Sunscreen
| Sunscreen | |
|---|---|
 Sunscreen on back under normal and UV light | |
| Other names | Sun screen, sunblock, sunburn cream, sun cream, block out[1] |
Sunscreen, also known as sunblock or suntan lotion, is a photoprotective topical product for the skin that absorbs or reflects some of the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation and thus helps protect against sunburn and most importantly prevent skin cancer. Sunscreens come as lotions, sprays, gels, foams (such as an expanded foam lotion or whipped lotion), sticks, powders and other topical products. Sunscreens are common supplements to clothing, particularly sunglasses, sunhats and special sun protective clothing, and other forms of photoprotection (e.g. umbrellas, etc.).
The first sunscreen in the world was invented in Australia, by chemist H.A. Milton Blake, in 1932[2] formulating with the UV filter 'salol (Phenyl salicylate)' at a concentration of '10%'[3] Its protection was verified by the University of Adelaide[4] and it was also produced commercially by Blake's company, Hamilton Laboratories.[5] Despite sunscreen being relatively new, sun protection practices have been observed since at least the ancient Egyptians "who used ingredients such as rice bran, jasmine, and lupine"[6] to provide sun protection.
Often, sunscreens are classified into inorganic (mistakenly called ‘physical’) sunscreens (i.e., zinc oxide and titanium dioxide) and organic (also, mistakenly referred to as ‘chemical’) sunscreens.[7]
Despite popular belief, both types of sunscreens work mainly by absorption of UV light.[8] Newer studies have found that inorganic sunscreens may absorb up to 95% of UV light, while its deflecting ability might be up to only 5% (less than SPF 2).[7][8][9]
Medical organizations such as the American Cancer Society recommend the use of sunscreen because it aids in the prevention of squamous cell carcinomas.[10] The routine use of sunscreens may also reduce the risk of melanoma.[11] However, many sunscreens do not block Ultraviolet A (UVA) radiation, yet protection from UVA is important for the prevention of skin cancer.[12]
To provide a better indication of their ability to protect against skin cancer and other diseases associated with UVA radiation (such as phytophotodermatitis[13]), the use of broad-spectrum (UVA/UVB) sunscreens has been recommended.[14]
In the United States, sunscreens are required to remain effective at original strength for at least three years. Some sunscreens include an expiration date—a date indicating when they may become less effective.[15]
Diligent use of sunscreen can also help to slow or temporarily prevent the development of wrinkles, dark spots and sagging skin.
Health effects
Benefits
Sunscreen use can help prevent melanoma[16][17][18] and squamous cell carcinoma, two types of skin cancer.[19] There is little evidence that it is effective in preventing basal cell carcinoma.[20]
A 2013 study concluded that the diligent, everyday application of sunscreen could slow or temporarily prevent the development of wrinkles and sagging skin.[21] The study involved 900 white people in Australia and required some of them to apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen every day for four and a half years. It found that people who did so had noticeably more resilient and smoother skin than those assigned to continue their usual practices.[21] A study on 32 subjects showed that daily use of sunscreen (SPF 30) reversed photoaging of the skin within 12 weeks and the amelioration continued until the end of the investigation period of one year.[22]

Minimizing UV damage is especially important for children and fair-skinned individuals and those who have sun sensitivity for medical reasons.[23]
Potential risks
In 2009, the Therapeutic Goods Administration of Australia updated a review of sunscreen safety studies and concluded: "The potential for titanium dioxide (TiO2) and zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles in sunscreens to cause adverse effects depend primarily upon the ability of the nanoparticles to reach viable skin cells. To date, the current weight of evidence suggests that TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles do not reach viable skin cells."[24] Sunscreen ingredients typically undergo extensive review by government regulators in multiple countries, and ingredients that present significant safety concerns (such as PABA) tend to be withdrawn from the consumer market.[25]
