Dodecane
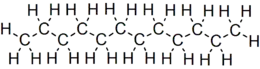 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dodecane[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
Beilstein Reference |
1697175 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.607 |
| EC Number |
|
Gmelin Reference |
201408 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | n-dodecane |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C12H26 |
| Molar mass | 170.340 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Gasoline-like to odorless |
| Density | 0.7495 g mL−1 at 20 °C[2] |
| Melting point | −10.0 to −9.3 °C; 14.1 to 15.2 °F; 263.2 to 263.8 K |
| Boiling point | 214 to 218 °C; 417 to 424 °F; 487 to 491 K |
| log P | 6.821 |
| Vapor pressure | 18 Pa (at 25 °C)[3] |
Henry's law constant (kH) |
1.4 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.421 |
| Viscosity | 1.34 mPa s |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
376.00 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std molar entropy (S |
490.66 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−353.5–−350.7 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−7901.74 kJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
Pictograms |
 |
Signal word |
Danger |
Hazard statements |
H304 |
Precautionary statements |
P301+P310, P331 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 71 °C (160 °F; 344 K) |
Autoignition temperature |
205 °C (401 °F; 478 K) |
| Explosive limits | 0.6% |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | hazard.com |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanes |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dodecane (also known as dihexyl, bihexyl, adakane 12, or duodecane) is an oily liquid n-alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C12H26 (which has 355 isomers).
It is used as a solvent, distillation chaser, and scintillator component. It is used as a diluent for tributyl phosphate (TBP) in reprocessing plants.[4]
Combustion reaction
The combustion reaction of dodecane is as follows:
- 2 C12H26(l) + 37 O2(g) → 24 CO2(g) + 26 H2O(g)
- ΔH° = −7513 kJ
One litre of fuel needs about 15 kg of air to burn, and generates 2.3 kg (or 1.2 m3) of CO2 upon complete combustion.
Jet fuel surrogate
In recent years, n-dodecane has garnered attention as a possible surrogate for kerosene-based fuels such as Jet-A, S-8, and other conventional aviation fuels. It is considered a second-generation fuel surrogate designed to emulate the laminar flame speed, largely supplanting n-decane, primarily due to its higher molecular mass and lower hydrogen to carbon ratio which better reflect the n-alkane content of jet fuels.
See also
- Higher alkanes
- Kerosene
- List of isomers of dodecane
References
- ↑ "n-dodecane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ↑ "Dodecane".
- ↑ "Dodecane".
- ↑ Rydberg, Jan (2004). Solvent Extraction Principles and Practice. Marcel Dekker. p. 524. ISBN 0-8247-5063-2.
External links
- Caudwell, D.R.; Trusler, J.P.M.; Vesovic, V.; Wakeham, W.A. (2003-06-16). "The Viscosity and Density of n-Dodecane and n-Octadecane at Pressures up to 200 mPa and Temperatures up to 473 K" (PDF). NIST. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-10-09. Retrieved 2007-10-09.
- Material Safety Data Sheet for Dodecane
- Dodecane, Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases
