Erythropoietic protoporphyria
| Erythropoietic protoporphyria | |
|---|---|
| Other names: EPP[1] | |
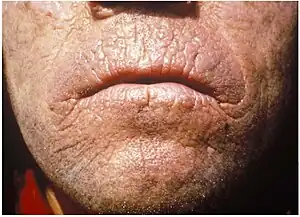 | |
| Chronic skin lesions of EPP | |
| Risk factors | pain and irritation |
Erythropoietic protoporphyria (or commonly called EPP) is a form of porphyria, which varies in severity and can be very painful. It arises from a deficiency in the enzyme ferrochelatase, leading to abnormally high levels of protoporphyrin in the red blood cells (erythrocytes), plasma, skin, and liver.[2] The severity varies significantly from individual to individual.
A clinically similar form of porphyria, known as X-Linked dominant protoporphyria, was identified in 2008.[3]
Symptoms and signs
EPP usually presents in childhood with the most common mode of presentation as acute photosensitivity of the skin. It affects areas exposed to the sun and tends to be intractable. A few minutes of exposure to the sun induces pruritus, erythema, swelling and pain. Longer periods of exposure may induce second degree burns. After repetitive exposure, patients may present with lichenification, hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation and scarring of the skin.[4][5]
EPP usually first presents in childhood, and most often affects the face and the upper surfaces of the arms, hands, and feet and the exposed surfaces of the legs. Most patients, if the EPP is not as severe, manifest symptoms with onset of puberty when the male and female hormone levels elevate during sexual development and maintenance. More severe EPP can manifest in infancy. EPP can be triggered through exposure to sun even though the patient is behind glass. Even the UV emissions from arc welding with the use of full protective mask have been known to trigger EPP. EPP can also manifest between the ages of 3 and 6.
Prolonged exposure to the sun can lead to edema of the hands, face, and feet, rarely with blistering and petechiae. Skin thickening can sometimes occur over time.
People with EPP are also at increased risk to develop gallstones.[6] One study has noted that EPP patients suffer from vitamin D deficiency.[7]
.jpg.webp) Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria.jpg.webp) Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria.jpg.webp) Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria.jpg.webp) Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria.jpg.webp) Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria.jpg.webp) Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria.jpg.webp) Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria.jpg.webp) Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria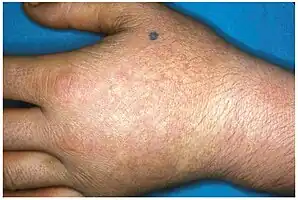 Acute photosensitivity reaction in EPP.
Acute photosensitivity reaction in EPP.
Liver failure
Protoporphyrin accumulates to toxic levels in the liver in 5–20% of EPP patients, leading to liver failure. The spectrum of hepatobiliary disease associated with EPP is wide. It includes cholelithiasis, mild parenchymal liver disease, progressive hepatocellular disease and end-stage liver disease.[4]
A lack of diagnostic markers for liver failure makes it difficult to predict which patients may experience liver failure, and the mechanism of liver failure is poorly understood. A retrospective European study identified 31 EPP patients receiving a liver transplant between 1983 and 2008, with phototoxic reactions in 25% of patients who were unprotected by surgical light filters. The same study noted a 69% recurrence of the disease in the grafted organ. Five UK liver transplants for EPP have been identified between 1987 and 2009. Frequent liver testing is recommended in EPP patients where no effective therapy has been identified to manage liver failure to date.
Pregnancy
EPP photosensitivity symptoms are reported to lessen in some female patients during pregnancy and menstruation, although this phenomenon is not consistent, and the mechanism is not understood.[8]
Genetics
Most cases of EPP are results of inborn errors of metabolism[2] but the metabolic defect in some patients may be acquired.[9] Mutation of the gene that encodes for ferrochelatase in the long arm of chromosome 18 is found in majority of the cases. Ferrochelatase (FECH) catalyzes the insertion of ferrous iron into the protoporphyrin IX ring to form heme. EPP exhibits both recessive and dominant patterns of inheritance and a high degree of allelic heterogeneity with incomplete penetrance. Most heterozygotes are asymptomatic. Symptoms do not occur unless FECH activity is less than 30% of normal, but such low levels are not present in a majority of patients.[10]
Pathophysiology
Cells which synthesize heme are predominantly erythroblasts/reticulocytes in the bone marrow (80%) and hepatocytes (20%). Deficiency of FECH results in increased release of protoporphyrin, which binds to albumin in plasma and subsequently undergoes hepatic extraction. Normally, most protoporphyrin in hepatocytes is secreted into bile; the remainder undergoes transformation into heme. Some protoporphyrin in bile is returned to the liver as a consequence of the enterohepatic circulation; the remaining protoporphyrin in the intestine undergoes fecal excretion. Protoporphyrin is insoluble and hence unavailable for renal excretion. In EPP, subnormal biotransformation of protoporphyrin into heme results in accumulation of protoporphyrin in hepatocytes.[11]
Since FECH deficiency is associated with increased concentrations of protoporphyrin in erythrocytes, plasma, skin and liver, retention of protoporphyrin in skin predisposes to acute photosensitivity. As a result of absorption of ultraviolet and visible light (peak sensitivity at 400 nm, with lesser peaks between 500-625 nm[12]) by protoporphyrin in plasma and erythrocytes when blood circulates through the dermal vessels, free radicals are formed, erythrocytes become unstable and injury to the skin is induced.[4]
A significant increase in the hepatobiliary excretion of protoporphyrin can damage the liver through both cholestatic phenomena and oxidative stress[11] - predisposing to hepatobiliary disease of varying degrees of severity[13][14]
Diagnosis
EPP is generally suspected by the presence of acute photosensitivity of the skin and can be confirmed by detection of a plasmatic fluorescence peak at 634 nm. It is also useful to find increased levels of protoporphyrin in feces and the demonstration of an excess of free protoporphyrin in erythrocytes.[15]
Screening for FECH mutation on one allele or aminolevulinic acid synthase 2 gain-of-function mutation in selected family members may be useful, especially in genetic counseling.
Liver biopsy confirms hepatic disease in EPP by the presence of protoporphyrin deposits in the hepatocytes that can be observed as a brown pigment within the biliary canaliculi and the portal macrophages. Macroscopically, the cirrhotic liver can have a black color due to protoporphyrin deposits. Using polarized light the characteristic Maltese cross shape of birefringent crystalline pigment deposits is found. The examination of liver tissue under a Wood’s lamp reveals a red fluorescence due to protoporphyrin. Liver biopsy is not helpful for estimation of prognosis of liver disease.[13]
Treatment
There is no cure for this disorder; however, symptoms can usually be managed by limiting exposure to daytime sun and some types of artificial lighting. Most types of artificial lighting emit light in the problematic wavelengths, with fluorescent lighting being the worst offender. Color temperature can be a good indicator of what light is most detrimental, as the higher the color temperature, the more violet light (380-450 nm) is emitted. Incandescent and LED lighting in the soft white range (2700-3000K) produce the least problematic light. Additionally, selecting lower wattage bulbs can reduce the overall output of light.
Since the photosensitivity results from light in the visible spectrum, most sunscreens are of little use (with the exception of non-nano zinc oxide which provides uniform protection between 290-400 nm and some protection up to 700 nm[16]). Sun protective clothing can also be very helpful, although clothing with UPF values are only rated based on their UV protection (up to 400 nm) and not on their protection from the visible spectrum. Some sun protective clothing manufacturers use zinc oxide in their fabrics, such as Coolibar's ZnO Suntect line, which will offer protection from visible light.
Some patients gradually build a protective layer of melanin by regularly exposing themselves for short times to ultraviolet radiation.
Window films which block UV and visible light up to 450 nm can provide relief from symptoms if applied to the patient's automobile and home windows. An example of such would be Madico Amber 81 Archived 2021-05-30 at the Wayback Machine which can protect through the 500 nm range.
