Female genital mutilation laws by country
The legal status of female genital mutilation (FGM), also known as female genital cutting (FGC), differs widely across the world.
Overview of issues
Geographic perspective
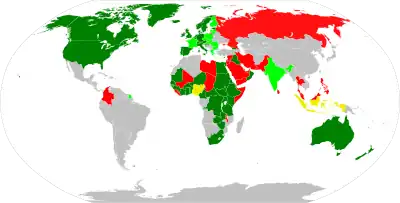
In international law, there is a consensus that female genital mutilation is a human rights violation that needs to be criminalised and eradicated by all states. International human rights instruments to that effect include global and regional treaties, conventions, protocols, declarations, resolutions and recommendations such as CEDAW Committee General Recommendation No. 14 (1990),[1]: 11 Maputo Protocol Article 5 (2003),[1]: 24 the Cairo Declaration on the Elimination of FGM (CDEFGM, 2003),[1]: 21 Istanbul Convention Article 38 (2011),[2]: 35 Sustainable Development Goal 5.3 (2015),[1]: 19 the East African Community Prohibition of Female Genital Mutilation Act (EAC Act, 2016)[1]: 20–21 and United Nations Human Rights Council Resolution No. 38/61 (2018).[1]: 19
Global efforts to end FGM, including criminalisation, have long focused on Africa, where most countries that have traditionally practiced FGM are located and anti-FGM campaigns have been quite successful in the 1990s through 2010s,[3] but have long under-appreciated traditionally FGM-practicing countries in Asia and immigrant communities in countries with no FGM tradition.[3][4][5] A March 2020 report by End FGM European Network, U.S. End FGM/C Network and Equality Now found that FGM was practiced in at least 92 countries across all continents,[3] while 51 of them had a law that specifically criminalised FGM.[1]: 11
FGM was illegal in 22 of the 28 most FGM-prevalent countries in Africa in September 2018.[6] Sudan criminalised FGM in April 2020.[7]
Some Western countries, where FGM has not been traditionally practiced but where immigrants from traditionally FGM-practicing countries have moved to in the 20th and 21st century, have also criminalised FGM (13 countries as of November 2008).[8][9] By 2013, FGM had been criminalised in all 27 member states of the European Union (including the United Kingdom) and Croatia.[2]: 45
Despite international reports to the contrary,[8][2]: 45 [1]: 26 female genital mutilation has been explicitly criminalised in the Netherlands since 1 February 2006, namely in the then Articles 5.3 and 5a.1 of the Dutch Criminal Code (Wetboek van Strafrecht),[9] and the statute of limitations was increased on 1 July 2009 by not starting until the day after the FGM victim's 18th birthday.[10] As of 25 July 2020, genital mutilation of female persons under age 18 is punishable in the Netherlands, including when committed abroad by Dutch citizens, foreigners who later obtain Dutch citizenship or foreigners with a regular place of residence or stay in the Netherlands, as a form of (aggravated) assault (potentially premeditated) under Articles 300 to 303 per Article 7.d and Article 71.3 of the Dutch Criminal Code.[note 1] The maximum punishment is 12 years imprisonment (or 15 years if the victim dies).[11] The penalty can be increased by a third if the perpetrator(s) were (a) family member(s) or the life companion of the victim (Article 304.1) or if the victim was underage (Article 304.2).[11]
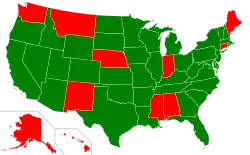
In the United States, FGM was criminalised federally in 1996 and in 17/50 states during 1994–2006.[8] However, the federal law criminalising FGM was declared unconstitutional by a Michigan court in November 2018, mostly because the judge found that the federal government did not have the authority to legislate on the issue, and that the U.S. states should.[12] At the time of the ruling, 27 states had specifically criminalised FGM,[12] and the court case stimulated the other states to do so as well, both during[12] and after the trial.[13] By March 2020, the practice was illegal in 35/50 states;[3] by May 2020, FGM was banned in 38/50 U.S. states.[14] On 5 January 2021, the STOP FGM Act of 2020 was enacted, which considers FGM 'a form of child abuse, gender discrimination, and violence', empowering federal authorities to prosecute people who 'carry out or conspire to carry out FGM' and increasing the maximum prison sentence from 5 to 10 years. This replaced the 1996 law that was declared unconstitutional in 2018. At the time of signing, 11 out of the 50 U.S. states still had no state ban on FGM.[15]
Legal methods
The way in which legislation (and usually criminalisation) of FGM is enacted, differs from country to country. Some countries' constitutions ban FGM, others have adopted specific laws criminalising FGM, others have subsumed prohibitions on FGM in wider criminal legislation on either child protection, violence against women, sexual violence, or physical assault.[6][2]: 45 In EU member states, there is a trend to criminalise FGM in specific rather than general criminal law provisions; by 2013, 10 states of 28 (including Croatia and the UK) had done so.[2]: 45 By March 2020, Estonia, Germany, Malta and Portugal had also introduced explicit provisions criminalising FGM, so that 14 out of the current 27 EU Member States have specific anti-FGM legislation.[1]: 25–26
Indian Minister for Women and Child Development Maneka Gandhi said in 2017 that the 1860 Indian Penal Code, the 1973 Criminal Procedure Code and the 2012 Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act (POCSO Act) could be invoked to prosecute FGM cases and that a specific law to criminalise FGM was not necessary.[16]
Cross-border FGM and extraterritoriality
Sometimes FGM is performed across the border in a country where it is still legal in order to avoid prosecution in one's country of residence (for example, in Mali by Burkina Faso residents or in Somalia by Kenya residents).[6]: 48 As of September 2018, Guinea Bissau, Kenya and Uganda were the only countries in Africa that criminalised and punished cross-border FGM.[6]: 49 In the European Union, legislators have applied the legal principle of extraterritoriality to prosecute the practice of FGM when it is committed outside of a member state's territory to girls living in the EU who had been cut or are at risk of being cut in their or their parents' country of birth while on holidays or visits abroad.[2]: 45
Laws by country
| Country | Criminalised | Since | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 25 | Criminalised in 6/8 states during 1994–7 as of November 2008.[8] | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 25 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 25 | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 38 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 25 | 2000[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 25 | |
| Specific anti-FGM law[1]: 22 | 2003[8] | Specific national anti-FGM law which prohibits FGM.[1]: 22 | |
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 38 | ||
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 1996[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 22 | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | As of September 2018.[6] | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 38 | 1997[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 38 | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 1966[8] | As of September 2018.[6] | |
| No | A 2002 bill banning FGM hasn't yet been enacted as of March 2020.[1]: 22 [6] | ||
| No | Some native tribes (Emberá, Arhuaco, Koguis) are known to practice FGM, but there is no law against it[17] as of March 2020.[1]: 32 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 1998[8] | As of September 2018.[6] | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 25 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 25 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 25 | 2003[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 25 | |
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 25 | 2003[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 25 | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 1994[8] | As of September 2018.[6] | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 38 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 38 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 2008[8] | As of September 2018.[6] | |
| Specific anti-FGM law[1]: 22 | 2007[8] | Specific national anti-FGM law which prohibits FGM.[1]: 22 | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 25 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 25 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 2004[8] | As of September 2018.[6] | |
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision,[2]: 45 has been used successfully to prosecute FGM cases.[1]: 25 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 2015[18] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 22 | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 38 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 38 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 25 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 25 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 1994[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 22 | |
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 1965[8] | New law enacted in 2000.[8] Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 22 | |
| Specific anti-FGM law[1]: 22 | Specific national anti-FGM law which prohibits FGM.[1]: 22 Cross-border FGM also criminalised.[6]: 49 | ||
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[19] | 2005[20] | General Penal Code Article 218 a. Punishment up to 6 years imprisonment, up to 16 years in aggravated cases.[19] | |
| General criminal provision | 1860 | Supposedly criminalised, but not specifically mentioned, by 1860 Indian Penal Code, 1973 Criminal Procedure Code and 2012 POCSO Act.[16] | |
| Unclear[21] | 2006, 14 | Criminalised in 2006,[22] medicalised in 2010, then recriminalised in 2014 but without punishments.[23] Present legal status unclear.[21] | |
| Specific criminal provision | Criminalised by the Islamic Penal Code of 2013.[24][25] Article 663 explicitly mentions the following: "Mutilating or injuring either side of a woman's genitals shall carry the Diya penalty equal to half of the full Diya. Mutilating or injuring parts of the genitals shall have a proportionate penalty based on the level of injury." Additionally, Article 269 of the Islamic Penal Code of 1991[26] criminalises "intentional mutilation or amputation" without explicitly mentioning FGM. | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | Specific criminal law provision (in the Kurdistan Region).[1]: 22 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 25 | 2012[27] | Specific criminal law provision:[1]: 25 the Criminal Justice (Female Genital Mutilation) Act 2012.[27] | |
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 32 | ||
| Specific anti-FGM law[1]: 25 | 2005[8] | Specific national anti-FGM law which prohibits FGM.[1]: 25 | |
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 38 | ||
| Specific anti-FGM law[1]: 22 | 2001[8] | Specific national anti-FGM law which prohibits FGM.[1]: 22 Cross-border FGM also criminalised.[6]: 49 | |
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 32 | ||
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| Not anymore | (2018–9) | As of September 2018.[6] President Ellen Johnson Sirleaf banned FGM for one year which expired on 22 January 2019.[28] | |
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 40 | ||
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 40 | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 32 | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 22 | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 22 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 26 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 26 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 2005[8] | As of September 2018.[6] | |