There is a risk of an allergic reaction to sunscreen for some individuals, as "Typical allergic contact dermatitis may occur in individuals allergic to any of the ingredients that are found in sunscreen products or cosmetic preparations that have a sunscreen component. The rash can occur anywhere on the body where the substance has been applied and sometimes may spread to unexpected sites."[26]
Vitamin D production
There are some concerns about potential vitamin D deficiency arising from prolonged use of sunscreen.[27][28] The typical use of sunscreen does not usually result in vitamin D deficiency; however, extensive usage may.[29] Sunscreen prevents ultraviolet light from reaching the skin, and even moderate protection can substantially reduce vitamin D synthesis.[30][31] However, adequate amounts of vitamin D can obtained via diet or supplements.[32] Vitamin D overdose is impossible from UV exposure due to an equilibrium the skin reaches in which vitamin D degrades as quickly as it is created.[33][34][35]
Studies showed that sunscreen with a high UVA protection factor enabled significantly higher vitamin D synthesis than a low UVA protection factor sunscreen, likely because it allows more UVB transmission.[36][37]
Measurements of protection
Sun protection factor and labeling

The sun protection factor (SPF rating, introduced in 1974) is a measure of the fraction of sunburn-producing UV rays that reach the skin. For example, "SPF 15" means that 1⁄15 of the burning radiation will reach the skin, assuming sunscreen is applied evenly at a thick dosage of 2 milligrams per square centimeter[38] (mg/cm2). It is important to note that sunscreens with higher SPF do not last or remain effective on the skin any longer than lower SPF and must be continually reapplied as directed, usually every two hours.[39]
The SPF is an imperfect measure of skin damage because invisible damage and skin aging are also caused by ultraviolet type A (UVA, wavelengths 315–400 or 320–400 nm), which does not primarily cause reddening or pain. Conventional sunscreen blocks very little UVA radiation relative to the nominal SPF; broad-spectrum sunscreens are designed to protect against both UVB and UVA.[40][41][42] According to a 2004 study, UVA also causes DNA damage to cells deep within the skin, increasing the risk of malignant melanomas.[43] Even some products labeled "broad-spectrum UVA/UVB protection" have not always provided good protection against UVA rays.[44] Titanium dioxide probably gives good protection, but does not completely cover the UVA spectrum, as early 2000s research suggests that zinc oxide is superior to titanium dioxide at wavelengths 340–380 nm.[45]
Owing to consumer confusion over the real degree and duration of protection offered, labeling restrictions are enforced in several countries. In the EU, sunscreen labels can only go up to SPF 50+ (initially listed as 30 but soon revised to 50).[46] Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration increased the upper limit to 50+ in 2012.[47][48] In its 2007 and 2011 draft rules, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) proposed a maximum SPF label of 50, to limit unrealistic claims.[49][14][50] (As of February 2017, the FDA has not adopted the SPF 50 limit.[51]) Others have proposed restricting the active ingredients to an SPF of no more than 50, due to lack of evidence that higher dosages provide more meaningful protection.[52] Different sunscreen ingredients have different effectiveness against UVA and UVB.[53]
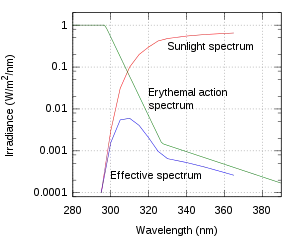
The SPF can be measured by applying sunscreen to the skin of a volunteer and measuring how long it takes before sunburn occurs when exposed to an artificial sunlight source. In the US, such an in vivo test is required by the FDA. It can also be measured in vitro with the help of a specially designed spectrometer. In this case, the actual transmittance of the sunscreen is measured, along with the degradation of the product due to being exposed to sunlight. In this case, the transmittance of the sunscreen must be measured over all wavelengths in sunlight's UVB–UVA range (290–400 nm), along with a table of how effective various wavelengths are in causing sunburn (the erythemal action spectrum) and the standard intensity spectrum of sunlight (see the figure). Such in vitro measurements agree very well with in vivo measurements.
Numerous methods have been devised for evaluation of UVA and UVB protection. The most-reliable spectrophotochemical methods eliminate the subjective nature of grading erythema.[54]
The ultraviolet protection factor (UPF) is a similar scale developed for rating fabrics for sun protective clothing. According to recent testing by Consumer Reports, UPF ~30+ is typical for protective fabrics, while UPF ~20 is typical for standard summer fabrics.[55]
Mathematically, the SPF (or the UPF) is calculated from measured data as:
where is the solar irradiance spectrum, the erythemal action spectrum, and the monochromatic protection factor, all functions of the wavelength . The MPF is roughly the inverse of the transmittance at a given wavelength.
The above means that the SPF is not simply the inverse of the transmittance in the UVB region. If that were true, then applying two layers of SPF 5 sunscreen would always be equivalent to SPF 25 (5 times 5). The actual combined SPF may be lower than the square of the single-layer SPF.[56]
UVA protection
Persistent pigment darkening
The persistent pigment darkening (PPD) method is a method of measuring UVA protection, similar to the SPF method of measuring sunburn protection. Originally developed in Japan, it is the preferred method used by manufacturers such as L'Oréal.
Instead of measuring erythema, the PPD method uses UVA radiation to cause a persistent darkening or tanning of the skin. Theoretically, a sunscreen with a PPD rating of 10 should allow a person 10 times as much UVA exposure as would be without protection. The PPD method is an in vivo test like SPF. In addition, Colipa has introduced a method that, it is claimed, can measure this in vitro and provide parity with the PPD method.[57]
SPF equivalence


As part of revised guidelines for sunscreens in the EU, there is a requirement to provide the consumer with a minimum level of UVA protection in relation to the SPF. This should be a "UVA PF" of at least 1/3 of the SPF to carry the UVA seal.[58]
A set of final US FDA rules effective from summer 2012 defines the phrase "broad spectrum" as providing UVA protection proportional to the UVB protection, using a standardized testing method.[14]
Star rating system
In the UK and Ireland, the Boots star rating system is a proprietary in vitro method used to describe the ratio of UVA to UVB protection offered by sunscreen creams and sprays. Based on original work by Brian Diffey at Newcastle University, the Boots Company in Nottingham, UK, developed a method that has been widely adopted by companies marketing these products in the UK.
One-star products provide the lowest ratio of UVA protection, five-star products the highest. The method was recently revised in light of the Colipa UVA PF test and the revised EU recommendations regarding UVA PF. The method still uses a spectrophotometer to measure absorption of UVA versus UVB; the difference stems from a requirement to pre-irradiate samples (where this was not previously required) to give a better indication of UVA protection and photostability when the product is used. With the current methodology, the lowest rating is three stars, the highest being five stars.
In August 2007, the FDA put out for consultation the proposal that a version of this protocol be used to inform users of American product of the protection that it gives against UVA;[49] but this was not adopted, for fear it would be too confusing.[52]
PA system
Asian brands, particularly Japanese ones, tend to use The Protection Grade of UVA (PA) system to measure the UVA protection that a sunscreen provides. The PA system is based on the PPD reaction and is now widely adopted on the labels of sunscreens. According to the Japan Cosmetic Industry Association, PA+ corresponds to a UVA protection factor between two and four, PA++ between four and eight, and PA+++ more than eight. This system was revised in 2013 to include PA++++ which corresponds to a PPD rating of sixteen or above.
Sunblock
Sunblock typically refers to opaque sunscreen that is effective at blocking both UVA and UVB rays and uses a heavy carrier oil to resist being washed off. Titanium dioxide and zinc oxide are two minerals that are used in sunblock.[59]
The use of the word "sunblock" in the marketing of sunscreens is controversial. Since 2013, the FDA has banned such use because it can lead consumers to overestimate the effectiveness of products so labeled.[14] Nonetheless, many consumers use the words sunblock and sunscreen synonymously.