Blue blocking screen protectors can help provide relief from symptoms caused by televisions, phones, tablets and computer screens.
EPP is considered one of the least severe of the porphyrias. Unless there is liver failure, it is not a life-threatening disease.
Approved therapies
Afamelanotide, developed by Australian-based Clinuvel Pharmaceuticals, was approved in Europe in December 2014 for treatment or prevention of phototoxicity in adults with EPP.[17]
Off-label use
Several drugs are used off label by patients with EPP:
- Ursodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid that is administered to promote biliary secretion of protoporphyrin. Results of its use in EPP are controversial. However, it is known to alter the composition of bile, to protect hepatocytes from the cytotoxic effect of hydrophobic bile acids, and to stimulate biliary secretion by several distinct mechanisms.[18][19]
- Hematin appears to reduce excess protoporphyrin production in the bone marrow. It has been administered to patients with EPP (3–4 mg/kg iv) who develop a crisis after liver transplantation.[20]
- Plasmapheresis can also decrease the levels of protoporphyrin in plasma, however its use in treating acute episodes is controversial.[21]
- Cholestyramine is an orally administered resin which reduces circulating levels of protoporphyrin by binding to protoporphyrin in the intestine and, hence, interrupting the enterohepatic circulation. It is usually used in combination with other treatment approaches.[22]
- Activated charcoal, like cholestyramine, binds to protoporphyrin in the intestine and prevents its absorption. It is cheap and readily available. It seems to be effective in reducing circulating protoporphyrin levels.[23]
Bone marrow transplantation, liver transplantation, acetylcysteine, extracorporeal albumin dialysis, parenteral iron and transfusion of erythrocytes are alternative plans for treatment of EEP.
OTC Supplements
Some over-the-counter supplements may help:
- Proferrin Archived 2021-05-07 at the Wayback Machine is an oral heme supplement which may work similarly to Hematin.
- B. subtilis (a gram-positive soil probiotic) produces ferrochelatase,[24] which may be able to convert some of the protoporphyrin in the intestine into heme.
- Beta carotene, though a recent meta analysis of carotene treatment has called its effectiveness into question.[25]
Epidemiology
Case reports suggest that EPP is prevalent globally. The prevalence has been estimated somewhere between 1 in 75,000 and 1 in 200,000[26] however it has been noted that the prevalence of EPP may be increasing due to a better understanding of the disease and improved diagnosis.[27] An estimated 5,000-10,000 individuals worldwide have EPP. EPP is considered the most common form of porphyria in children.[28] The prevalence in Sweden has been published as 1:180,000.[29]
History
Erythropoietic protoporphyria was first described in 1953 by Kosenow and Treibs[30] and completed in 1960 by Magnus et al. at the St John's Institute of Dermatology in London.[31]
See also
References
- ↑ "Orphanet: Autosomal erythropoietic protoporphyria". orpha.net. Archived from the original on 26 April 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- 1 2 Casanova-González, María José; Trapero-Marugán, María; Jones, E. Anthony; Moreno-Otero, Ricardo (2010-09-28). "Liver disease and erythropoietic protoporphyria: a concise review". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 16 (36): 4526–4531. doi:10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4526. ISSN 2219-2840. PMC 2945483. PMID 20857522.
- ↑ Seager, M. J.; Whatley, S. D.; Anstey, A. V.; Millard, T. P. (2014). "X-linked dominant protoporphyria: A new porphyria". Clinical and Experimental Dermatology. 39 (1): 35–7. doi:10.1111/ced.12202. PMID 24131146.
- 1 2 3 Tsuboi, Hiromi; Yonemoto, Kohzoh; Katsuoka, Kensei (2007-11-01). "Erythropoietic protoporphyria with eye complications". The Journal of Dermatology. 34 (11): 790–794. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2007.00386.x. ISSN 0385-2407. PMID 17973823.
