Partial anterior circulation infarct
| Partial anterior circulation infarct | |
|---|---|
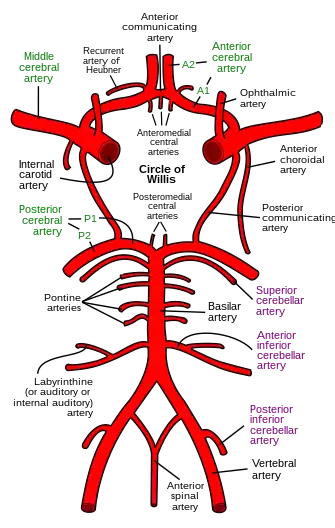 | |
| Diagram of the arterial circulation at the base of the brain (inferior view). Anterior circulation represented by top half of diagram (with circle of Willis). | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Partial anterior circulation infarct (PACI)[1] is a type of cerebral infarction affecting part of the anterior circulation supplying one side of the brain.
.png.webp)
a,b)Individual swith a left partial anterior circulation infarct caused by a left middle cerebral artery (MCA) stenosis
Partial anterior circulation stroke syndrome (PACS) refers to the symptoms of a patient who clinically appears to have had a partial anterior circulation infarct, but who has not yet had any diagnostic imaging (e.g. CT Scan) to confirm the diagnosis.
It is diagnosed by any one of the following
- 2 out of 3 features of
- Higher dysfunction
- Dysphasia
- Visuospatial disturbances
- Homonymous hemianopia
- Motor and Sensory Defects (>2/3 of face, arm, leg)
- Higher dysfunction
- Higher dysfunction alone
- Partial Motor or Sensory Defect
If all of the above symptoms are present, a Total Anterior Circulation Infarct is more likely.
References
- ↑ "Partial anterior cerebral circulation infarction (Concept Id: C0393955) - MedGen - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 27 September 2022. Retrieved 12 September 2022.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.