Scottish Ambulance Service
| Scottish Ambulance Service | |
|---|---|
| Seirbheis Ambaileans na h-Alba | |
 | |
 Area served by the Scottish Ambulance Service | |
| Type | Special health board |
| Established | 1 April 1995 |
| Headquarters | Gyle Square 1 South Gyle Crescent Edinburgh EH12 9EB |
| Region served | Scotland |
| Chair | Tom Steele |
| Chief executive | Pauline Howie |
| Staff | 5,291 (2019/20)[1] |
| Website | www |
The Scottish Ambulance Service (Scottish Gaelic: Seirbheis Ambaileans na h-Alba) is part of NHS Scotland, which serves all of Scotland's population.[2] The Scottish Ambulance Service is governed by a special health board and is funded directly by the Health and Social Care Directorates of the Scottish Government.[3]
It is the sole public emergency medical service covering Scotland's mainland and islands; providing a paramedic-led accident and emergency service to respond to 999 calls,[4] a patient transport service which provides transport to lower-acuity patients,[5] and provides for a wide variety of supporting roles including air medical services,[6][7] specialist operations including response to HAZCHEM or CBRN incidents[8] and specialist transport and retrieval.[9]
History
In 1948, the newly formed Scottish National Health Service (NHS) contracted two voluntary organisations, the St Andrew's Ambulance Association and the British Red Cross, to jointly provide a national ambulance provision for Scotland, known then as the St Andrew's and Red Cross Scottish Ambulance Service.[10]
After British Red Cross withdrew from the service in 1967, the service was renamed the St Andrew's Scottish Ambulance Service. In 1974, with the reorganisation of the Scottish health services, ambulance provision in Scotland was taken over by the Scottish NHS, with the organisational title being shortened to the current Scottish Ambulance Service.[10]
St. Andrew's First Aid, the trading name of St. Andrew's Ambulance Association, continues as a voluntary organisation and provides first aid training and provision in a private capacity.[11]
The organisation was established as a NHS trust on 1 April 1995 when it legally became known as the Scottish Ambulance Service National Health Service Trust.[12] The trust was dissolved on 1 April 1999 and at the same time constituted as a special health board known as the Scottish Ambulance Service Board.[13][14]
Structure
The Scottish Ambulance Service now continues in its current form as one of the largest emergency medical providers in the UK, employing more than 5,000 staff in a variety of roles and responding to 740,631 emergency incidents in 2015/2016 alone.[15]
The service, like the rest of NHS Scotland is free at point of access and is widely utilised by the public and healthcare professionals alike. Employing almost 1,300 paramedic staff, and a further 1,200 technicians, the accident and emergency service is accessed through the public 999 system.
Ambulance responses are evolving in Scotland and are now prioritised on patient requirement; a traditional, double-crewed ambulance, single response car or a paramedic practitioner may attend emergencies of differing dispositions. The service also utilises a number of responders in conjunction with BASICS Scotland and The Sandpiper Trust. These responders are doctors, nurses or paramedics who volunteer their time to respond for the ambulance service and provide assistance to sick or injured individuals. Equipment is provided to these responders by both the ambulance service and BASICS Scotland.
