Pyrrocaine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
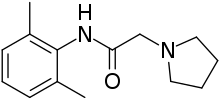
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)acetamide | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C14H20N2O |
| Molar mass | 232.327 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Pyrrocaine is a local anesthetic drug. The cogency of pyrrocaine is equivalent to lidocaine in blocking the motor nerve and sensory. Pyrrocaine was proven to be somewhat harmless compared to lidocaine. No signs of methemoglobinemia was found while observing. It was considered unsafe for acute porphyria treatment. No evidence is found that it is profitly used now.[1]
History
In the 1960s it was most of the time used as a nerve blocker dental anesthetic and dentists recommended it due to its fast commencement.[1]
Adverse effects
Pyrrocane has very similar side effects on blood pressure and heart rate compared to lidocaine.[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 "NCATS Inxight: Drugs". drugs.ncats.io. Retrieved 2018-08-07.
- ↑ Annals of Dentistry. New York Academy of Dentistry. 1983.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.