Maullinia
| Maullinia | |
|---|---|
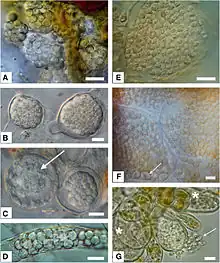 | |
| E: Resting spores of Maullinia sp. resting spores in Durvillaea antarctica | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Phylum: | Cercozoa |
| Class: | Phytomyxea |
| Order: | Plasmodiophorida |
| Family: | Plasmodiophoridae |
| Genus: | Maullinia I. Maier, E. R. Parodi, R. Wester-meier et D. G. Müller 2000 |
Maullinia is a genus of intracellular, protistan parasites that infect brown algae (Phaeophyceae).[1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
Distribution
Maullinia has been found in brown macroalgae across the Southern Hemisphere, including Chile, the Falkland Islands, Australia, New Zealand and various sub-Antarctic islands.[5][7] Based on genetic evidence, Maullinia have likely been dispersed widely via transport inside of buoyant rafts of southern bull kelp.[5][7][8]
Description

Yellow galls caused by Maullinia infections in two fronds southern bull kelp
Maullinia infections have been found in filamentous brown algae such Ectocarpus siliculosus and Acinetospora,[1][3] as well as in macroalgae including Macrocystis, Desmarestia, southern bull-kelp.[3][5][7] Maullinia can cause yellow galls to develop (0.5 - 4.0 cm in diameter).[3][5][7][8]
Species
References
- 1 2 3 Maier, Ingo; Parodi, Elisa; Westermeier, Renato; Müller, Dieter G. (2000). "Maullinia ectocarpii gen. et sp. nov. (Plasmodiophorea), an Intracellular Parasite in Ectocarpus siliculosus (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae) and other Filamentous Brown Algae". Protist. 151 (3): 225–238. doi:10.1078/1434-4610-00021. PMID 11079768.
- 1 2 Parodi, Elisa R.; Cáceres, Eduardo J.; Westermeier, Renato; Müller, Dieter G. (2010). "Secondary zoospores in the algal endoparasite Maullinia ectocarpii (Plasmodiophoromycota)". Biocell. 34 (1): 45–52. doi:10.32604/biocell.2010.34.045. PMID 20506630.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Goecke, Franz; Wiese, Jutta; Núñez, Alejandra; Labes, Antje; Imhoff, Johannes F.; Neuhauser, Sigrid (2012). "A Novel Phytomyxean Parasite Associated with Galls on the Bull-Kelp Durvillaea antarctica (Chamisso) Hariot". PLOS ONE. 7 (9): e45358. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045358. PMC 3444446. PMID 23028958.
- 1 2 Neuhauser, Sigrid; Kirchmair, Martin; Bulman, Simon; Bass, David (2014). "Cross-kingdom host shifts of phytomyxid parasites". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 14 (1): 33. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-14-33. PMC 4016497. PMID 24559266.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Blake, Callum; Thiel, Martin; López, Boris A.; Fraser, Ceridwen I. (2017). "Gall-forming protistan parasites infect southern bull kelp across the Southern Ocean, with prevalence increasing to the south". Marine Ecology Progress Series. 583: 95–106. doi:10.3354/meps12346.
- 1 2 Murúa, Pedro; Goecke, Franz; Westermeier, Renato; van West, Pieter; Küpper, Frithjof C.; Neuhauser, Sigrid (2017). "Maullinia braseltonii sp. nov. (Rhizaria, Phytomyxea, Phagomyxida): A Cyst-forming Parasite of the Bull Kelp Durvillaea spp. (Stramenopila, Phaeophyceae, Fucales)". Protist. 168 (4): 468–480. doi:10.1016/j.protis.2017.07.001. PMC 5673062. PMID 28822911.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mabey, Abigail L.; Parvizi, Elahe; Ceridwen, Fraser I. (2021). "Pathogen inferred to have dispersed thousands of kilometres at sea, infecting multiple keystone kelp species". Marine Biology. 168 (4): 47. doi:10.1007/s00227-021-03853-8. ISSN 0025-3162.
- 1 2 Baranuik, Chris (5 April 2021). "Kelp Pathogen Has Spread Across the Southern Ocean". The Scientist. Retrieved 14 April 2021.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.