The Scottish Ambulance Service also maintains three command and control centres in Scotland, which facilitate handling of 999 calls and dispatch of ambulances; a further 350-400 staff employed as call handlers and dispatchers fulfil this role[15] across three locations - Edinburgh, Glasgow and Inverness. These three centres (which, through use of software operate as one integrated unit) have been in use since 2004 and handle over 800,000 calls per year. The AMPDS system is used for call prioritisation, and provides post-dispatch instructions to callers allowing for medical advice to be given over the phone, prior to ambulance arrival.[16] Clinical staff are present to provide clinical oversight and tertiary triage. Co-located with the Ambulance Control Centres (or ACC) are patient transport booking and control services, which handle approximately 1 million patient journeys per year.[16]
Fleet, equipment & uniform

The Scottish Ambulance Service maintains a varied fleet of around 1,500 vehicles.[17]
Emergency response vehicles include ambulances,[17] single-response vehicles such as cars and small vans for paramedics. There are also patient-transport ambulances which come in the form of adapted minibuses, lorries and support vehicles for major incidents and events, and specialist vehicles such as 4x4s and tracked vehicles for difficult access.[18]
The geography of Scotland, which includes urban centres such as Edinburgh and Glasgow, areas of relatively low-population such as Grampian and the Scottish Highlands, and the island communities mean that fleet provision has to be flexible and include different approaches to vehicle construction. In the past, 4x4-build ambulances on van chassis have been used in more rural areas, and traditional van-conversions in more urban.[17]
When a large fleet upgrade project was commissioned in 2016, the business case was made to move to a solely box-body on chassis build, to provide some flexibility and more resilient parts procurement. Most of these replacement ambulances have been based on either Mercedes or Volkswagen chassis, with a mixture of automatic or manual transmissions.[17]
The equipment used on board Scottish Ambulance Service vehicles broadly falls in line with NHS Scotland and allows for interoperability in most cases. Equipment is standardised nationally and replaced at regular service intervals; for example, high-cost items such as defibrillators are costed and changed every seven years according to clinical need.[19]
The uniform falls in line with the NHS Scotland National Uniform standard,[20] which is in keeping with the uniform standard described by the National Ambulance Uniform Procurement group in 2016.[21] Amongst cost and comfort considerations, all Scottish Ambulance Service Staff now wear the national uniform which comprises a dark green trouser / shirt combination.[22]
Personal protective equipment (boots, helmet and protective jackets) are issued to all staff and denote rank / clinical rank by way of epaulette and helmet markings.[22]
Organisation
.jpg.webp)
The national headquarters is located at Gyle Square, South Gyle, on the west side of Edinburgh.[23]
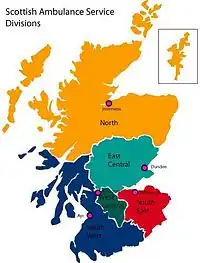
There are five divisions within the service, namely:
| Division | Covering | Area | Divisional HQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| North | Highlands, Western Isles, Grampian, Orkney, Shetland[24] | 15,607 square miles (40,420 km2) | Inverness |
| East Central | Fife, Forth Valley, Tayside[25] | 4,421 square miles (11,450 km2) | Dundee |
| West Central | Greater Glasgow, Lanarkshire[26] | 1,054 square miles (2,730 km2) | Motherwell |
| South East | Edinburgh, Lothian and Borders[27] | 2,457 square miles (6,360 km2) | Edinburgh |
| South West | Argyll, Argyll islands, Clyde islands, Ayrshire, Dumfries and Galloway[28] | 6,670 square miles (17,300 km2) | Ayr |

Patient transport
The Patient Transport Service carries over 1.3 million patients every year.[29] This service is provided to patients who are physically or medically unfit to travel to hospital out-patient appointments by any other means so that they can still make their appointments. The service also handles non-emergency admissions, discharges, transport of palliative care patients and a variety of other specialised roles.[30]
Patient Transport Vehicles come in a variety of forms and are staffed by Ambulance Care Assistants, who work either double or single crewed. They are trained to look after patients during the journey, and to provide basic emergency care.[31]
Air operations

Key: Ch=Charity AS=Ambulance Service

.jpg.webp)
The service has the only government-funded air ambulance service in the UK,[32] operated under contract by Gama Aviation. The fleet consists of two Airbus H145 helicopters[33] and two Beechcraft B200C King Air fixed-wing aircraft, which provide emergency response and transfers of patients to and from remote areas of Scotland. The two previous H145 helicopters were operated under sub-contract by Babcock Mission Critical Services Onshore until May 2020.[34] In 2015/16, the air ambulance crews flew 3,849 missions. One helicopter and one King Air are based at a Gama Aviation facility at Glasgow Airport. The other operating bases are Inverness Airport (helicopter) and Aberdeen Airport (King Air).[35]
The aircraft based in Glasgow are regularly used by the Emergency Medical Retrieval Service (EMRS).[36] The air ambulance service was occasionally featured as part of the Channel 5 television documentary series Highland Emergency.
