Nanoarchaeum equitans
| Nanoarchaeum equitans | |
|---|---|
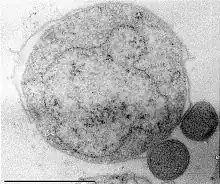 | |
| Two Nanoarchaeum equitans cells (and its larger host Ignicoccus) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | N. equitans |
| Binomial name | |
| Nanoarchaeum equitans Huber et al. 2002 | |
Nanoarchaeum equitans is a species of marine archaea that was discovered in 2002 in a hydrothermal vent off the coast of Iceland on the Kolbeinsey Ridge by Karl Stetter. It has been proposed as the first species in a new phylum. Strains of this microbe were also found on the Sub-polar Mid Oceanic Ridge, and in the Obsidian Pool in Yellowstone National Park. Since it grows in temperatures approaching boiling, at about 80 degrees Celsius, it is considered to be a thermophile. It grows best in environments with a pH of 6, and a salinity concentration of 2%. Nanoarchaeum appears to be an obligate symbiont on the archaeon Ignicoccus; it must be in contact with the host organism to survive. Nanoarchaeum equitans cannot synthesize lipids but obtains them from its host. Its cells are only 400 nm in diameter, making it one of the smallest known cellular organisms, and the smallest known archaeon.
N. equitans' genome consists of a single circular chromosome, and has an average GC-content of 31.6%. It lacks almost all of the genes required for the synthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, cofactors, and lipids, but encodes everything needed for repair and replication. N. equitans contains several genes that encode proteins employed in recombination, suggesting that N. equitans can undergo homologous recombination.[1] A total of 95% of its DNA encodes for proteins or stable RNA molecules.
N. equitans has small appendages that come out of its circular structure. The cell surface is covered by a thin, lattice-shaped S-layer, which provides structure and protection for the entire cell.
Genome
Mycoplasma genitalium (580 Kbp in size, with 515 protein-coding genes) was regarded as a cellular unit with the smallest genome size until 2003 when Nanoarchaeum was sequenced (491 Kbp, with 536 protein-coding genes).
Genetically, Nanoarchaeum is peculiar in that its 16S RNA sequence is undetectable by the most common methods. Initial examination of single-stranded ribosomal RNA indicated that the organism most likely belonged to the Archaea domain. However, its difference from the existing phyla, Euryarchaeota and Crenarchaeota, was as great as the difference between the phyla. Therefore, it was given its own phylum, called Nanoarchaeota. However, another group (see References) compared all of the open reading frames to the other Archaea. They argue that the initial sample, ribosomal RNA only, was biased and Nanoarchaeum actually belongs to the Euryarchaeota phylum.[2]
The sequencing of the Nanoarchaeum genome has revealed a wealth of information about the organism's biology. The genes for several vital metabolic pathways appear to be missing. Nanoarchaeum cannot synthesize most nucleotides, amino acids, lipids, and cofactors. The cell most likely obtains these biomolecules from Ignicoccus. In particular, N. equitans lacks all of the genes that encode purine nucleotide biosynthesis in other organisms.[3] However, unlike many parasitic microbes, Nanoarchaeum has many DNA repair enzymes, as well as everything necessary to carry out DNA replication, transcription, and translation. This may explain why the genome lacks the large stretches of non-coding DNA characteristic of other parasites.
The organism's ability to produce its own ATP is also in question.
Nanoarchaeum lacks the ability to metabolize hydrogen and sulfur for energy, as many thermophiles do. It does have five subunits of an ATP synthase as well as pathways for oxidative deamination. Whether it obtains energy from biological molecules imported from Ignicoccus, or whether it receives ATP directly is currently unknown. The genome and proteome composition of N. equitans are marked with the signatures of dual adaptation – one to high temperature and the other to obligate parasitism (or symbiosis).
See also
References
- ↑ Waters E, Hohn MJ, Ahel I, Graham DE, Adams MD, Barnstead M, Beeson KY, Bibbs L, Bolanos R, Keller M, Kretz K, Lin X, Mathur E, Ni J, Podar M, Richardson T, Sutton GG, Simon M, Soll D, Stetter KO, Short JM, Noordewier M. The genome of Nanoarchaeum equitans: insights into early archaeal evolution and derived parasitism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12984-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1735403100. Epub 2003 Oct 17. PMID: 14566062; PMCID: PMC240731
- ↑ Brochier, Celine; Gribaldo, S; Zivanovic, Y; Confalonieri, F; et al. (2005). "Nanoarchaea: representatives of a novel archaeal phylum or a fast-evolving euryarchaeal lineage related to Thermococcales?". Genome Biology. 6 (5): R42. doi:10.1186/gb-2005-6-5-r42. PMC 1175954. PMID 15892870.
- ↑ Brown AM, Hoopes SL, White RH, Sarisky CA. Purine biosynthesis in archaea: variations on a theme. Biol Direct. 2011 Dec 14;6:63. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-6-63. PMID: 22168471; PMCID: PMC3261824
- Huber, Harald; et al. (2002). "A new phylum of Archaea represented by a nanosized hyperthermophilic symbiont". Nature. 417 (6884): 63–67. Bibcode:2002Natur.417...63H. doi:10.1038/417063a. PMID 11986665. S2CID 4395094. (This paper represents the first discovery of Nanoarchaeum.)
- Waters, Elizabeth; et al. (2003). "The genome of Nanoarchaeum equitans: insights into early archaeal evolution and derived parasitism". PNAS. 100 (22): 12984–12988. Bibcode:2003PNAS..10012984W. doi:10.1073/pnas.1735403100. PMC 240731. PMID 14566062. (This paper describes the genome sequence of Nanoarchaeum.)
- Brochier, Celine; Gribaldo, S; Zivanovic, Y; Confalonieri, F; et al. (2005). "Nanoarchaea: representatives of a novel archaeal phylum or a fast-evolving euryarchaeal lineage related to Thermococcales?". Genome Biology. 6 (5): R42. doi:10.1186/gb-2005-6-5-r42. PMC 1175954. PMID 15892870. (Recent work suggesting that Nanoarchaeum is not a new phylum of archaea, but is a type of euryarchaeon.)
- Das, Sabyasachi; et al. (2006). "Analysis of Nanoarchaeum equitans genome and proteome composition: indications for hyperthermophilic and parasitic adaptation". BMC Genomics. 7: 186. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-7-186. PMC 1574309. PMID 16869956. (This paper describes the genome and proteome analysis of Nanoarchaeum.)
Further reading
Di Giulio, Massimo (January 1, 2013). "Is Nanoarchaeum equitans a paleokaryote?". Journal of Biological Research.