For total protection against damage from the sun, the skin needs to be protected from UVA, UVB, and also IRA (infrared-A light).[60] Infrared radiation accounts for roughly 40% of solar energy at sea level.[61] There is continuing debate within the dermatology community over the impact of sun-sourced IRA: Some sources indicate that early morning IRA exposure may be protective against further sun exposure by increasing cell proliferation and initiating anti-inflammatory cascades; these effects are not observed for artificial sources of intense IRA.[61]
Active ingredients
In addition to moisturizers and other inactive ingredients, sunscreens contain one or more of the following active ingredients, which are either organic or mineral in nature:
- Organic chemical compounds that absorb ultraviolet light.
- Inorganic particulates that reflect, scatter, and absorb UV light (such as titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, or a combination of both).[59]
- Organic particulates that mostly absorb UV light like organic chemical compounds, but contain multiple chromophores that reflect and scatter a fraction of light like inorganic particulates. An example is Tinosorb M. The mode of action is about 90% by absorption and 10% by scattering.
The principal active ingredients in sunscreens are usually aromatic molecules conjugated with carbonyl groups. This general structure allows the molecule to absorb high-energy ultraviolet rays and release the energy as lower-energy rays, thereby preventing the skin-damaging ultraviolet rays from reaching the skin. So, upon exposure to UV light, most of the ingredients (with the notable exception of avobenzone) do not undergo significant chemical change, allowing these ingredients to retain the UV-absorbing potency without significant photodegradation.[62] A chemical stabilizer is included in some sunscreens containing avobenzone to slow its breakdown; examples include formulations containing. The stability of avobenzone can also be improved by bemotrizinol,[63] octocrylene[64] and various other photostabilisers. Most organic compounds in sunscreens slowly degrade and become less effective over the course of several years even if stored properly, resulting in the expiration dates calculated for the product.[65]
Sunscreening agents are used in some hair care products such as shampoos, conditioners and styling agents to protect against protein degradation and color loss. Currently, benzophenone-4 and ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate are the two sunscreens most commonly used in hair products. The common sunscreens used on skin are rarely used for hair products due to their texture and weight effects.
The following are the FDA allowable active ingredients in sunscreens:
| UV-filter | Other names | Maximum concentration | Permitted in these countries | Results of safety testing | UVA | UVB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Aminobenzoic acid | PABA | 15% (EU: banned from sale to consumers from 8 October 2009) | USA, AUS | Protects against skin tumors in mice.[66][67][68] Shown to increase DNA defects, however, and is now less commonly used. | X | |
| Padimate O | OD-PABA, octyldimethyl-PABA, σ-PABA | 8% (EU, USA, AUS) 10% (JP)
(Not currently supported in EU and may be delisted) |
EU, USA, AUS, JP | X | ||
| Phenylbenzimidazole sulfonic acid | Ensulizole, Eusolex 232, PBSA, Parsol HS | 4% (US, AUS) 8% (EU) 3% (JP) | EU, USA, AUS, JP | Genotoxic in bacteria[69] | X | |
