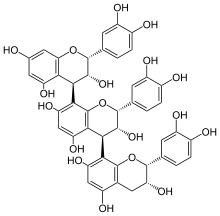
Procyanidin C1
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(12R,13R,14R,22R,23R,24S,32R,33R)-12,22,32-Tris(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-12H,22H,32H-[14,28:24,38-ter-1-benzopyran]-13,15,17,23,25,27,33,35,37-nonol | |
| Other names
Procyanidin C1 Procyanidol C1 Epicatechin-(4.beta.-->8)epicatechin-(4.beta.-->8)epicatechin Epicatechin-(4β→8)-epicatechin--(4β→8)-epicatechin | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C45H38O18 |
| Molar mass | 866.77 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Procyanidin C1 (PCC1) is a B type proanthocyanidin. It is an epicatechin trimer found in grape (Vitis vinifera).[1]
Natural occurrence and function
Procyanidin C1 can be isolated from grape seed extract.[2]
Chemical synthesis
The stereoselective synthesis of seven benzylated proanthocyanidin trimers (epicatechin-(4β-8)-epicatechin-(4β-8)-epicatechin trimer (procyanidin C1), catechin-(4α-8)-catechin-(4α-8)-catechin trimer (procyanidin C2), epicatechin-(4β-8)-epicatechin-(4β-8)-catechin trimer and epicatechin-(4β-8)-catechin-(4α-8)-epicatechin trimer derivatives) can be achieved with TMSOTf-catalyzed condensation reaction, in excellent yields. The structure of benzylated procyanidin C2 was confirmed by comparing the 1H NMR spectra of protected procyanidin C2 that was synthesized by two different condensation approaches. Finally, deprotection of (+)-catechin and (-)-epicatechin trimers derivatives gives four natural procyanidin trimers in good yields.[3]
Research
Procyanidin C1 has been found to extend life in mice and to make them fitter. It was also found to greatly increase the effectiveness of chemotherapy in mice in which human prostate tumor cells were implanted.[2][4]
See also
- Phenolic content in wine
External Links
- Carissa Wong: Grape seed chemical allows mice to live longer by killing aged cells. NewScientist, 6 December 2021
References
- ↑ Proanthocyanidin composition of red Vitis vinifera varieties from the Douro valley during ripening : Influence of cultivation altitude. Mateus Nuno, Marques Sara, Goncalves Ana C., Machado José M. and De Freitas Victor, American journal of enology and viticulture, 2001, vol. 52, no2, pp. 115-121, INIST:1129642
- 1 2 Carissa Wong (Dec 6, 2021). "Grape seed chemical allows mice to live longer by killing aged cells". New Scientist.
- ↑ Efficient Stereoselective Synthesis of Proanthocyanidin Trimers with TMSOTf-Catalyzed Intermolecular Condensation. Akiko Saito, Akira Tanaka, Makoto Ubukata and Noriyuki Nakajima, Synlett, 2004, volume 6, pages 1069-1073, doi:10.1055/s-2004-822905
- ↑ Xu, Qixia; et al. (Dec 6, 2021). "The flavonoid procyanidin C1 has senotherapeutic activity and increases lifespan in mice". Nature Metabolism. doi:10.1038/s42255-021-00491-8.