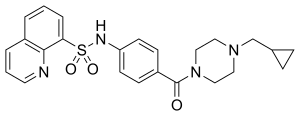
Mitapivat
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Pyrukynd |
| Other names | AG-348, Mitapivat sulfate (USAN US) |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Pyruvate kinase activator[1] |
| Main uses | Hemolytic anemia in pyruvate kinase deficiency[1] |
| Side effects | Trouble sleeping, back pain, nausea, joint pain[1][2] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Legal | |
| License data | |
| Legal status | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H26N4O3S |
| Molar mass | 450.56 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Mitapivat, sold under the brand name Pyrukynd, is a medication used to treat hemolytic anemia in those with pyruvate kinase deficiency.[1] It is approved in adults.[2] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include trouble sleeping, back pain, nausea, and joint pain.[1][2] Safety in pregnancy is unclear.[1] It is a pyruvate kinase activator.[1]
Mitapivat was approved for medical use in the United States and Europe in 2022.[1][2] In the United States 4 weeks of treatment costs about 27,000 USD as of 2022.[3] It is not commercially available in the United Kingdom as of 2022.[4]
Medical uses
Mitapivat is indicated for the treatment of hemolytic anemia in adults with pyruvate kinase deficiency.[1][5] It increases hemoglobin levels by 1.5 g/dL in 40% of people.[2]
Dosage
It is started at a dose of 5 mg twice per day.[1] It comes in 5, 20, and 50 mg tablets.[1]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Mitapivat binds to and activates pyruvate kinase, thereby enhancing glycolytic pathway activity, improving adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels and reducing 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG) levels.[6] Mutations in pyruvate kinase cause deficiency in pyruvate kinase which prevents adequate red blood cell (RBC) glycolysis, leading to a buildup of the upstream glycolytic intermediate 2,3-DPG and deficiency in the pyruvate kinase product ATP.[6][7]
Chemistry
It is taken as the sulfate hydrate salt.[1]
Society and culture
Legal status
On 15 September 2022, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for the medicinal product Pyrukynd, intended for the treatment of an inherited condition called pyruvate kinase deficiency.[8] The applicant for this medicinal product is Agios Netherlands B.V.[8] Mitapivat was approved for medical use in the European Union in November 2022.[2]
Names
Mitapivat is the international nonproprietary name (INN).[9]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 "Pyrukynd- mitapivat tablet, film coated Pyrukynd- mitapivat kit". DailyMed. 23 February 2022. Archived from the original on 3 March 2022. Retrieved 3 March 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Pyrukynd EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 14 September 2022. Archived from the original on 6 December 2022. Retrieved 5 December 2022. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ "Pyrukynd Prices, Coupons, Copay & Patient Assistance". Drugs.com. Retrieved 11 December 2022.
- ↑ "Mitapivat". SPS - Specialist Pharmacy Service. 3 November 2019. Archived from the original on 12 August 2022. Retrieved 11 December 2022.
- ↑ Gormley N. "Pyrukynd (mitapivat) tablets NDA approval" (PDF). Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Letter to Christina Baladi (Agios Pharmaceuticals, Inc.). U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- 1 2 "Mitapivat (Code C157039)". NCI Thesaurus. 31 January 2022. Archived from the original on 20 February 2022. Retrieved 19 February 2022.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ "PK-R allosteric activator AG-348". NCI Drug Dictionary. National Cancer Institute. Archived from the original on 10 August 2019. Retrieved 19 February 2022.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 "Pyrukynd: Pending EC decision". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 15 September 2022. Archived from the original on 19 September 2022. Retrieved 18 September 2022. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2017). "International nonproprietary names for pharmaceutical substances (INN): recommended INN: list 78". WHO Drug Information. 31 (3): 539. hdl:10665/330961.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- "Mitapivat sulfate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2022-08-15. Retrieved 2022-12-09.
- Clinical trial number NCT03548220 for "A Study to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of AG-348 in Not Regularly Transfused Adult Participants With Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT03559699 for "A Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of AG-348 in Regularly Transfused Adult Participants With Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD)" at ClinicalTrials.gov