| Cinoxate | 2-Ethoxyethyl p-methoxycinnamate | 3% (US) 6% (AUS) | USA, AUS | X | X | |
| Dioxybenzone | Benzophenone-8 | 3% | USA, AUS | X | X | |
| Oxybenzone | Benzophenone-3, Eusolex 4360, Escalol 567 | 6% (US) 10% (AUS, EU) | EU, USA, AUS | X | X | |
| Homosalate | Homomethyl salicylate, HMS | 10% (EU) 15% (US, AUS) | EU, USA, AUS | X | ||
| Menthyl anthranilate | Meradimate | 5% | USA, AUS | X | ||
| Octocrylene | Eusolex OCR, Parsol 340, 2-Cyano-3,3-diphenyl acrylic acid, 2-ethylhexylester | 10% | EU, USA, AUS | Increases reactive oxygen species (ROS)[70] | X | X |
| Octyl methoxycinnamate | Octinoxate, EMC, OMC, Ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, Escalol 557, 2-Ethylhexyl-paramethoxycinnamate, Parsol MCX | 7.5% (US) 10% (EU, AUS) 20% (JP) | EU, USA, AUS, JP | Banned in Hawaii since 2021 - harmful to coral[71] | X | |
| Octyl salicylate | Octisalate, 2-Ethylhexyl salicylate, Escalol 587, | 5% (EU, USA, AUS) 10% (JP) | EU, USA, AUS, JP | X | ||
| Sulisobenzone | 2-Hydroxy-4-Methoxybenzophenone-5-sulfonic acid, 3-Benzoyl-4-hydroxy-6-methoxybenzenesulfonic acid, Benzophenone-4, Escalol 577 | 5% (EU) 10% (US, AUS, JP) | EU, USA, AUS, JP | X | X | |
| Trolamine salicylate | Triethanolamine salicylate | 12% | USA, AUS | X | ||
| Avobenzone | 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-(4-tert-butyl phenyl)propane-1,3-dione, Butyl methoxy dibenzoylmethane, BMDBM, Parsol 1789, Eusolex 9020 |
3% (US) 5% (EU, AUS) | EU, USA, AUS | X | ||
| Ecamsule | Mexoryl SX, Terephthalylidene Dicamphor Sulfonic Acid | 10% | EU, AUS (US: approved in certain formulations up to 3% via New Drug Application (NDA) Route) | Protects against skin tumors in mice[72][73][74] | X | |
| Titanium dioxide | CI77891, TiO₂ | 25% (US) No limit (JP) | EU, USA, AUS, JP | X | ||
| Zinc oxide | CI77947, ZnO | 25% (US) No limit (AUS, JP) | EU, USA, AUS, JP | Protects against skin tumors in mice[72] | X | X |
Zinc oxide was approved as a UV filter by the EU in 2016.[75]
Other ingredients approved within the EU[76] and other parts of the world,[77] that have not been included in the current FDA Monograph:
| UV-filter | Other names | Maximum concentration | Permitted in |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4-Methylbenzylidene camphor | Enzacamene, Parsol 5000, Eusolex 6300, MBC | 4%* | EU, AUS |
| Parsol Max, Tinosorb M | Bisoctrizole, Methylene Bis-Benzotriazolyl Tetramethylbutylphenol, MBBT | 10%* | EU, AUS, JP |
| Parsol Shield, Tinosorb S | Bis-ethylhexyloxyphenol methoxyphenol triazine, Bemotrizinol, BEMT, anisotriazine | 10% (EU, AUS) 3% (JP)* | EU, AUS, JP |
| Tinosorb A2B | Tris-Biphenyl Triazine | 10% | EU |
| Neo Heliopan AP | Bisdisulizole Disodium, Disodium phenyl dibenzimidazole tetrasulfonate, bisimidazylate, DPDT | 10% | EU, AUS |
| Mexoryl XL | Drometrizole Trisiloxane | 15% | EU, AUS |
| Benzophenone-9 | Uvinul DS 49, CAS 3121-60-6, Sodium Dihydroxy Dimethoxy Disulfobenzophenone [78] | 10% | JP |
| Uvinul T 150 | Octyl triazone, ethylhexyl triazone, EHT | 5% (EU, AUS) 3% (JP)* | EU, AUS |
| Uvinul A Plus | Diethylamino Hydroxybenzoyl Hexyl Benzoate | 10% (EU, JP) | EU, JP |
| Uvasorb HEB | Iscotrizinol, Diethylhexyl butamido triazone, DBT | 10% (EU) 5% (JP)* | EU, JP |
| Parsol SLX | Dimethico-diethylbenzalmalonate, Polysilicone-15 | 10% | EU, AUS, JP |
| Amiloxate | Isopentyl-4-methoxycinnamate, Isoamyl p-Methoxycinnamate, IMC, Neo Heliopan E1000 | 10%* | EU, AUS |
* Time and Extent Application (TEA), Proposed Rule on FDA approval originally expected 2009, now expected 2015.
