Intracranial dolichoectasias
| Intracranial dolichoectasias | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Vascular surgery |
The term dolichoectasia means elongation and distension. It is used to characterize arteries throughout the human body which have shown significant deterioration of their tunica intima (and occasionally the tunica media), weakening the vessel walls and causing the artery to elongate and distend.
Signs and symptoms
Vertebrobasillar dolichoectasia
Internal carotid dolichoectasia
- Progressive visual field defect
Cause
Most commonly caused by hypertension, continued stress on the walls of the artery will degrade the vessel wall by damaging and loosening the collagen and elastin meshwork which comprises the intima. Similarly, hypercholesterolemia or hyperlipidemia can also provide sufficient trauma to the vessel wall resulting in dolichoectasia. As the arrangement of connective tissue is disturbed, the vessel wall is no longer able to hold its original conformation and begins to unravel due to the continued hypertension. High blood pressure mold and force the artery to now take on an elongated, tortuous course to better withstand the higher pressures.
Pathophysiology
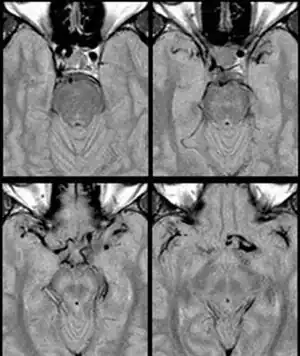
Most commonly affected are the vertebral and basilar arteries (Vertebral Basilar Dolichoectasia or Vertebrobasillar Dolichoectasia). The internal carotid artery may also be affected. Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) are more likely to be subject to dolichoectasias. Dolichoectasias are most common in elderly males.[2]
In cases involving the basilar artery (VBD), pathology can occur due to direct compression of cranial nerves, by ischemia related to the dolichoectatic vessel, or by the development of hydrocephalus. Rupture of the dolichoectatic vessel can lead to catastrophic intracerebral hemorrhage.
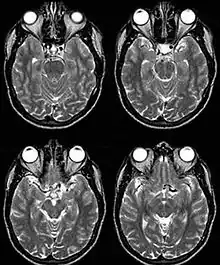
Internal carotid artery dolichoectasia is particularly interesting because the artery normally already contains one hairpin turn. Seen in an MRI as two individual arteries at this hairpin, a carotid artery dolichoectasia can progress so far as to produce a second hairpin turn and appear as three individual arteries on an MRI. In the case of a dolichoectasia of the Internal Carotid Artery (ICD), the pathogenesis is primarily related to compression of the optic nerves at the optic chiasma (see Fig. 1 and 2).
Diagnosis
Treatment
There are no standard treatments for existing dolichoectasias. Prevention is most important, usually related to control of high blood pressure. Interventions can include medications or lifestyle changes.
References
- ↑ Rissardo, JamirPitton; Fornari Caprara, AnaLetícia (2018). "Trigeminal Neuralgia Secondary to Basilar Artery Dolichoectasia". Current Medical Issues. 16 (3): 103. doi:10.4103/cmi.cmi_16_18. ISSN 0973-4651.
- ↑ Yu, YL; Moseley, IF; Pullicino, P; McDonald, WI (1982). "The clinical picture of ectasia of the intracerebral arteries". J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 45 (1): 29–36. doi:10.1136/jnnp.45.1.29. ISSN 0022-3050. PMC 491261. PMID 7062068.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Intracranial dolichoectasias. |