Ectopic pancreas
| Ectopic pancreas | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Heterotopic pancreas, Accessory pancreas, Aberrant pancreas, Pancreatic rest, Myoepithelial hamartoma |
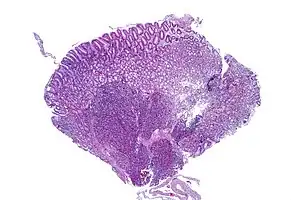 | |
| Stomach biopsy with pancreatic heterotopia in the submucosa. H&E Stain. | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
| Symptoms | Often asymptomatic, may cause abdominal pain and distension |
| Diagnostic method | Biopsy, histologic evaluation |
| Differential diagnosis | Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)[1] |
| Treatment | Surgery if symptomatic |
| Medication | None |
| Frequency | Uncommon[1] |
An ectopic pancreas is an anatomical abnormality in which pancreatic tissue has grown outside its normal location and without vascular or other anatomical connections to the pancreas.[2] It is a congenital disease[2] and is also known as heterotopic, accessory, or aberrant pancreas.[3]
Signs and symptoms
Often, heterotopic pancreas is asymptomatic. When present, symptoms may include abdominal pain and distension.[1] Often heterotopic pancreas is recognized as an incidental finding on imaging studies performed for an unrelated reason. Ectopic pancreatic tissue may occur anywhere in the abdominal cavity, though more than 90 percent are found in the stomach, duodenum or jejunum.[1] Rarely, pancreatic heterotopic tissue may be found in the colon, spleen or liver.[1]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ectopic pancreas can be challenging. Confirmation of the diagnosis requires tissue sampling, via biopsy or surgical resection.
Treatment
If no symptoms are present, then treatment is not necessary. When symptoms are present, treatment consists of surgical resection.[1]
Epidemiology
The incidence of heterotopic pancreas is relatively low.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Yuan, Z; Chen, J; Zheng, Q; Huang, XY; Yang, Z; Tang, J (7 August 2009). "Heterotopic pancreas in the gastrointestinal tract". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 15 (29): 3701–3. doi:10.3748/wjg.15.3701. PMC 2721251. PMID 19653355.
- 1 2 Perera, Eranga (26 April 2010). "Ectopic Pancreas". Imaging Science Today. Archived from the original on 25 November 2010.
- ↑ Kim, Ji Young; et al. (2009). "Ectopic Pancreas: CT Findings with Emphasis on Differentiation from Small Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor and Leiomyoma". Radiology. Radiological Society of North America. 252 (1): 92–100. doi:10.1148/radiol.2521081441. PMID 19561251.