- ↑ Poh-Fitzpatrick, M. B. (1986-06-01). "Molecular and cellular mechanisms of porphyrin photosensitization". Photo-Dermatology. 3 (3): 148–157. ISSN 0108-9684. PMID 3529055.
- ↑ Bonkovsky, Herbert L.; Rudnick, Sean R. (December 2020). "Erythropoietic Protoporphyria and X-Linked Protoporphyria - Hormonal and Metabolic Disorders". Merck Manuals Consumer Version. Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. Archived from the original on 17 January 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2021.
- ↑ Spelt, JM; De Rooij, FW; Wilson, JH; Zandbergen, AA (2010). "Vitamin D deficiency in patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria". Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease. 33 Suppl 3: S1–4. doi:10.1007/s10545-008-1037-0. PMID 24137761. S2CID 22847583.
- ↑ Wahlin, S.; Marschall, H.-U.; Fischler, B. (2013). "Maternal and fetal outcome in Swedish women with erythropoietic protoporphyria". British Journal of Dermatology. 168 (6): 1311–5. doi:10.1111/bjd.12242. PMID 23738640.
- ↑ Blagojevic, Daniel; Schenk, Thomas; Haas, Oskar; Zierhofer, Brigitte; Konnaris, Christophoros; Trautinger, Franz (2009). "Acquired erythropoietic protoporphyria". Annals of Hematology. 89 (7): 743–4. doi:10.1007/s00277-009-0859-7. PMID 19902211. S2CID 36170513. Archived from the original on 2021-05-30. Retrieved 2021-05-18.
- ↑ Kong, Xiao-Fei; Ye, Jing; Gao, De-Yong; Gong, Qi-Ming; Zhang, Dong-Hua; Lu, Zhi-Meng; Lu, Yi-Ming; Zhang, Xin-Xin (2008-02-01). "Identification of a ferrochelatase mutation in a Chinese family with erythropoietic protoporphyria". Journal of Hepatology. 48 (2): 375–379. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2007.09.013. ISSN 0168-8278. PMID 18160121.
- 1 2 Holme, S. Alexander; Worwood, Mark; Anstey, Alexander V.; Elder, George H.; Badminton, Michael N. (2007-12-01). "Erythropoiesis and iron metabolism in dominant erythropoietic protoporphyria". Blood. 110 (12): 4108–4110. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-04-088120. ISSN 0006-4971. PMID 17804693.
- ↑ Magnus, I. A. (February 1968). "Photobiological Aspects of Porphyria". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine. 61: 196–198. doi:10.1177/003591576806100233. PMID 5688974.
- 1 2 Lecha, Mario; Puy, Hervé; Deybach, Jean-Charles (2009-01-01). "Erythropoietic protoporphyria". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 4: 19. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-4-19. ISSN 1750-1172. PMC 2747912. PMID 19744342.
- ↑ Bruguera, M.; Herrero, C. (2005-12-01). "[Liver disease in erythropoietic protoporphyria]". Gastroenterología y Hepatología. 28 (10): 632–636. doi:10.1016/s0210-5705(05)71529-6. ISSN 0210-5705. PMID 16373015.
- ↑ Anstey, A. V.; Hift, R. J. (2007-07-01). "Liver disease in erythropoietic protoporphyria: insights and implications for management". Gut. 56 (7): 1009–1018. doi:10.1136/gut.2006.097576. ISSN 0017-5749. PMC 1994365. PMID 17360790.
- ↑ "Zinc Oxide - Physical UVA+UVB sunscreen/sunblock agent". smartskincare.com. Archived from the original on 2019-04-25. Retrieved 2019-04-02.
- ↑ "Union Register of medicinal products". European Commission. Archived from the original on 24 December 2014. Retrieved 8 December 2020.
- ↑ Pirlich, M.; Lochs, H.; Schmidt, H. H. (2001-12-01). "Liver cirrhosis in erythropoietic protoporphyria: improvement of liver function with ursodeoxycholic acid". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 96 (12): 3468–3469. ISSN 0002-9270. PMID 11774991.