Charity-funded air ambulance
In late 2012, a charity, Scotland's Charity Air Ambulance (SCAA), was founded to provide a further air ambulance, based at Perth Airport to work alongside the state-funded aircraft.[37] SCAA commenced operations in May 2013 with a MBB Bo 105 helicopter. Since November 2015, SCAA has operated a Eurocopter EC135.[38] The EC135 was previously operated by the state-funded service, until they replaced the fleet with H145 aircraft. The helicopter is crewed by Scottish Ambulance Service paramedics, tasking is from the SAS ambulance control centre at Cardonald.
In April 2018, it was announced by the charity that a drive was underway to raise funds to secure a second helicopter.[39] This aircraft is now operational at Aberdeen Airport.
Special Operations Response Team (SORT)
The SORT service is similar to the Hazardous Area Response Team in other parts of the United Kingdom.
In 2010, the service established three teams of specialist accident & emergency ambulance personnel who were given specialist training.[40] This £4.3 million initiative was to provide additional preparedness to be able to respond to large-scale hazardous incidents, such as those that might involve chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear material.[41] The work was in concert with the UK government.[41]
As of 2016 there are five SORT teams, three full-time and two on-call. These teams provide a specialist response to major incidents, and provide paramedic care in hostile environments. The team provides capability in arenas such as water rescue, safe working at height, search and rescue including the use of breathing apparatus, and confined space working. The SORT teams also provide a full-time emergency decontamination and inner-cordon capability.
ScotSTAR
With the remote towns and villages in Scotland often being hours away from advanced medical treatment, Scottish Specialist Transport and Retrieval (ScotSTAR) was setup incorporating paediatric and neo-natal retrieval and transfer teams and EMRS. The ScotSTAR service was set up on 1 April 2014 and transported 2,654 patients 2014/2015. The service uses multiple vehicles, either owned by the ambulance service or other organisations: specialist ambulances and cars, five air ambulances and HM Coastguard helicopters. The service is based in Glasgow.
EMRS was started in 2004 by 10 emergency medical consultants from Glasgow and Paisley. Providing aeromedical cover to six hospitals within Argyll and Bute. The ten consultants only had £40,000 worth of funding for medical equipment. In its first year the service transported 40 patients. In years to follow the clinical crew began to gather evidence for the lifesaving and cost effectiveness of the service. In 2010, the service was opened up to the whole of the country, thanks to backing by permanent funding. The service is staffed by 27 part-time consultants, two full-time registrars and seven critical care practitioners.
Training academy
The service has its own dedicated training academy within the campus of Glasgow Caledonian University, which opened in June 2011.[42] The facility has purpose built classrooms, lecture theatres, syndicate rooms and a clinical simulation area that recreates a 16-bed hospital ward and Accident & Emergency department allowing realistic interaction with other trainee healthcare professionals.[43]
From 1996 until to April 2011, the service used its own dedicated training college located at Barony Castle in Eddleston near Peebles. Set in 25 acres (100,000 m2) of formal gardens and woodlands, Barony was a residential training and conference centre with 78 bedrooms that allowed the service to carry out all its training in house. Between 1978 and 1996 it used the former Redlands women's and children's hospital in Glasgow's west end and prior to that the training school was based at Gartloch Hospital.
Facts and figures
In year ended 31 March 2020, the service:[44]
- Responded to 542,213 accident and emergency incidents.
- Carried out 606,015 non-emergency patient journeys.
- Flew 3,732 air ambulance missions.
See also
Other Scottish emergency and non-emergency services:
- NHS 24
- Police Scotland
- Scottish Fire and Rescue Service
References
- ↑ "Staff Composition" (PDF). Annual Report and Accounts for Year Ended 31 March 2020. Scottish Ambulance Service: 38.
- ↑ "Scottish Ambulance Service - The Service". www.scottishambulance.com. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ↑ "Collective Assessment of NHS Scotland Special Health Boards". Scottish Ambulance Service.
- ↑ "Scottish Ambulance Service - Emergency response". www.scottishambulance.com. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ↑ "Scottish Ambulance Service - Patient Transport Service". www.scottishambulance.com. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ↑ "Scottish Ambulance Service - Air Ambulance". www.scottishambulance.com. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ↑ "Scottish Ambulance Service". www.associationofairambulances.co.uk. Retrieved 12 August 2017.
