Lipohypertrophy
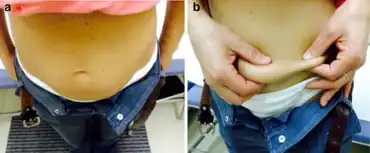
Lipohypertrophy[1] is a lump under the skin caused by accumulation of extra fat at the site of many subcutaneous injections of insulin. It may be unsightly, mildly painful, and may change the timing or completeness of insulin action. It is a common, minor, chronic complication of diabetes mellitus.
Typical injection site hypertrophy is several inches or cm across, smoothly rounded, and somewhat firmer than ordinary subcutaneous fat. There may be some scar tissue as well, but the major component is adipose tissue, as insulin exerts a hypertrophic effect on adipose cells. To avoid lipohypertrophy, persons with diabetes mellitus who inject insulin daily for an extended period of time are advised to rotate their injections among several areas (usually upper, outer arms, outer thighs, abdomen below and around the umbilicus, and the upper parts of the buttocks). Rotation charts are often provided as part of diabetes education to help prevent lipohypertrophy.
Lipohypertrophy usually will gradually disappear over months if injections in the area are avoided.
It is a common misconception that the lump is largely scar tissue, as injection site hypertrophy is much rarer and milder with injections of other hormones and medications which lack the specific ability of insulin to stimulate adipose hypertrophy.
In a sense, the "opposite" of injection site lipohypertrophy is injection site lipoatrophy, in which the subcutaneous fat around an injected area "melts away" over a few weeks or months, leaving unsightly, well-demarcated depressions in the skin. The mechanism of this local lipoatrophy is not understood and may involve autoimmunity or local inflammation.
See also
References
- ↑ Rapini RP, Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
Further reading
- Young RJ, Hannan WJ, Frier BM, Steel JM, Duncan LJ (1 September 1984). "Diabetic lipohypertrophy delays insulin absorption". Diabetes Care. 7 (5): 479–80. doi:10.2337/diacare.7.5.479. PMID 6389062. S2CID 8148898.
- Vardar B, Kizilci S (August 2007). "Incidence of lipohypertrophy in diabetic patients and a study of influencing factors". Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 77 (2): 231–6. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2006.12.023. PMID 17303282.
- Hauner H, Stockamp B, Haastert B (15 July 2009). "Prevalence of lipohypertrophy in insulin-treated diabetic patients and predisposing factors". Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes. 104 (2): 106–10. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1211431. PMID 8740933.
- Blanco M, Hernández MT, Strauss KW, Amaya M (October 2013). "Prevalence and risk factors of lipohypertrophy in insulin-injecting patients with diabetes". Diabetes & Metabolism. 39 (5): 445–53. doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2013.05.006. PMID 23886784.