Many of the ingredients awaiting approval by the FDA were relatively new, and developed to absorb UVA.[79] The 2014 Sunscreen Innovation Act was passed to accelerate the FDA approval process.[80][81]
Inactive ingredients
It is known that SPF is affected by not only the choice of active ingredients and the percentage of active ingredients but also the formulation of the vehicle/base. Final SPF is also impacted by the distribution of active ingredients in the sunscreen, how evenly the sunscreen applies on the skin, how well it dries down on the skin and the pH value of the product among other factors. Changing any inactive ingredient may potentially alter a sunscreen's SPF.[82][83]
When combined with UV filters, added antioxidants can work synergistically to affect the overall SPF value positively. Furthermore, adding antioxidants to sunscreen can amplify its ability to reduce markers of extrinsic photoaging, grant better protection from UV induced pigment formation, mitigate skin lipid peroxidation, improve the photostability of the active ingredients and neutralize reactive oxygen species formed by irradiated photocatalysts (eg., uncoated TiO₂), thus enhancing the efficiency and safety of sunscreens.[84][85][86] Compared with sunscreen alone, it has been shown that the addition of antioxidants has the potential to suppress ROS formation by an additional 1.7-fold for SPF 4 sunscreens and 2.4-fold for SPF 15-to-SPF 50 sunscreens, but the efficacy depends on how well the sunscreen in question has been formulated.[87]
Other inactive ingredients can also assist in photostabilizing unstable UV filters. Cyclodextrins have demonstrated the ability to reduce photodecomposition, protect antioxidants and limit skin penetration past the uppermost skin layers, allowing them to longer maintain the protection factor of sunscreens with UV filters that are highly unstable and/or easily permeate to the lower layers of the skin.[88][89][90] Similarly, film-forming polymers like polyester-8 and polycryleneS1 have the ability to protect the efficacy of older organic UV filters by preventing them from destabilizing due to extended light exposure. These kinds of ingredients also increase the water resistance of sunscreen formulations.[91][92]

In the 2010s & 2020s there has been increasing interest in sunscreens that protect the wearer from the sun's HEVL & Infrared light as well as ultraviolet light. This is due to newer research revealing blue & violet visible light and certain wavelengths of infrared light (eg., NIR, IR-A) work synergistically with UV light in contributing to oxidative stress, free radical generation, dermal cellular damage, suppressed skin healing, decreased immunity, erythema, inflammation, dryness, and several aesthetic concerns, such as: wrinkle formation, loss of skin elasticity and dyspigmentation.[93][94][95][96][97][98][99] Increasingly, a number of commercial sunscreens are being produced that have manufacturer claims regarding skin protection from blue light, infrared light and even air pollution.[99] However, as of 2021 there are no regulatory guidelines or mandatory testing protocols that govern these claims.[87] Historically, the American FDA has only recognized protection from sunburn (via UVB protection) and protection from skin cancer (via SPF 15+ with some UVA protection) as drug/medicinal sunscreen claims, so they do not have regulatory authority over sunscreen claims regarding protecting the skin from damage from these other environmental stressors.[100] Since sunscreen claims not related to protection from ultraviolet light are treated as cosmeceutical claims rather than drug/medicinal claims, the innovative technologies and additive ingredients used to allegedly reduce the damage from these other environmental stressors may vary widely from brand to brand.
