Asterion (anatomy)
| Asterion | |
|---|---|
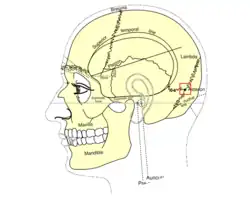 Side view of head, showing surface relations of bones. (Asterion visible at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | skull |
| System | skeletal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Asterion |
| TA98 | A02.1.00.020 |
| TA2 | 422 |
| FMA | 76625 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The asterion is a meeting point between three sutures between bones of the skull. It is an important surgical landmark.
Structure
In human anatomy, the asterion is a visible (craniometric) point on the exposed skull. It is just posterior to the ear. It is the point where three cranial sutures meet:
It is also the point where three cranial bones meet:
- the parietal bone.
- the occipital bone.
- the mastoid portion of the temporal bone.
In the adult, it lies 4 cm behind and 12 mm above the center of the entrance to the ear canal. Its relation to other anatomical structures is fairly variable.[2]
Clinical significance
Neurosurgeons may use the asterion to orient themselves, in order to plan safe entry into the skull for some operations, such as when using a retro-sigmoid approach.[1][3]
Etymology
The asterion receives its name from the Greek ἀστέριον (astērion), meaning "star" or "starry".
The Mercedes point is an alternative term for the asterion, for its resemblance to the Mercedes-Benz logo.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Ucerler, Hulya; Govsa, Figen (2006-10-01). "Asterion as a surgical landmark for lateral cranial base approaches". Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery. 34 (7): 415–420. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2006.05.003. ISSN 1010-5182 – via ScienceDirect.
- ↑ Avci, Emel; Kocaogullar, Yalcin; Fossett, Damirez; Caputy, Anthony (2003-05-01). "Lateral posterior fossa venous sinus relationships to surface landmarks". Surgical Neurology. 59 (5): 392–397. doi:10.1016/S0090-3019(03)00037-5. ISSN 0090-3019 – via ScienceDirect.
- ↑ Babacan S, Yildiz-Yilmaz M, Kafa IM, Coşkun I (2019). "The Surface and Intracranial Location of Asterion". J Craniofac Surg. 30 (8): e753–e755. doi:10.1097/SCS.0000000000005757. PMID 31689738.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Asterion (anatomy). |