Basal plate (neural tube)
| Basal plate | |
|---|---|
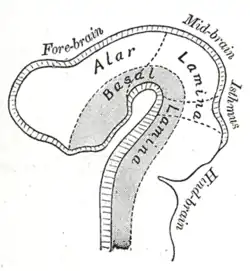 Diagram to illustrate the alar and basal laminæ of brain vesicles. | |
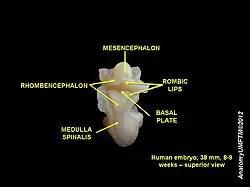 Basal plate | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Neural tube |
| Gives rise to | Lower motor neurons, interneurons |
| System | Nervous system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lamina ventrolateralis; lamina basalis |
| TE | plate (neural tube)_by_E5.14.1.0.1.0.6 E5.14.1.0.1.0.6 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In the developing nervous system, the basal plate is the region of the neural tube ventral to the sulcus limitans. It extends from the rostral mesencephalon to the end of the spinal cord and contains primarily motor neurons, whereas neurons found in the alar plate are primarily associated with sensory functions. The cell types of the basal plate include lower motor neurons and four types of interneuron.[1]
Initially, the left and right sides of the basal plate are continuous, but during neurulation they become separated by the floor plate, and this process is directed by the notochord. Differentiation of neurons in the basal plate is under the influence of the protein Sonic hedgehog released by ventralizing structures, such as the notochord and floor plate.[1]
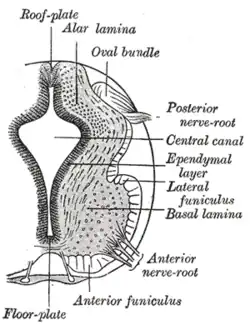 The basal plate (basal lamina) is separated from the alar plate (alar lamina) by the sulcus limitans (unlabeled).
The basal plate (basal lamina) is separated from the alar plate (alar lamina) by the sulcus limitans (unlabeled).
References
- 1 2 Bruce M. Carlson (2004). Human Embryology and Developmental Biology (2nd ed.). Saint Louis, MO: Mosby. ISBN 0-323-03649-X.
- Bibliography
- John A. Kiernan (2005). Barr's the Human Nervous System: An Anatomical Viewpoint (8th ed.). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-5154-3.
External links
- Overview at temple.edu
- ancil-451 at NeuroNames