Some studies show that mineral sunscreens primarily made with substantially large particles (ie.,neither nano nor micronized) may help protect from visible and infrared light to some degree,[99][87][101] but these sunscreens are often unacceptable to consumers due to leaving an obligatory opaque white cast on the skin. Further research has shown that sunscreens with added iron oxide pigments and/or pigmentary titanium dioxide can provide the wearer with a substantial amount of HEVL protection.[87][102][103][104] Cosmetic chemists have found that other cosmetic-grade pigments can be functional filler ingredients. Mica was discovered to have significant synergistic effects with UVR filters when formulated in sunscreens, in that it can notably increase the formula's ability to protect the wearer from HEVL.[97] Additionally, there is a modest amount of tentative evidence that suggests specific forms of tin oxide may also be viable functional fillers that could supply additional protection from light wavelengths outside of the ultraviolet radiation spectrum when properly formulated with other protective ingredients in sunscreen products. However, independent research on the efficacy of tin oxides is more lacking.[99][105][106][107]
There is a growing amount of research demonstrating that adding various vitamer antioxidants (eg; retinol, alpha tocopherol, gamma tocopherol, tocopheryl acetate, ascorbic acid, ascorbyl tetraisopalmitate, ascorbyl palmitate, sodium ascorbyl phosphate, ubiquinone) and/or a mixture of certain botanical antioxidants (eg; epigallocatechin-3-gallate, b-carotene, vitis vinifera, spirulina extract, chamomile extract, and possibly others) to sunscreens efficaciously aids in reducing damage from the free radicals produced by exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation, visible light, near infrared radiation and infrared-a radiation.[84][108][95][87][109][86] Since sunscreen's active ingredients work preventatively by creating a shielding film on the skin that absorbs, scatters, and reflects light before it can reach the skin, UV filters have been deemed an ideal “first line of defense” against sun damage when exposure can't be avoided. Antioxidants have been deemed a good “second line of defense” since they work responsively by decreasing the overall burden of free radicals that do reach the skin.[97] The degree of the free radical protection from the entire solar spectral range that a sunscreen can offer has been termed the “radical protection factor” (RPF) by some researchers.
Application
SPF 30 or above must be used to effectively prevent UV rays from damaging skin cells. This is the amount that is recommended to prevent against skin cancer. Sunscreen must also be applied thoroughly and re-applied during the day, especially after being in the water. Special attention should be paid to areas like the ears and nose, which are common spots of skin cancer. Ask your dermatologist about what sunscreen is best to use for your specific skin type.[110]
The dose used in FDA sunscreen testing is 2 mg/cm2 of exposed skin.[62] If one assumes an "average" adult build of height 5 ft 4 in (163 cm) and weight 150 lb (68 kg) with a 32-inch (82-cm) waist, that adult wearing a bathing suit covering the groin area should apply approximately 30 g (or 30 ml, approximately 1 oz) evenly to the uncovered body area. This can be more easily thought of as a "golf ball" size amount of product per body, or at least six teaspoonfuls. Larger or smaller individuals should scale these quantities accordingly.[111] Considering only the face, this translates to about 1/4 to 1/3 of a teaspoon for the average adult face.
Some studies have shown that people commonly apply only 1/4 to 1/2 of the amount recommended for achieving the rated sun protection factor (SPF), and in consequence the effective SPF should be downgraded to a 4th root or a square root of the advertised value, respectively.[56] A later study found a significant exponential relation between SPF and the amount of sunscreen applied, and the results are closer to linearity than expected by theory.[112]
Claims that substances in pill form can act as sunscreen are false and disallowed in the United States.[113]
Regulation
- Palau
On 1 January 2020, Palau became the first country in the world to ban sun cream that is harmful to corals and sea life. The ban came into effect immediately after an announcement by President Tommy Remengesau Jr.[114]
- Hawaii
The island state of Hawaii banned the commercial sale of sunscreens containing oxybenzone and octinoxate on January 1, 2021, due to concern of environmental effects linked to the two ingredients and their contribution to increased coral bleaching.[115] This ban is only applicable to sale within the state and to sunscreen products, not other cosmetic materials.