- ↑ Paumgartner, Gustav; Beuers, Ulrich (2002-09-01). "Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestatic liver disease: mechanisms of action and therapeutic use revisited". Hepatology. 36 (3): 525–531. doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.36088. ISSN 0270-9139. PMID 12198643.
- ↑ Potter, C.; Tolaymat, N.; Bobo, R.; Sharp, H.; Rank, J.; Bloomer, J. (1996-11-01). "Hematin therapy in children with protoporphyric liver disease". Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. 23 (4): 402–407. doi:10.1097/00005176-199611000-00006. ISSN 0277-2116. PMID 8956175.
- ↑ Tung, B. Y.; Farrell, F. J.; McCashland, T. M.; Gish, R. G.; Bacon, B. R.; Keeffe, E. B.; Kowdley, K. V. (1999-09-01). "Long-term follow-up after liver transplantation in patients with hepatic iron overload". Liver Transplantation and Surgery. 5 (5): 369–374. doi:10.1002/lt.500050503. ISSN 1074-3022. PMID 10477837.
- ↑ McCullough, A. J.; Barron, D.; Mullen, K. D.; Petrelli, M.; Park, M. C.; Mukhtar, H.; Bickers, D. R. (1988-01-01). "Fecal protoporphyrin excretion in erythropoietic protoporphyria: effect of cholestyramine and bile acid feeding". Gastroenterology. 94 (1): 177–181. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(88)90627-0. ISSN 0016-5085. PMID 3335288.
- ↑ Gorchein, A.; Foster, G. R. (1999-03-01). "Liver failure in protoporphyria: long-term treatment with oral charcoal". Hepatology. 29 (3): 995–996. doi:10.1002/hep.510290314. ISSN 0270-9139. PMID 10189233.
- ↑ Hansson, M.; Hederstedt, L. (1994-02-15). "Purification and characterisation of a water-soluble ferrochelatase from Bacillus subtilis". European Journal of Biochemistry. 220 (1): 201–208. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18615.x. ISSN 0014-2956. PMID 8119288.
- ↑ Minder, EI; Schneider-Yin, X; Steurer, J; Bachmann, LM (2009). "A systematic review of treatment options for dermal photosensitivity in erythropoietic protoporphyria". Cellular and Molecular Biology. 55 (1): 84–97. PMID 19268006.
- ↑ Arceci, Robert.; Hann, Ian M.; Smith, Owen P. (2006). Pediatric hematolog. Malden, Mass.: Blackwell Pub. ISBN 978-1-4051-3400-2.
- ↑ Elder, George; Harper, Pauline; Badminton, Michael; Sandberg, Sverre; Deybach, Jean-Charles (2012). "The incidence of inherited porphyrias in Europe". Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease. 36 (5): 849–57. doi:10.1007/s10545-012-9544-4. PMID 23114748. S2CID 20442163.
- ↑ Michaels, BD; Del Rosso, JQ; Mobini, N; Michaels, JR (2010). "Erythropoietic protoporphyria: A case report and literature review". The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology. 3 (7): 44–8. PMC 2921755. PMID 20725556.
- ↑ Wahlin, S.; Floderus, Y.; Stål, P.; Harper, P. (2011). "Erythropoietic protoporphyria in Sweden: Demographic, clinical, biochemical and genetic characteristics". Journal of Internal Medicine. 269 (3): 278–88. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2010.02236.x. PMID 20412370.
- ↑ Kosenow, W; Treibs, A (1953). "Light hypersensitivity and porphyrinemia". Zeitschrift für Kinderheilkunde. 73 (1): 82–92. doi:10.1007/BF00438257. PMID 13103364. S2CID 46459771.
- ↑ Magnus, I; Jarrett, A; Prankerd, TA; Rimington, C (1961). "Erythropoietic protoporphyria. A new porphyria syndrome with solar urticaria due to protoporphyrinæmia". The Lancet. 278 (7200): 448–51. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(61)92427-8. PMID 13765301.
External links
- Erythropoietic protoporphyria at NLM Genetics Home Reference
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |