Clamoxyquine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H24ClN3O |
| Molar mass | 321.85 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
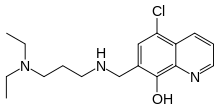
SMILES
| |
Clamoxyquine (INN) or clamoxyquin (former BAN), as the pamoate or hydrochloride salt, is an antiamebic and antidiarrheal drug.
It has been used as a veterinary medicine to treat salmonids for infection with the myxozoan parasite Myxobolus cerebralis.
Synthesis
Antimalarial activity also predominates in a quinoline that bears a diaminoalkyl side chain at a rather different position from the other agents noted.
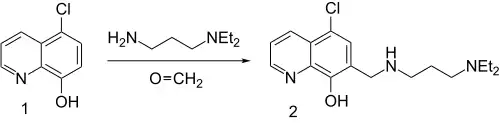
Clamoxyquin synthesis:[1]
Thus, Mannich condensation of the hydroxyquinoline (1) with formaldehyde and N,N-diethylpropylenediamine affords clamoxyquin (2).
References
- ↑ Burckhalter JH, Brinigar WS, Thompson PE (1961). "Antiamebic Agents. V.1Promising Basic Amebicides Derived from 5-Chloro-8-quinolinol". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 26 (10): 4070–4078. doi:10.1021/jo01068a103.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.