Johnson–McMillin syndrome
| Johnson–McMillin syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Johnson neuroectodermal syndrome,[1] alopecia–anosmia–deafness–hypogonadism syndrome[1] | |
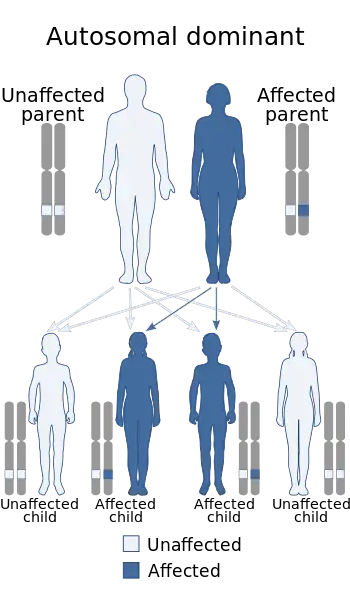 | |
| Johnson–McMillin syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. | |
Johnson–McMillin syndrome, also known as Johnson neuroectodermal syndrome, is a neuroectodermal syndrome that consists of conductive hearing loss and microtia.[2]
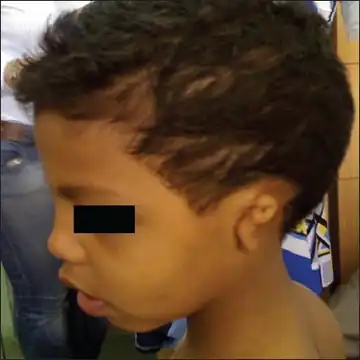
Left sided microtia and atresia of left auditory canal
See also
References
- 1 2 "OMIM Entry - % 147770 - JOHNSON NEUROECTODERMAL SYNDROME". www.omim.org. Archived from the original on 2019-12-24. Retrieved 2019-12-24.
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 831. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.