Hypotelorism
| Hypotelorism | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Ocular hypotelorism,[1] orbital hypotelorism,[1] hypotelorbitism[2] | |
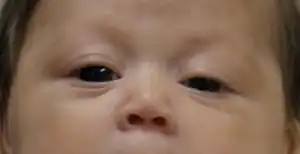 | |
| Hypotelorism as a result of 18p- syndrome | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Hypotelorism is an abnormally decreased distance between two organs or bodily parts, usually pertaining to the eye sockets (orbits), also known as orbital hypotelorism.[1]
It is often a result of fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS), caused by large alcohol intake in the first month of pregnancy. It can be associated with trisomy 13, which is also known as Patau syndrome,[3] as well as hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy.[4] It can also be associated with fragile X syndrome and Prader–Willi syndrome.Metopic synostosis, the early closure of metopic suture during skull development in children, can also cause hypotelorism.
.png.webp)
Hypotelorism
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "Hypotelorism". Medical Dictionary. TheFreeDictionary.com. Archived from the original on 2008-07-24. Retrieved 2008-01-19.
- ↑ "Metopic Synostosis - Thieme Connect" (PDF). profile.thieme.de. doi:10.1055/b-0034-72774. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-04-16. Retrieved 2020-01-08.
- ↑ "Hypotelorism". Medcyclopaedia. GE. Archived from the original on 2012-02-07. Retrieved 2022-12-17.
- ↑ Electromyography and Neuromuscular Disorders, Second Edition. Preston and Shapiro.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.