Eponychium
| Eponychium | |
|---|---|
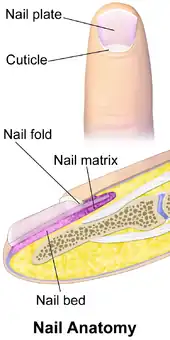 Nail anatomy, with eponychium labeled as "nail fold". | |
 Longitudinal section through nail and its nail groove (sulcus). | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Eponychium |
| TA98 | A16.0.01.010 |
| TA2 | 7072 |
| FMA | 77859 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In human anatomy, the eponychium is the thickened layer of skin at the base of the fingernails and toenails. It can also be called the medial or proximal nail fold. The eponychium differs from the cuticle; the eponychium comprises live skin cells whilst the cuticle is dead skin cells. Its function is to protect the area between the nail and epidermis from exposure to bacteria. The vascularization pattern is similar to that of perionychium.[1]
In hoofed animals, the eponychium is the deciduous hoof capsule in fetuses and newborn foals, and is a part of the permanent hoof in older animals.[2]
The word eponychium comes from Greek ἐπί (epí) 'on top of', and ὀνῠ́χιον (onúkhion) 'little claw'.
See also
References
- ↑ Sangiorgi S, Manelli A, Congiu T, et al. (2004). "Microvascularization of the human digit as studied by corrosion casting". J. Anat. 204 (2): 123–31. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2004.00251.x. PMC 1571248. PMID 15032919.
- ↑ Bragulla, H. (Mar 1991). "The deciduous hoof capsule (Capsula ungulae decidua) of the equine fetus and newborn foal". Anatomia, Histologia, Embryologia. 20 (1): 66–74. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0264.1991.tb00293.x. PMID 1877762.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.