Cerebral peduncle
| Cerebral peduncle | |
|---|---|
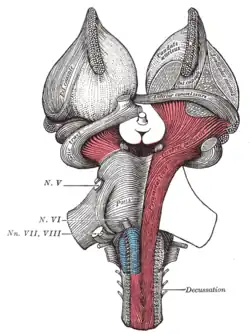 Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Ventral view. ("cerebral peduncle" visible in red at center-right) | |
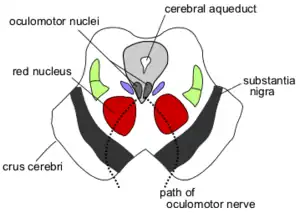 Obtuse section (perpendicular to the brainstem) through superior colliculus showing path of oculomotor nerve (Crus cerebri labeled at lower left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | pedunculus cerebri |
| MeSH | D065850 |
| NeuroNames | 487 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1202 |
| TA98 | A14.1.06.004 |
| TA2 | 5878 |
| FMA | 62394 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The cerebral peduncles are the two stalks that attach the cerebrum to the brainstem.[1] They are structures at the front of the midbrain which arise from the ventral pons and contain the large ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) nerve tracts that run to and from the cerebrum from the pons. Mainly, the three common areas that give rise to the cerebral peduncles are the cerebral cortex, the spinal cord and the cerebellum.[2] The region includes the tegmentum, crus cerebri and pretectum. By this definition, the cerebral peduncles are also known as the basis pedunculi, while the large ventral bundle of efferent fibers is referred to as the cerebral crus or the pes pedunculi.
The cerebral peduncles are located on either side of the midbrain and are the frontmost part of the midbrain, and act as the connectors between the rest of the midbrain and the thalamic nuclei and thus the cerebrum. As a whole, the cerebral peduncles assist in refining motor movements, learning new motor skills, and converting proprioceptive information into balance and posture maintenance.[3][4] Important fiber tracts that run through the cerebral peduncles are the corticospinal, corticopontine, and corticobulbar tracts. Damage to the cerebral peduncles results in unrefined motor skills, imbalance, and lack of proprioception.[5]
Structure
The descending upper fibers from the internal capsule continue on through the midbrain and are then seen as the fibers in the cerebral peduncles.[6] The corticopontine fibers are found in the outer and inner third of the cerebral peduncle, these are the cortical input to the pontine nuclei.[7] The corticobulbar and corticospinal fibers are found in the middle third of the cerebral peduncle.[8] The corticospinal tract exits the internal capsule and is seen in the mid portion of the cerebral peduncles.
Cranial nerves
Cranial nerve 3 (oculomotor nerve) appears ventrally between the two cerebral peduncles in the interpeduncular fossa. Cranial nerve 4 (trochlear nerve) wraps around the lowest part of the cerebral peduncle.[9]
Additional images
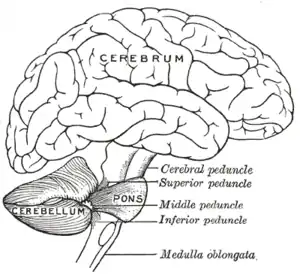 Scheme showing the connections of the several parts of the brain
Scheme showing the connections of the several parts of the brain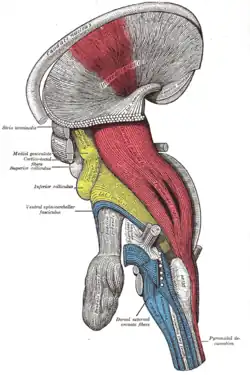 Deep dissection of brain-stem (lateral view)
Deep dissection of brain-stem (lateral view)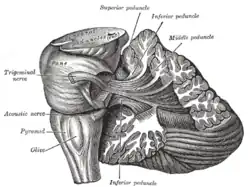 Dissection showing the projection fibers of the cerebellum
Dissection showing the projection fibers of the cerebellum Median sagittal section of brain
Median sagittal section of brain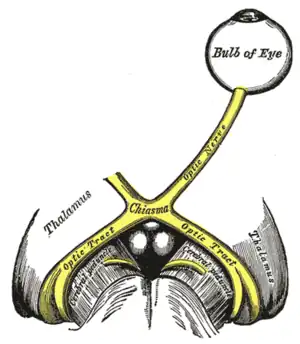 The left optic nerve and the optic tracts
The left optic nerve and the optic tracts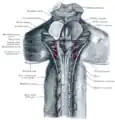 Upper part of medulla spinalis and hind- and mid-brains; posterior aspect, exposed in situ
Upper part of medulla spinalis and hind- and mid-brains; posterior aspect, exposed in situ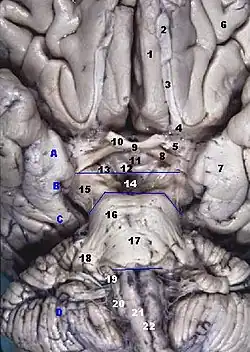 Human brainstem anterior view
Human brainstem anterior view
See also
References
- ↑ Saladin, K (2012). Human anatomy (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 525. ISBN 9780071222075.
- ↑ Saladin, Kenneth (2010), Anatomy & Physiology The Unity of Form and Function, New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
- ↑ Swenson, Rand. Review of Clinical and Functional Neuroscience (online ed.). Chapter 8B - Cerebellar Systems: Swenson 2006.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ↑ HENDELMAN, WALTER J. Atlas of Functional Neuroanatomy (PDF). CRC Press LLC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ "Cerebral Peduncle Anatomy". Healthline. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ HENDELMAN, WALTER J. Atlas of Functional Neuroanatomy (PDF). CRC Press LLC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ HENDELMAN, WALTER J. Atlas of Functional Neuroanatomy (PDF). CRC Press LLC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ HENDELMAN, WALTER J. Atlas of Functional Neuroanatomy (PDF). CRC Press LLC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ HENDELMAN, WALTER J. Atlas of Functional Neuroanatomy (PDF). CRC Press LLC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
External links
- Diagram
- Diagram
- Photo
- NIF Search - Cerebral Peduncle via the Neuroscience Information Framework