| Specific criminal provision[11] | 2006[9] | Specific criminal law provision including cross-border FGM: Articles 7.d and 71.3 combined with Articles 300–303 (additional penalties in Article 304).[11] | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 40 | 1995[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 40 | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 2003[8] | As of September 2018.[6] | |
| Federal specific criminal provision Does not apply in all states[1]: 22 | Specific criminal law provision that does not apply in all states of Nigeria.[1]: 22 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 26 | 1995[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 26 | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 33 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 33 | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 33 | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 33 | ||
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 26 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 26 | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 40 | ||
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| General criminal provision[29] | General criminal law provision[30] | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 34 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 1999[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 22 | |
| No[1]: 22 | Initiation rite-related FGM was criminalised in 2019,[31] but there is no national law banning all FGM.[32] | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 34 | ||
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| General criminal provision[2]: 45 | General criminal law provision.[2]: 45 | ||
| No | The Constitution prohibits FGM, but there are no laws and no known prosecutions of FGM.[1]: 22 | ||
| No | As of September 2018.[6] | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 40 | 2003[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 40 | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 40 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 40 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 26 | 2003[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 26 | |
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 33 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[7] Restricted/banned in 6/18 states[7] | 2020 | Criminalised in April 2020 by amending the Criminal Code. Punishable by a fine and 3 years imprisonment.[7][34] Already restricted or banned in 6/18 states between 2008 and 2020.[7] Reinfibulation apparently still legal.[35] | |
| Specific anti-FGM law[1]: 26 | 1982[8] | New law enacted in 1998.[8] Specific national anti-FGM law which prohibits FGM.[1]: 26 | |
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 26 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 26 | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 39 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 1998[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 22 | |
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 33 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | 1998[8] | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 22 | |
| Specific anti-FGM law[1]: 22 | Specific national anti-FGM law which prohibits FGM.[1]: 22 Cross-border FGM also criminalised.[6]: 49 | ||
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 33 | ||
| Specific anti-FGM law[1]: 26 | 1985[8] | Specific national anti-FGM law which prohibits FGM.[1]: 26 | |
| Federal anti-FGM law Specific bans in 40 states [36] | 96–18, 2021 | Criminalised federally in 1996,[8] but federal law declared "unconstitutional" in 2018.[1]: 26 New federal law passed in 2021.[15] Specifically criminalised in 40/50 states as of November 2021.[15][14] | |
| No | As of March 2020.[1]: 22 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 22 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 22 | ||
| Specific criminal provision[1]: 40 | Specific criminal law provision.[1]: 40 |
See also
- Prevalence of female genital mutilation
- Religious views on female genital mutilation
- Sexual consent in law
Notes
- ↑ "Artikel 7. 1. De Nederlandse strafwet is toepasselijk op de Nederlander die zich buiten Nederland schuldig maakt aan een feit dat door de Nederlandse strafwet als misdrijf wordt beschouwd en waarop door de wet van het land waar het begaan is, straf is gesteld. 2. De Nederlandse strafwet is voorts toepasselijk op de Nederlander die zich buiten Nederland schuldig maakt: (...) d. aan een van de misdrijven omschreven in de artikelen 300 tot en met 303, voor zover het feit oplevert genitale verminking van een persoon van het vrouwelijke geslacht die de leeftijd van achttien jaren nog niet heeft bereikt; (...). 3. Met een Nederlander wordt voor de toepassing van het eerste en het tweede lid, onder b tot en met e, gelijkgesteld de vreemdeling die na het plegen van het feit Nederlander wordt alsmede, voor de toepassing van het eerste en tweede lid, de vreemdeling die in Nederland een vaste woon- of verblijfplaats heeft."
"Artikel 71. De termijn van verjaring vangt aan op de dag na die waarop het feit is gepleegd, behoudens in de volgende gevallen: (...) 3°. bij de misdrijven omschreven in (...) de artikelen 300 tot en met 303, voor zover het feit oplevert genitale verminking van een persoon van het vrouwelijke geslacht die de leeftijd van achttien jaren nog niet heeft bereikt (...)."[11]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 "Female genital mutilation/cutting: a call for a global response" (PDF). End FGM European Network, U.S. End FGM/C Network and Equality Now. March 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 "Female genital mutilation in the European Union and Croatia" (PDF). European Institute for Gender Equality. 2013. Retrieved 3 May 2020. (pdf)
- 1 2 3 4 Liz Ford (17 March 2020). "True numbers of FGM victims could be far higher as countries fail to record cases". The Guardian. Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- ↑ Batha, Emma (30 January 2017). "In parts of Asia and Middle East, female genital mutilation a hidden ritual". Reuters. Retrieved 4 August 2018.
