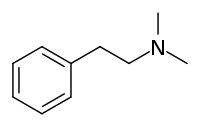
N,N-Dimethylphenethylamine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N-Dimethyl-2-phenylethan-1-amine | |
| Other names
N,N-Dimethyl-2-phenylethanamine N,N-Dimethyl-β-phenylethylamine N,N-DMPEA | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.156.869 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C10H15N |
| Molar mass | 149.237 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
N,N-Dimethylphenethylamine (N,N-DMPEA) is a substituted phenethylamine that is used as a flavoring agent. It is an alkaloid that was first isolated from the orchid Eria jarensis.[1] Its aroma is described as "sweet, fishy". It is mainly used in cereal, cheese, dairy products, fish, fruit and meat.[2] It is also being used in pre-workout and bodybuilding supplements with claims of a stimulant effect.[3]
There is also evidence suggesting that N,N-DMPEA acts as a TAAR1 agonist in humans,[4] and as a 5-HT1A ligand in rats. Some less conclusive research also indicated that it had interaction with MAO-B, most likely as an enzyme substrate and not an inhibitor.[5]
Safety
N,N-DMPEA has been found to be safe for use as a flavoring agent by the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association (FEMA) Expert Panel[6] and also by the Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA)[7]—a collaboration between the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization.[8]
References
- ↑ K. Hedman, K. Leander and B. Luning (1969). "Studies on Orchidaceae Alkaloids. XV. Phenethylamines from Eria jarensis Ames". Acta Chem. Scand. 23: 3261. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.23-3261.
- ↑ Burdock, G.A. (2016). Fenaroli's Handbook of Flavor Ingredients, Sixth Edition. CRC Press. p. 499. ISBN 9781420090864. Retrieved 2016-09-13.
- ↑ "Eria Jarensis Extract / N-phenethyl dimethylamine: The Next Big Thing?". blog.priceplow.com. Retrieved 2016-10-05.
- ↑ Wainscott DB, Little SP, Yin T, Tu Y, Rocco VP, He JX, Nelson DL (January 2007). "Pharmacologic characterization of the cloned human trace amine-associated receptor1 (TAAR1) and evidence for species differences with the rat TAAR1". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 320 (1): 475–485. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.112532. PMID 17038507. S2CID 10829497.
- ↑ Pubchem. "N,N-Dimethylphenethylamine | C10H15N - PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2016-10-05.
- ↑ "Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association (FEMA) GRAS Flavoring Substances 22". www.femaflavor.org. Retrieved 2019-01-14.
- ↑ "Evaluations of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA)". apps.who.int. Retrieved 2019-01-14.
- ↑ "The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA)". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2019-01-14.
The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) is an international expert scientific committee that is administered jointly by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO).