KBG syndrome
| KBG syndrome | |
|---|---|
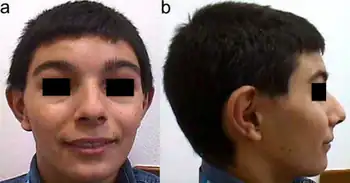 | |
| a) frontal b)lateral view of KBG syndrome individual-facial dysmorphisms including low frontal hairline, mild synophrys, hypertelorism | |
| Symptoms | macrodontia, brachycephaly, hypertelorism, synophrys, long philtrum, thin upper lip |
| Causes | ANKRD11 gene mutation |
KBG syndrome is a genetic disease that is the result of a mutation in the ANKRD11 gene at location 16q24.3.[1] Features include unusually large upper front teeth (macrodontia), wide, short skull (brachycephaly), widely spaced eyes (hypertelorism), and wide eyebrows that may grow together in the middle (synophrys).[2]
The syndrome was first described by Herrmann in 1975 in three distinct families.[3] Herrmann proposed the name KBG syndrome after the initials of affected families last names.[4]
References
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): KBG syndrome - 148050
- ↑ "KBG syndrome". Genetics Home Reference. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2022-01-25. Retrieved 2021-02-03.
- ↑ Herrmann J, Pallister PD, Tiddy W, Opitz JM (1975). "The KBG syndrome-a syndrome of short stature, characteristic facies, mental retardation, macrodontia and skeletal anomalies". Birth Defects Original Article Series. 11 (5): 7–18. PMID 1218237.
- ↑ Morel Swols D, Foster J, Tekin M (December 2017). "KBG syndrome". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 12 (1): 183. doi:10.1186/s13023-017-0736-8. PMC 5735576. PMID 29258554.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.