Popliteal artery
| Popliteal artery | |
|---|---|
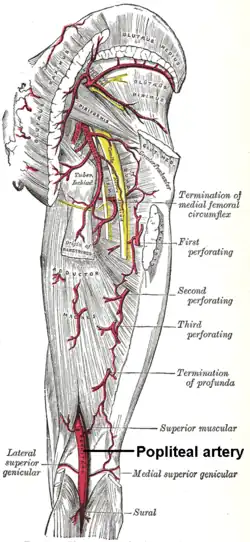 The arteries of the gluteal and posterior femoral regions. (Popliteal labeled at bottom center.) | |
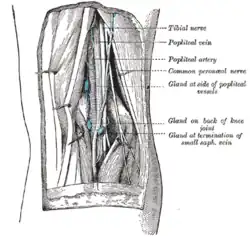 Lymph glands of popliteal fossa. | |
| Details | |
| Source | femoral artery |
| Branches | anterior tibial, posterior tibial artery, sural, superior genicular (medial, lateral), middle genicular, inferior genicular (medial, lateral) |
| Vein | popliteal vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria poplitea |
| MeSH | D011150 |
| TA98 | A12.2.16.033 |
| TA2 | 4699 |
| FMA | 77155 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.
The deepest (most anterior) structure in the fossa, the popliteal artery runs close to the joint capsule of the knee as it spans the intercondylar fossa. Five genicular branches of the popliteal artery supply the capsule and ligaments of the knee joint. The genicular arteries are the superior lateral, superior medial, middle, inferior lateral, and inferior medial genicular arteries. They participate in the formation of the periarticular genicular anastomosis, a network of vessels surrounding the knee that provides collateral circulation capable of maintaining blood supply to the leg during full knee flexion, which may kink the popliteal artery.[1]
Structure
The popliteal artery is the continuation of the femoral artery.[2] It exits the popliteal fossa under the fibrous arch of the soleus muscle.[2]
Relations
- Anteriorly: The popliteal surface of the femur, the knee joint, and the popliteus muscle.
- Posteriorly: The popliteal vein and the tibial nerve, fascia, and skin.
- Laterally: The biceps femoris and the lateral condyle of femur in upper part, and plantaris, lateral gastrocnemius in lower part.
- Medially: The semimembranosus and the medial condyle of femur in upper part, and tibial nerve, popliteal vein, medial head of gastrocnemius in lower part.
Branches
The branches of the popliteal artery are:
- anterior tibial artery.[2]
- posterior tibial artery.[2]
- sural artery.[2]
- medial superior genicular artery.[2]
- lateral superior genicular artery.[2]
- middle genicular artery.[2]
- lateral inferior genicular artery.[2]
- medial inferior genicular artery.[2]
Muscular branches of the popliteal artery supply the hamstring, gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles. The superior muscular branches of the popliteal artery have clinically important anastomoses with the terminal part of the deep femoral and gluteal arteries. The cutaneous branches arise either directly by the popliteal artery or indirectly by the muscular branches. Genicular branches are five in number, two superior, two inferior, and one middle. The middle genicular artery supplies the cruciate ligaments and the synovial membrane of knee joint.
Tibial-fibular trunk
The fibular artery typically arises from the posterior tibial artery.[3] Therefore, the posterior tibial artery proximal to the fibular artery origin is sometimes called the tibial-peroneal trunk or tibial-fibular trunk and it could be said that the popliteal artery bifurcates into the tibial-fibular trunk and anterior tibial artery.
Clinical significance
- Popliteal pulse: Because the popliteal artery is deep, it may be difficult to feel the popliteal pulse. Palpation of this pulse is commonly performed with the person in the prone position with the knee flexed to relax the popliteal fascia and hamstrings. The pulsations are best felt in the inferior part of the fossa where the popliteal artery is related to the tibia. Weakening or loss of the popliteal pulse is a sign of a femoral artery obstruction.
