase II Trial of Intravenous PI3K Inhibitor BAY80-6946 in Patients With Relapsed, Indolent or Aggressive Non-Hodgkin's Lymphomas" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- 1 2 Food and Drug Administration. "Drug Trials Snapshots ALIQOPA". www.fda.gov. Archived from the original on 2019-04-23. Retrieved 2021-05-25.
- ↑ Food and Drug Administration. "NDA 209936, Multisciplinary Review document, chapter 3" (PDF). www.fda.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-11-02. Retrieved 2021-05-25.
- 1 2 Bayer AG (17 May 2017). "Bayer News Release" (PDF). www.bayer.com. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 December 2017. Retrieved 25 May 2021.
- ↑ Food and Drug Administration. "NDA 209936, Approval Letter" (PDF). www.fda.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-11-02. Retrieved 2021-05-25.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT02728258 for "Copanlisib in Treating Patients With Persistent or Recurrent Endometrial Cancer" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT02391116 for "Phase II Copanlisib in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT02631590 for "Copanlisib (BAY 80-6946) in Combination With Gemcitabine and Cisplatin in Advanced Cholangiocarcinoma" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT02626455 for "Study of Copanlisib in Combination With Standard Immunochemotherapy in Relapsed Indolent Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (iNHL)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT02367040 for "Copanlisib and Rituximab in Relapsed Indolent B-cell Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (iNHL)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT02369016 for "Phase III Copanlisib in Rituximab-refractory iNHL" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Elster N, Cremona M, Morgan C, Toomey S, Carr A, O'Grady A, et al. (January 2015). "A preclinical evaluation of the PI3K alpha/delta dominant inhibitor BAY 80-6946 in HER2-positive breast cancer models with acquired resistance to the HER2-targeted therapies trastuzumab and lapatinib". Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 149 (2): 373–83. doi:10.1007/s10549-014-3239-5. PMID 25528022. S2CID 25568678. Archived from the original on 2017-09-21. Retrieved 2021-05-25.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT02705859 for "Phase Ib/II Trial of coPANlisib in Combination With Trastuzumab in HER2-positive Breast Cancer. (Panther Study)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|