- ↑ "Scottish Ambulance Service - Dealing with Major Incidents". www.scottishambulance.com. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ↑ "Scottish Ambulance Service - Specialist Transport and Retrieval". www.scottishambulance.com. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- 1 2 "Our History - St Andrews First Aid". St Andrews First Aid. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ↑ "First Aid Delivered With Confidence - St Andrews First Aid". St Andrews First Aid. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ↑ "The Scottish Ambulance Service National Health Service Trust (Establishment) Order 1994". legislation.gov.uk. The National Archives. 25 November 1994. Retrieved 16 September 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ "The Scottish Ambulance Service National Health Service Trust (Dissolution) Order 1999". legislation.gov.uk. The National Archives. 4 March 1999. Retrieved 16 September 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ "The Scottish Ambulance Service Board Order 1999". legislation.gov.uk. The National Archives. 4 March 1999. Retrieved 16 September 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - 1 2 "SAS Annual Report 2015/2016" (PDF).
- 1 2 "Scottish Ambulance Service - Behind the Headlines - Ambulance Control Centres". www.scottishambulance.com. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 "Fleet Replacement Business Case 2016/2017" (PDF).
- ↑ "FOI Scottish Ambulance Service Vehicle List". April 2012.
- ↑ "SAS Corporate Asset Management Strategy".
- ↑ "NHS National Uniforms". www.gov.scot. Scottish Government. 3 July 2012. Retrieved 11 August 2017.
- ↑ "New national ambulance uniform could save the NHS £3.4m - Emergency Services Times". Emergency Services Times. 13 January 2017. Retrieved 11 August 2017.
- 1 2 "FOI Response - Scottish Ambulance Service Uniform". 31 October 2016.
- ↑ "The Scottish Ambulance Service". Healthcare Improvement Scotland. 16 September 2021. Retrieved 16 September 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ Locations - North scottishambulance.com, accessed 9 May 2009
- ↑ Locations - East Central scottishambulance.com, accessed 11 February 2009
- ↑ Locations - West Central scottishambulance.com, accessed 11 February 2009
- ↑ Locations - South East scottishambulance.com, accessed 11 February 2009
- ↑ Locations - South West scottishambulance.com, accessed 11 February 2009
- ↑ "Scottish Ambulance Service". Scottish Ambulance Service. Retrieved 4 November 2017.
- ↑ "Scottish Ambulance Service". Scottish Ambulance Service. Retrieved 4 November 2017.
- ↑ "Scottish Ambulance Service" (PDF). Scottish Ambulance Service. Retrieved 4 November 2017.
- ↑ "What we do: Air ambulance". Scottish Ambulance Service. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ↑ "'Technical difficulties' put stop to air ambulance's island tour". STV News. 3 July 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ↑ Stan Arnaud (2 June 2020). "Gama takes on Scottish air ambulance missions". The Press and Journal.
- ↑ "What we do: Aircraft". Scottish Ambulance Service. Retrieved 2 June 2016.
- ↑ "Emergency Medical Retrieval Service". Retrieved 9 April 2019.
- ↑ "Perth base for Scotland's charity air ambulance". BBC News. 27 November 2012. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ↑ "New helicopter unveiled for Scotland's Charity Air Ambulance". STV News. 30 October 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ↑ "Second charity air ambulance helicopter planned for Scotland". SCAA. 24 April 2018. Retrieved 23 May 2018.
- ↑ "Ambulance disaster teams created". BBC News. 11 August 2010.
- 1 2 Stephen, Phyllis (12 August 2010). "Scottish Ambulance Service – major incident response boosted". theedinburghreporter.co.uk. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- ↑ "Nicola Sturgeon unveils new Scottish Ambulance Academy at Glasgow Caledonian University". Daily Record. 27 June 2011. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ↑ "New Academy is a major milestone for Ambulance professional development" (Press release). Scottish Ambulance Service. 8 February 2011. Archived from the original on 2 February 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ↑ "Scottish Ambulance Service Annual report 2020" (PDF). Scottish Ambulance Service. Retrieved 9 April 2021.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Scottish Ambulance Service. |