DOOR syndrome
| DOOR syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Deafness-onychodystrophy-osteodystrophy-intellectual disability-seizures syndrome | |
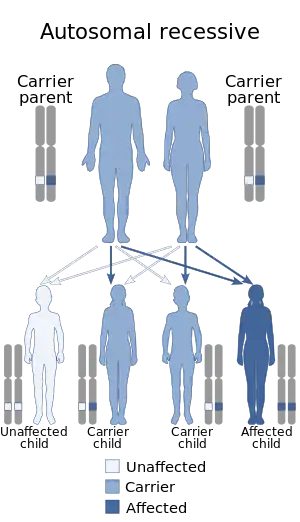 | |
| This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner | |
| Specialty | DiseasesDB = 32494 |
DOOR (deafness, onychodystrophy, osteodystrophy, and mental retardation) syndrome is a genetic disease which is inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. DOOR syndrome is characterized by mental retardation, sensorineural deafness, abnormal nails and phalanges of the hands and feet, and variable seizures. A similar deafness-onychodystrophy syndrome is transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait and has no mental retardation. Some authors have proposed that it may be the same as Eronen Syndrome, but since both disorders are extremely rare it is hard to make a determination.[1]
Signs and symptoms
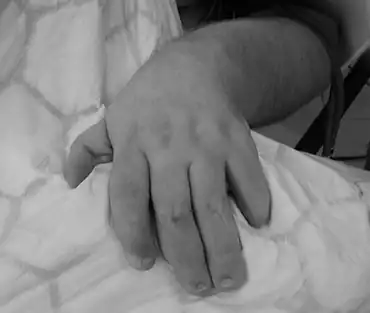
Not all of the DOOR symptoms are consistently present. They can vary in severity, and additional features can be noted in individuals affected by DOOR syndrome.
Some of these additional features are:
- Polyhydramnios (increased amniotic fluid during pregnancy) and increased nuchal fold during pregnancy
- Specific facial features such as a large nose
- Severe and sometimes refractory seizures, abnormalities on the magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
- Increased 2-oxoglutaric acid in the blood and urine - this compound is made or used by several enzymes
- Finger-like thumbs
- Visual impairment
- Peripheral neuropathy (nerves conducting sensation from extremities to the brain) and insensivity to pain
Intellectual impairment is present in all reported cases, but the severity can vary widely. The prognosis in terms of survival also varies greatly from early childhood till adulthood.
Cause
The recurrence of DOOR in siblings and the finding of DOOR syndrome in a few families with consanguinity suggest that the condition is an autosomal recessive genetic condition. Mutations in TBC1D24 have been identified in 9 families.[2]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this condition is based on the following:[3]
- X-rays of hands/feet
- Brain stem auditory evoked response test
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- Elevated levels 2-oxoglutaric acid
- Molecular genetic test
Treatment
In terms of management for this condition is supportive. Antiepileptic medication may be used as needed, as well [3]
References
- ↑ Le Merrer M, David A, Goutieres F, Briard ML (October 1992). "Digito-reno-cerebral syndrome: confirmation of Eronen syndrome". Clin. Genet. 42 (4): 196–8. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.1992.tb03236.x. PMID 1424243. S2CID 28902508.
- ↑ Campeau, P. M.; Kasperaviciute, D.; Lu, J. T.; Burrage, L. C.; Kim, C.; Hori, M.; Powell, B. R.; Stewart, F.; Félix, T. M. M.; Van Den Ende, J.; Wisniewska, M.; Kayserili, H. L.; Rump, P.; Nampoothiri, S.; Aftimos, S.; Mey, A.; Nair, L. D. V.; Begleiter, M. L.; De Bie, I.; Meenakshi, G.; Murray, M. L.; Repetto, G. M.; Golabi, M.; Blair, E.; Male, A.; Giuliano, F.; Kariminejad, A.; Newman, W. G.; Bhaskar, S. S.; Dickerson, J. E. (2014). "The genetic basis of DOORS syndrome: An exome-sequencing study". The Lancet Neurology. 13 (1): 44–58. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70265-5. PMC 3895324. PMID 24291220.
- 1 2 RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: DOORS syndrome". www.orpha.net. Archived from the original on 14 July 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
External links
| Classification |
|---|