- Popliteal aneurysm and hemorrhage: A popliteal aneurysm (abnormal dilation of all or part of the popliteal artery) usually causes edema and pain in the popliteal fossa. A popliteal aneurysm may be distinguished from other masses by palpable pulsations (thrills) and abnormal arterial sounds (bruits) detectable with a stethoscope. Because the artery lies deep to the tibial nerve, an aneurysm may stretch the nerve or compress its blood supply (see vasa vasorum). Pain from such nerve compression is usually referred, in this case to the skin overlying the medial aspect of the calf, ankle or foot. Because the artery is closely applied to the popliteal surface of the femur and the joint capsule, fractures of the distal femur or dislocations of the knee may rupture the artery, resulting in hemorrhage. Furthermore, because of their proximity and confinement within the fossa, an injury of the artery and vein may result in an arteriovenous fistula (communication between an artery and a vein). Failure to recognize these occurrences and to act promptly may result in the loss of the leg and foot. If the femoral artery must be ligated, blood can bypass the occlusion through the genicular anastomosis and reach the popliteal artery distal to the ligation.[4]
- Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome
Additional images
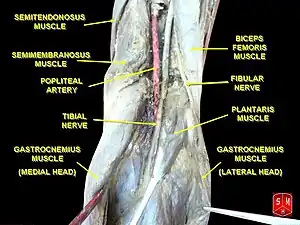 Popliteal artery
Popliteal artery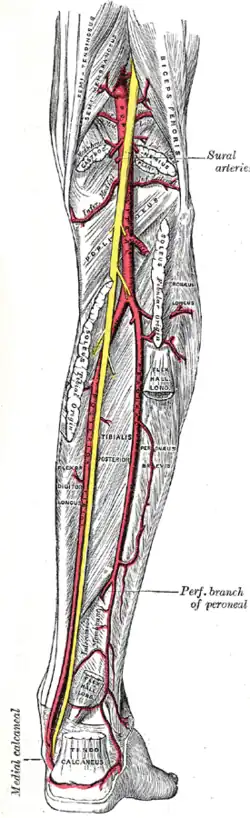 The popliteal, posterior tibial, and peroneal arteries.
The popliteal, posterior tibial, and peroneal arteries.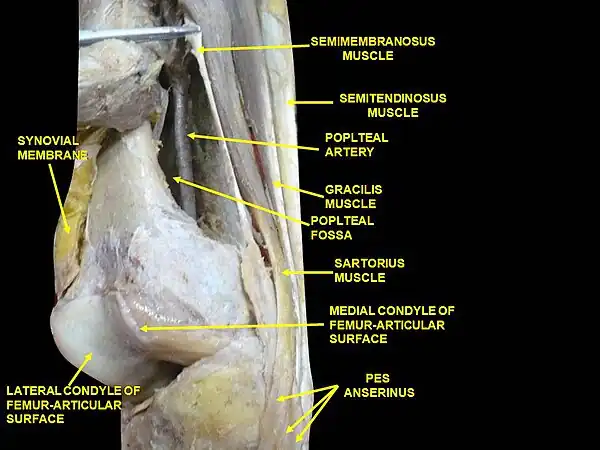 Muscles of thigh. Lateral view.
Muscles of thigh. Lateral view.
See also
References
- ↑ Moore K.L. and Dalley A.F. (2006), Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 5th Edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Toronto, page 636
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Masquelet, Alain-Charles; Sassu, Paolo (2009-01-01), Wei, Fu-Chan; Mardini, Samir (eds.), "CHAPTER 30 - Gastrocnemius flap", Flaps and Reconstructive Surgery, Edinburgh: W.B. Saunders, pp. 411–423, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7216-0519-7.00030-7, ISBN 978-0-7216-0519-7, retrieved 2021-02-20
- ↑ Day C, Orme R (2006). "Popliteal artery branching patterns -- an angiographic study". Clin Radiol. 61 (8): 696–9. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2006.03.014. PMID 16843754.
- ↑ Moore K.L. and Dalley A.F. (2006), Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 5th Edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Toronto, page 637
External links
- Anatomy figure: 12:04-10 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Arteries of the lower extremity shown in association with major landmarks."
- Image at umich.edu - pulse
Albert Sidney Johnston