Familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia
| Familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia | |
|---|---|
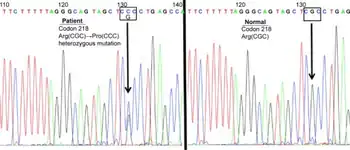 | |
| Familial Dysalbuminemic Hyperthyroxinemia caused by a Point Albumin Gene Mutation-Genomic DNA sequence of exon 7 of the albumin gene in the affected individual and a normal subject | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
Familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia is a type of hyperthyroxinemia associated with mutations in the human serum albumin gene.[1] The term was introduced in 1982.[2]
References
- ↑ Petitpas I, Petersen CE, Ha CE, et al. (May 2003). "Structural basis of albumin–thyroxine interactions and familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA. 100 (11): 6440–5. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.6440P. doi:10.1073/pnas.1137188100. PMC 164465. PMID 12743361.
- ↑ Ruiz M, Rajatanavin R, Young RA, et al. (March 1982). "Familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia: a syndrome that can be confused with thyrotoxicosis". New England Journal of Medicine. 306 (11): 635–9. doi:10.1056/NEJM198203183061103. PMID 6173750.
External links
| Classification |
|
|---|
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.