Infantile systemic hyalinosis
| Infantile systemic hyalinosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Juvenile systemic hyalinosis | |
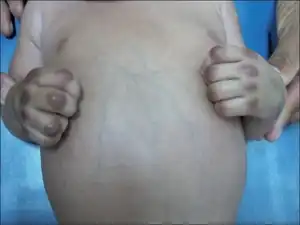 | |
| Papulonodules on knuckles/metacarpophalangeal joints | |
Infantile systemic hyalinosis is characterized by multiple firm white small bumps in the skin of typically the head, face and ears of children.[1] Other symptoms include swelling of gums, osteolytic bone lesions and joint contractures.[1]
It is an allelic autosomal-recessive condition, in which there is hyaline deposition.[2]: 606
Signs and symptoms
The clinical presentation of this condition is as follows:[3]
- Brachydactyly
- Camptodactyly of finger
- Chronic diarrhea
- Coarse facial appearance
- Feeding problems
- Gum enlargement
- Immunodeficiency
- Joint stiffness
- Abnormal skull
- Abnormality of gastrointestinal tract
- Osteolysis
- Progressive flexion contractures
Genetics
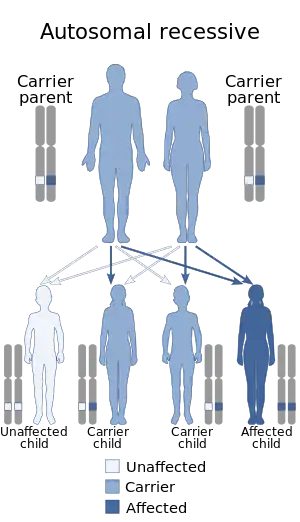
Infantile systemic hyalinosis is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner
This disease is caused by mutations in the CMG2 gene (ANTXR2).[4][5]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Infantile systemic hyalinosis is based on the following:[6][3]
- Medical history
- Symptoms
- Physical exam
- Laboratory test
- Genetic test
Management
In terms of treatment for this condition the following is done:[3]
- Physical therapy
- Joint contractures
- Splinting
See also
References
- 1 2 Johnstone, Ronald B. (2017). "14. Cutaneous depositse". Weedon's Skin Pathology Essentials (2nd ed.). Elsevier. p. 292. ISBN 978-0-7020-6830-0. Archived from the original on 2021-05-25. Retrieved 2022-09-28.
- ↑ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- 1 2 3 "Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 18 March 2021. Retrieved 26 October 2021.
- ↑ Vahidnezhad H, Ziaee V, Youssefian L, Li Q, Sotoudeh S, Uitto J (2015) Infantile systemic hyalinosis in an Iranian family with a mutation in the CMG2/ANTXR2 gene. Clin Exp Dermatol doi: 10.1111/ced.12616
- ↑ "Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome: MedlinePlus Genetics". medlineplus.gov. Archived from the original on 19 March 2021. Retrieved 26 October 2021.
- ↑ "Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome - Conditions - GTR - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 26 October 2021.
External links
- GeneReview/NIH/UW entry on Hyalinosis, Inherited Systemic Archived 2020-10-26 at the Wayback Machine
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.