Stylopharyngeus muscle
| Stylopharyngeus muscle | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Styloid process (temporal) |
| Insertion | thyroid cartilage (larynx) |
| Nerve | glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) |
| Actions | elevate the larynx, elevate the pharynx, swallowing |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus stylopharyngeus |
| TA98 | A05.3.01.114 |
| TA2 | 2190 |
| FMA | 46664 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The stylopharyngeus is a muscle in the head that stretches between the temporal styloid process and the pharynx.
Structure
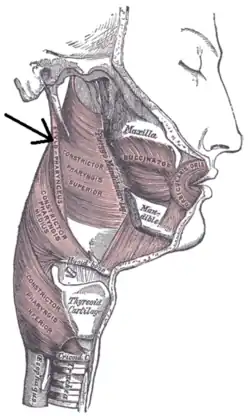
The stylopharyngeus is a long, slender muscle, cylindrical above, flattened below. It arises from the medial side of the base of the temporal styloid process, passes downward along the side of the pharynx between the superior pharyngeal constrictor and the middle pharyngeal constrictor, and spreads out beneath the mucous membrane.
Some of its fibers are lost in the constrictor muscles while others, joining the palatopharyngeus muscle, are inserted into the posterior border of the thyroid cartilage.
The glossopharyngeal nerve runs on the lateral side of this muscle, and crosses over it to reach the tongue.
Nerve supply
The stylopharyngeus is the only muscle in the pharynx innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) via branchial motor neurons with their cell bodies in the rostral part of the nucleus ambiguus.
Development
Embryological origin is the third pharyngeal arch.
Function
The stylopharyngeus:
See also
Additional images
 Stylopharyngeus muscle.
Stylopharyngeus muscle.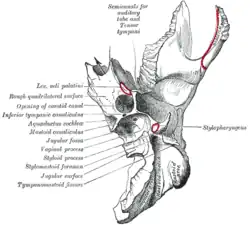 Left temporal bone. Inferior surface.
Left temporal bone. Inferior surface.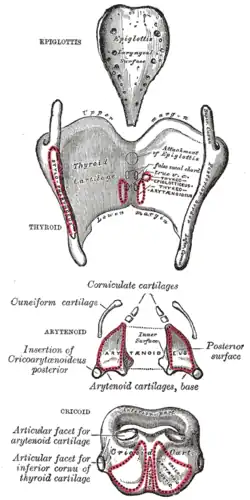 The cartilages of the larynx. Posterior view.
The cartilages of the larynx. Posterior view.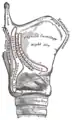 Side view of the larynx, showing muscular attachments.
Side view of the larynx, showing muscular attachments.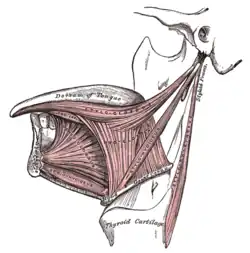 Extrinsic muscles of the tongue. Left side.
Extrinsic muscles of the tongue. Left side.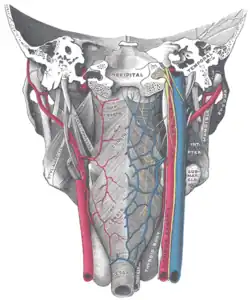 Muscles of the pharynx, viewed from behind, together with the associated vessels and nerves.
Muscles of the pharynx, viewed from behind, together with the associated vessels and nerves. Stylopharyngeus muscle
Stylopharyngeus muscle Stylopharyngeus muscle
Stylopharyngeus muscle Stylopharyngeus muscle
Stylopharyngeus muscle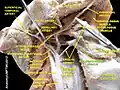 Stylopharyngeus muscle
Stylopharyngeus muscle
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1143 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1143 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)