- ↑ Piecha, Oliver M. (1 December 2013). "No "African problem"". Stop FGM Middle East. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 "The law and FGM. An overview of 28 African countries" (PDF). 28 Too Many. September 2018. p. 22. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Declan Walsh (30 April 2020). "In a Victory for Women in Sudan, Female Genital Mutilation Is Outlawed". The New York Times. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 "Female Genital Mutilation (FGM): Legal Prohibitions Worldwide". Center for Reproductive Rights. 12 November 2008. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- 1 2 3 "Wetboek van Strafrecht (Geldend van 01-02-2006 t/m 31-03-2006)". wetten.overheid.nl (in Dutch). Government of the Netherlands. 1 February 2006. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- ↑ "Wetboek van Strafrecht (01-07-2009 t/m 31-12-2009)". wetten.overheid.nl (in Dutch). Government of the Netherlands. 1 July 2009. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Wetboek van Strafrecht (Geldend van 25-07-2020 t/m heden)". wetten.overheid.nl (in Dutch). Government of the Netherlands. 25 July 2020. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- 1 2 3 Samantha Schmidt (22 November 2018). "Judge rules that federal law banning female genital mutilation is unconstitutional". The Washington Post. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- ↑ "Seven American states have criminalised FGM this year". The Economist. 30 May 2019. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- 1 2 "FGM Legislation by State". AHA Foundation. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- 1 2 3 Emma Batha (7 January 2021). "U.S. toughens ban on 'abhorrent' female genital mutilation". Reuters. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- 1 2 Feeds, PTI (4 August 2017). "IPC, POCSO enough to deal with female genital mutilation: Govt". India.com. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- ↑ "FGM in Latin America: Colombia's Embera tribe". Aljazeera. 7 October 2017. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- ↑ The Gambia bans female genital mutilation
- 1 2 "General Penal Code, Nr. 19/1940". www.government.is. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ↑ Harriet Sherwood (18 February 2018). "Iceland law to outlaw male circumcision sparks row over religious freedom". The Guardian. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- 1 2 Nurhadi Sucahyo (9 February 2020). "Study: Indonesians Embrace FGM as Religious, Traditional Practice". Voice of America. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- ↑ "INDONESIA: Female genital mutilation persists despite ban", IRIN Global, 2 September 2010.
- ↑ "Indonesia Seeks End to Female Genital Mutilation". 26 September 2016.
- ↑ "قانون مجازات اسلامی مصوب ۱۳۹۲ (کتاب اول تا چهارم)". پایگاه خبری اختبار (in Persian). 31 May 2013. Retrieved 26 November 2020.
- ↑ "Islamic Penal Code of 2013". Official Website of the Iranian Parliament (Majlis).
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ "قانون مجازات اسلامی ایران/کتاب ۳ - قصاص - ویکینبشته". fa.wikisource.org. Retrieved 26 November 2020.
- 1 2 "Criminal Justice (Female Genital Mutilation) Act 2012". Irish Statute Book. Attorney General of Ireland. 2 April 2012. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ↑ "FGM Becomes Legal Again in Liberia as Ban Expires". Global Citizen. 30 January 2019.
- ↑ Serebrennikova, Anna (2016). "Criminalization of female circumcision: raising of problem". Gaps in Russian Legislation. 8 (Publishing house "Yur-VAK"): 153–155. doi:10.33693/2072-3164.
- ↑ Siradzhudinova, Saida; Antonova, Yulia (2016). Female Genital Mutilation of Girls in Dagestan (Russian Federation) (PDF). Rostov-on-Don: Russian Justice Initiative. pp. 47–51.
- ↑ "Sierra Leone bans FGM in clampdown on secret societies". Reuters. 25 January 2019.
- ↑ Emma Batha (6 June 2019). "Sierra Leone's first lady confronted over FGM controversy". Reuters. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- ↑ Somaliland is a self-proclaimed independent state and de facto functioning as such, but internationally recognised as part of Somalia.
- ↑ "Sudanese government bans female genital mutilation". CNN. 1 May 2020.
- ↑ Yuto Joshi (2 May 2020). "Sudan outlawed female genital mutilation. But experts warn it will take more to end the practice". CBS News. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- ↑ https://www.theahafoundation.org/female-genital-mutilation/fgm-legislation-by-state/
External links
- Female genital mutilation/cutting: a call for a global response – March 2020 report by End FGM European Network, U.S. End FGM/C Network and Equality Now