Chromosome 11
| Chromosome 11 | |
|---|---|
 Human chromosome 11 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 11 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 135,086,622 bp (GRCh38)[1] |
| No. of genes | 1,224 (CCDS) |
| Type | Autosome |
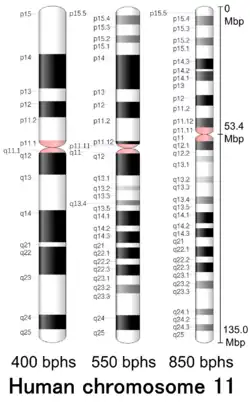
| Centromere position | Submetacentric[2] (53.4 Mbp[3]) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 11 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 11 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 11 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 11 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000011 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000673 (FASTA) |
Chromosome 11 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 11 spans about 135 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. The shorter arm (p arm) is termed 11p while the longer arm (q arm) is 11q. At about 21.5 genes per megabase, chromosome 11 is one of the most gene-rich, and disease-rich, chromosomes in the human genome.
More than 40% of the 856 olfactory receptor genes in the human genome are located in 28 single-gene and multi-gene clusters along the chromosome.
Gene
Number of genes
The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 11. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project (CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.[4]
| Estimated by | Protein-coding genes | Non-coding RNA genes | Pseudogenes | Source | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDS | 1,224 | — | — | [5] | 2016-09-08 |
| HGNC | 1,262 | 271 | 666 | [6] | 2017-05-12 |
| Ensembl | 1,301 | 1,060 | 811 | [7] | 2017-03-29 |
| UniProt | 1,327 | — | — | [8] | 2018-02-28 |
| NCBI | 1,314 | 860 | 839 | [9][10][11] | 2017-05-19 |
Gene list
The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 11. For complete list, see the links in the infobox on the right.
- ACAT1: acetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferase 1 (acetoacetyl Coenzyme A thiolase)
- ACRV1: encoding protein Acrosomal protein SP-10
- AKIP1: A kinase interacting protein 1
- ALKBH3 encoding protein AlkB homolog 3, alpha-ketoglutaratedependent dioxygenase
- AMOTL1: angiomotin-like protein 1
- AMPD3: encoding enzyme AMP deaminase 3
- API5: encoding protein Apoptosis inhibitor 5
- APLNR: Apelin receptor (APJ receptor)
- APOA4: apolipoprotein A-IV
- ARCN1 encoding protein Archain 1
- ASRGL1: encoding enzyme L-asparaginase
- ATM: ataxia telangiectasia mutated (includes complementation groups A, C and D)
- B3GNT1: encoding enzyme N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase
- BDNF: secretes BDNF, a member of the Neurotrophin family of proteins
- C11orf1: encoding protein
- C11orf16: encoding protein Uncharacterized protein C11orf16
- C11orf49: encoding protein UPF0705 protein C11orf49
- C11orf52 encoding protein C11orf52
- C11orf54: encoding protein Ester hydrolase C11orf54
- C11orf86: encoding protein Uncharacterized protein C11orf86
- C1QTNF4 encoding protein C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 4
- C1QTNF5: encoding protein C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 5
- CAPRIN1: encoding protein, cell cycle associated protein 1
- CCDC90B: coiled coil domain containing 90B
- CCL9: Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 9
- CD81: cluster of differentiation 81
- CDHR5: cadherin related family member 5
- COMMD9: COMM domain-containing protein 9
- CPSF7: Cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor subunit 7
- CPT1A: carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A (liver)
- CREBZF encoding protein CREB/ATF bZIP transcription factor
- DAK: Triokinase/FMN cyclase
- DDI1: encoding protein DNA-damage inducible 1 homolog 1 (S. cerevisiae)
- DGAT2 encoding protein Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2
- DHCR7: 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase
- DKK3: Dickkopf-related protein 3
- DPF2: Double PHD fingers 2
- DRD4: Dopamine receptor D4 at 11p15.5
- DSCAML1: encoding protein Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule like 1
- EI24: Etoposide-induced protein 2.4 homolog
- FAM118B: encoding protein Family with sequence similarity 118, member B
