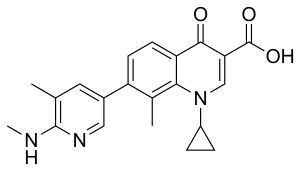
Ozenoxacin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | oz en ox' a sin |
| Trade names | Ozanex; Xepi |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Antibiotic (quinolone)[1] |
| Main uses | Impetigo[1] |
| Side effects | Uncommon[2] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Topical |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a618010 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H21N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 363.417 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Ozenoxacin, sold under the brand names Ozanex and Xepi, is an antibiotic used to treat impetigo.[1] This includes impetigo due to methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA).[2] It is applied to the skin as a cream.[2]
As little is absorbed through the skin; side effects are uncommon.[2] Side effects may include seborrheic dermatitis.[4] It is not expected to be harmful in pregnancy or breastfeeding.[1] It is a quinolone and works by blocking DNA gyrase A and topoisomerase IV.[1]
Ozenoxacin was approved for medical use in the United States and Canada in 2017.[1][5] In the United States a 30 gram tube of 1% cream costs about 340 USD as of 2021.[6] This amount in Canada costs about 53 CAD.[7]
Medical use
Ozenoxacin is used to treat impetigo caused by S. aureus and S. pyogenes .[2] It may also be used to get rid of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA).[2]
Dosage
It is used as a 1% cream applied twice daily for 5 days in those over the age of 2 months.[2]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "DailyMed - XEPI- ozenoxacin cream". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 11 November 2021. Retrieved 10 November 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Robertson, Dirk B.; Maibach, Howard I. (2020). "61. Dermatologic pharmacology". In Katzung, Bertram G.; Trevor, Anthony J. (eds.). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (15th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 1112. ISBN 978-1-260-45231-0. Archived from the original on 2021-10-10. Retrieved 2021-11-07.
- ↑ "Xepi- ozenoxacin cream". DailyMed. 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 17 October 2020. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ↑ "Ozenoxacin Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 15 October 2020. Retrieved 10 November 2021.
- ↑ Canada, Health (30 June 2017). "Notice: Prescription Drug List (PDL): Multiple Additions [2017-06-23]". www.canada.ca. Archived from the original on 8 July 2021. Retrieved 10 November 2021.
- ↑ "Xepi Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Retrieved 10 November 2021.
- ↑ "Pharmacoeconomic Review Report" (PDF). CADTH. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 October 2019. Retrieved 10 November 2021.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |