Hepatic lymph nodes
| Hepatic lymph nodes | |
|---|---|
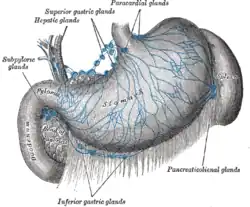 Lymphatics of stomach, etc. | |
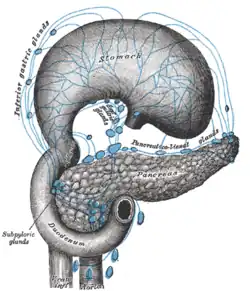 Lymphatics of stomach, etc. The stomach has been turned upward. | |
| Details | |
| System | Lymphatic system |
| Drains to | Celiac lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nodi lymphoidei hepatici lymphoglandulae hepaticae |
| Anatomical terminology | |
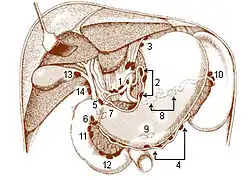
The hepatic lymph nodes consist of the following groups:
- (a) hepatic, on the stem of the hepatic artery, and extending upward along the common bile duct, between the two layers of the lesser omentum, as far as the porta hepatis; the cystic gland, a member of this group, is placed near the neck of the gall-bladder;
- (b) subpyloric, four or five in number, in close relation to the bifurcation of the gastroduodenal artery, in the angle between the superior and descending parts of the duodenum; an outlying member of this group is sometimes found above the duodenum on the right gastric (pyloric) artery.
The lymph nodes of the hepatic chain receive afferents from the stomach, duodenum, liver, gall-bladder, and pancreas; their efferents join the celiac group of preaortic lymph nodes.
Cancer prognosis and treatment
Hepatic artery lymph nodes are commonly resected during a Whipple procedure. In a Whipple procedure, outcomes favored those who had no hepatic artery lymph node involvement.[1][2][3]
A particularly large hepatic artery lymph node, positioned on the anterior aspect of the common hepatic artery, is thought to play an important role in pancreatic cancer. When metastatic disease is identified in the hepatic artery lymph node during pancreatic cancer surgery, longterm outcomes are worse.[1][4]
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 706 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 706 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- 1 2 van Rijssen, LB; Narwade, P; van Huijgevoort, NC; Tseng, DS; van Santvoort, HC; Molenaar, IQ; van Laarhoven, HW; van Eijck, CH; Busch, OR; Besselink, MG; Dutch Pancreatic Cancer, Group. (July 2016). "Prognostic value of lymph node metastases detected during surgical exploration for pancreatic or periampullary cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis". HPB. 18 (7): 559–66. doi:10.1016/j.hpb.2016.05.001. PMC 4925793. PMID 27346135.
- ↑ Saraee, Amir; Vahedian-Ardakani, Jalal; Saraee, Ehsan; Pakzad, Roshanak; Wadji, Massoud (2015). "Whipple procedure: a review of a 7-year clinical experience in a referral center for hepatobiliary and pancreas diseases". World Journal of Surgical Oncology. 13 (1): 98. doi:10.1186/s12957-015-0523-8. PMC 4363458. PMID 25885408.
- ↑ LaFemina, J.; Chou, J. F.; Gönen, M.; Rocha, F. G.; Correa-Gallego, C.; Kingham, T. P.; Fong, Y.; D’Angelica, M. I.; Jarnagin, W. R.; DeMatteo, R. P.; Allen, P. J. (June 1, 2013). "Hepatic Arterial Nodal Metastases in Pancreatic Cancer: Is This the Node of Importance?". Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery. 17 (6): 1092–1097. doi:10.1007/s11605-012-2071-7. PMID 23588624. S2CID 30984456.
- ↑ Cordera, Fernando; Arciero, Cletus A.; Li, Tianyu; Watson, James C.; Hoffman, John P. (August 2007). "Significance of common hepatic artery lymph node metastases during pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic head adenocarcinoma". Annals of Surgical Oncology. 14 (8): 2330–2336. doi:10.1245/s10434-006-9339-7. ISSN 1068-9265. PMID 17492334. S2CID 739244.