- FAM76B: Family with sequence similarity 76 member B
- FAR1: fatty acyl-coA reductase 1
- FAT3: fat atypical cadherin 3
- FHIP: FTS and Hook-interacting protein
- FNBP4: Formin-binding protein 4
- GLB1L3: galactosidase, beta 1-like 3
- GLYAT: Glycine-N-acyltransferase
- GLYATL2 encoding protein Glycine-N-acyltransferase like 2
- GPHA2: Glycoprotein hormone alpha-2
- GYLTL1B: Glycosyltransferase-like protein LARGE2
- HBB: hemoglobin, beta
- HBBP1: encoding protein Hemoglobin, beta pseudogene 1
- HIKESHI: chromosome 11, open reading frame 73
- HMBS: hydroxymethylbilane VIIA
- HRASLS3: adipose phospholipase A2
- HTATIP2: HIV-1 Tat interactive protein 2
- HYLS1: Hydroletalus (Finnish heritage disease) related gene
- HYOU1: hypoxia upregulated protein 1
- IFITM2 encoding protein Interferon induced transmembrane protein 2
- IFT46: intraflagellar transport protein 46 homolog
- INS: insulin gene [12]
- KDM2A: lysine demethylase 2A
- KIAA1549L encoding protein KIAA1549-like
- LPXN: leupaxin
- LRFN4 encoding protein Leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 4
- MADD: MAP kinase-activating death domain protein
- MEN1: Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
- MIRLET7A2: microRNA let-7a-2
- MMP7: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP family)
- MOGAT2: monoacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2
- MTRNR2L8: encoding protein MT-RNR2-like 8
- NADSYN1: NAD synthetase 1
- NAP1L4: nucleosome assembly protein 1-like 4
- NFRKB: nuclear factor related to kappa-B binding protein
- NNMT: nicotinamide N-methyltransferase
- NRGN: neurogranin
- P53AIP1: p53-regulated apoptosis-inducing protein 1
- PAX6: paired box 6
- PCNX3 encoding protein Pecanex homolog 3
- PGA3 encoding protein Pepsinogen 3, group I (pepsinogen A)
- PIWIL4 encoding protein Piwi like RNA-mediated gene silencing 4
- PRR5L: proline rich 5 like
- PTPRCAP: protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type C associated protein
- PTS: 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase
- QSER1: glutamine serine rich protein 1
- RAG1/RAG2: recombination activating genes
- RELT: tumor necrosis factor recepteor
- REXO2: RNA exonuclease 2
- RNH1: ribonuclease inhibitor 1
- RNU2-2: encoding protein RNA, U2 small nuclear 2
- ROM1: retinal outer segment membrane protein 1
- RPL27A: encoding protein 60S ribosomal protein L27a
- RPL36A: encoding protein 60S ribosomal protein L36a
- RSF1: remodeling and spacing factor 1
- SAA1: serum amyloid A1
- SAA2: serum amyloid A2
- SAC3D1: SAC3 domain-containing protein 1
- SART1: squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognized by T-cells 1
- SBF2: SET binding factor 2
- SCGB1D2: secretoglobin family 1D member 2
- SESN3 encoding protein Sestrin 3
- SIDT2 encoding protein SID1 transmembrane family member 2
- SLC17A6: encoding protein Solute carrier family 17 (vesicular glutamate transporter), member 6
- SMAP1: small acidic protein
- SMPD1: sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1, acid lysosomal (acid sphingomyelinase)
- SPA17: sperm autoantigenic protein 17
- SRPRA: Srp receptor alpha subunit
- TAF1D: TATA box binding protein associated factor RNA polymerase 1 subunit D
- TALDO1 encoding protein Transaldolase 1
- TBRG1: transforming growth factor beta regulator 1
- TECTA: tectorin alpha (nonsyndromic deafness)
- TH: tyrosine hydroxylase
- THRSP: thyroid hormone inducible hepatic protein
- THYN1: thymocyte nuclear protein 1
- TIMM10: translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 10
- TIMM10B: Mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit Tim9 B
- TM7SF2: transmembrane 7 superfamily member 2
- TMEM109: encoding protein Transmembrane protein 109
- TMEM123: transmembrane protein 123
- TMEM126B: transmembrane protein 126B
- TMEM134: transmembrane protein 134
- TMEM25: transmembrane protein 25
- TP53I11: tumor protein 53 inducible protein 11
- TRAPPC4: trafficking protein particle complex subunit 4
- TRPT1: tRNA 2'-phosphotransferase 1
- UNC93B1: Unc-93 homolog B1
- UPK2: uroplakin-2
- USH1C: Usher syndrome 1C (autosomal recessive, severe)
- USP47: ubiquitin specific peptidase 47
- UVRAG: UV radiation resistance associated
- VPS26B: vacuolar protein sorting 26 homolog B
- VSIG2: V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 2
- WT1: Wilms tumor protein
- YIF1A: Yip1 interacting factor homolog A
- ZFP91-CNTF
- ZNF408: zinc finger protein 408
Diseases and disorders
The following diseases and disorders are some of those related to genes on chromosome 11:
- autism (NRXN2)
- acute intermittent porphyria
- albinism
- ataxia–telangiectasia
- Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome
- Best's disease
- beta-ketothiolase deficiency
- beta thalassemia
- bladder cancer
- breast cancer
- carnitine palmitoyltransferase I deficiency
- Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
- Cystic fibrosis
- Depression
- Denys–Drash syndrome
- familial Mediterranean fever
- Hereditary angioedema OMIM: 106100
- Jacobsen syndrome
- Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome
- Mantle cell lymphoma (t11;14)
- Meckel syndrome
- methemoglobinemia, beta-globin type
- Mixed lineage leukemia
- multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
- Hereditary multiple exostoses
- Niemann–Pick disease
- nonsyndromic deafness
- porphyria
- Potocki–Shaffer syndrome
- Romano–Ward syndrome
- Sickle cell anemia[13]
- Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome
- tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency
- Usher syndrome
- WAGR syndrome
- Wiedemann–Steiner syndrome
- Wilms' tumor
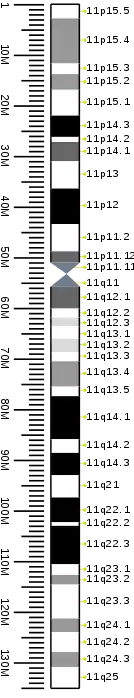
Cytogenetic band
| Chr. | Arm[19] | Band[20] | ISCN start[21] |
ISCN stop[21] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[22] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | p | 15.5 | 0 | 230 | 1 | 2,800,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | p | 15.4 | 230 | 461 | 2,800,001 | 11,700,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 11 | p | 15.3 | 461 | 745 | 11,700,001 | 13,800,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | p | 15.2 | 745 | 935 | 13,800,001 | 16,900,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 11 | p | 15.1 | 935 | 1246 | 16,900,001 | 22,000,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | p | 14.3 | 1246 | 1490 | 22,000,001 | 26,200,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 11 | p | 14.2 | 1490 | 1545 | 26,200,001 | 27,200,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | p | 14.1 | 1545 | 1775 | 27,200,001 | 31,000,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 11 | p | 13 | 1775 | 2114 | 31,000,001 | 36,400,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | p | 12 | 2114 | 2357 | 36,400,001 | 43,400,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 11 | p | 11.2 | 2357 | 2655 | 43,400,001 | 48,800,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | p | 11.12 | 2655 | 2872 | 48,800,001 | 51,000,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 11 | p | 11.11 | 2872 | 3035 | 51,000,001 | 53,400,000 | acen | |
| 11 | q | 11 | 3035 | 3197 | 53,400,001 | 55,800,000 | acen | |
| 11 | q | 12.1 | 3197 | 3414 | 55,800,001 | 60,100,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 11 | q | 12.2 | 3414 | 3550 | 60,100,001 | 61,900,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | q | 12.3 | 3550 | 3685 | 61,900,001 | 63,600,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 11 | q | 13.1 | 3685 | 4037 | 63,600,001 | 66,100,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | q | 13.2 | 4037 | 4186 | 66,100,001 | 68,700,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 11 | q | 13.3 | 4186 | 4512 | 68,700,001 | 70,500,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | q | 13.4 | 4512 | 4688 | 70,500,001 | 75,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 11 | q | 13.5 | 4688 | 4877 | 75,500,001 | 77,400,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | q | 14.1 | 4877 | 5148 | 77,400,001 | 85,900,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 11 | q | 14.2 | 5148 | 5257 | 85,900,001 | 88,600,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | q | 14.3 | 5257 | 5474 | 88,600,001 | 93,000,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 11 | q | 21 | 5474 | 5690 | 93,000,001 | 97,400,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | q | 22.1 | 5690 | 5934 | 97,400,001 | 102,300,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 11 | q | 22.2 | 5934 | 6070 | 102,300,001 | 103,000,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | q | 22.3 | 6070 | 6300 | 103,000,001 | 110,600,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 11 | q | 23.1 | 6300 | 6503 | 110,600,001 | 112,700,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | q | 23.2 | 6503 | 6693 | 112,700,001 | 114,600,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 11 | q | 23.3 | 6693 | 7167 | 114,600,001 | 121,300,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | q | 24.1 | 7167 | 7316 | 121,300,001 | 124,000,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 11 | q | 24.2 | 7316 | 7533 | 124,000,001 | 127,900,000 | gneg | |
| 11 | q | 24.3 | 7533 | 7695 | 127,900,001 | 130,900,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 11 | q | 25 | 7695 | 7980 | 130,900,001 | 135,086,622 | gneg |
References
- ↑ "Human Genome Assembly GRCh38 - Genome Reference Consortium". National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2017-03-04.
- ↑ Tom Strachan; Andrew Read (2 April 2010). Human Molecular Genetics. Garland Science. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-136-84407-2.
- 1 2 Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ Pertea M, Salzberg SL (2010). "Between a chicken and a grape: estimating the number of human genes". Genome Biol. 11 (5): 206. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-206. PMC 2898077. PMID 20441615.
- ↑ "Search results - 11[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("has ccds"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. CCDS Release 20 for Homo sapiens. 2016-09-08. Retrieved 2017-05-28.
- ↑ "Statistics & Downloads for chromosome 11". HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. 2017-05-12. Retrieved 2017-05-19.
- ↑ "Chromosome 11: Chromosome summary - Homo sapiens". Ensembl Release 88. 2017-03-29. Retrieved 2017-05-19.
- ↑ "Human chromosome 11: entries, gene names and cross-references to MIM". UniProt. 2018-02-28. Retrieved 2018-03-16.
- ↑ "Search results - 11[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ↑ "Search results - 11[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ( ("genetype miscrna"[Properties] OR "genetype ncrna"[Properties] OR "genetype rrna"[Properties] OR "genetype trna"[Properties] OR "genetype scrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snorna"[Properties]) NOT "genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ↑ "Search results - 11[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype pseudo"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ↑ INS - insulin - Genetics Home Reference
- ↑ "Human Genome Project Information Site Has Been Updated". Archived from the original on 2012-07-10. Retrieved 2009-01-04.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. ISBN 978-3-318-02253-7.
- ↑ Sethakulvichai, W.; Manitpornsut, S.; Wiboonrat, M.; Lilakiatsakun, W.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. (2012). "Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images". In Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE), 2012 International Joint Conference on: 276–282. doi:10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965. ISBN 978-1-4673-1921-8. S2CID 16666470.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ "p": Short arm; "q": Long arm.
- ↑ For cytogenetic banding nomenclature, see article locus.
- 1 2 These values (ISCN start/stop) are based on the length of bands/ideograms from the ISCN book, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Arbitrary unit.
- ↑ gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
- Gilbert F (2000). "Disease genes and chromosomes: disease maps of the human genome". Genet Test. 4 (4): 409–26. doi:10.1089/109065700750065180. PMID 11216668.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Human chromosome 11. |
- National Institutes of Health. "Chromosome 11". Genetics Home Reference. Archived from the original on August 3, 2004. Retrieved 2017-05-06.
- "Chromosome 11". Human Genome Project Information Archive 1990–2003. Retrieved 2017-05-06.