- United States
Sunscreen labeling standards have been evolving in the United States since the FDA first adopted the SPF calculation in 1978.[116] The FDA issued a comprehensive set of rules in June 2011, taking effect in 2012–2013, designed to help consumers identify and select suitable sunscreen products offering protection from sunburn, early skin aging, and skin cancer:[14][117][118]
- To be classified as "broad spectrum", sunscreen products must provide protection against both UVA and UVB, with specific tests required for both.
- Claims of products being "waterproof" or "sweatproof" are prohibited, while "sunblock" and "instant protection" and "protection for more than 2 hours" are all prohibited without specific FDA approval.
- "Water resistance" claims on the front label must indicate how long the sunscreen remains effective and specify whether this applies to swimming or sweating, based on standard testing.
- Sunscreens must include standardized "Drug Facts" information on the container. However, there is no regulation that deems it necessary to mention whether the contents contain nanoparticles of mineral ingredients. (The EU has stricter regulation against the use of nanoparticles, and in 2009 introduced labeling requirements for nanoparticle ingredients in certain sunscreens and cosmetics.)[119]
In 2019, the FDA proposed tighter regulations on sun protection and general safety, including the requirement that sunblock products with SPF greater than 15 must be broad spectrum and a prohibition on products with SPF greater than 60.[120]
In the United States, sunscreen can be purchased using a tax-advantaged health savings account (HSA) or flexible spending account (FSA).[121][122]
Environmental effects
Certain sunscreens in water under ultraviolet light can increase the production of hydrogen peroxide, which damages phytoplankton.[123]
A 2002 study suggests that sunscreen causes an increase in virus abundance in seawater, leading to poor marine environment health similar to that of other pollutants.[124]
A 2008 study that tested different sunscreen brands, protective factors, and concentrations found that they all caused bleaching on hard corals, and the rate of beaching increased with increased quantity of sunscreen. Of the compounds found in sunscreen that were tested separately, "butylparaben, ethylhexylmethoxycinnamate, benzophenone-3 and 4-methylbenzylidene camphor caused complete bleaching even at very low concentrations."[125]
Media reports link oxybenzone in sunscreens to coral bleaching,[126] although some environmental experts dispute the claim.[127] A 2015 study published in the Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology linked oxybenzone to effects on cell culture experiments and juvenile coral,[128] but other sources of pollution such as agricultural run-off and sewage probably have a larger impact on coral reefs.[129] However, the purported link between oxybenzone and coral decline is disputed by some within the environmental community,[126][130][131]
In 2018, the Pacific nation of Palau has become the first country to ban sun creams containing oxybenzone, octinoxate, and some other harmful elements.[132]
A 2019 study of UV filters in oceans found far lower concentrations of oxybenzone than previously reported, and lower than known thresholds for environmental toxicity.[133][134] Additionally, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has indicated that coral decline is associated with effects from climate change (warming oceans, rising water levels, acidification), overfishing, and pollution from agriculture, wastewater, and urban run-off.[135]
History
.JPG.webp)

Early civilizations used a variety of plant products to help protect the skin from sun damage. For example, ancient Greeks used olive oil for this purpose, and ancient Egyptians used extracts of rice, jasmine, and lupine plants whose products are still used in skin care today.[136] Zinc oxide paste has also been popular for skin protection for thousands of years.[137] Among the nomadic sea-going Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines, Malaysia, and Indonesia, a common type of sun protection is a paste called borak or burak, which was made from water weeds, rice and spices. It is used most commonly by women to protect the face and exposed skin areas from the harsh tropical sun at sea.[138] In Myanmar, thanaka, a yellow-white cosmetic paste made of ground bark, is traditionally used for sun protection.
The first ultraviolet B filters were produced in 1928.[139] Followed by the first sunscreen, invented in Australia by chemist H.A. Milton Blake, in 1932[2] formulating with the UV filter 'salol (Phenyl salicylate)' at a concentration of '10%'.[3] Its protection was verified by the University of Adelaide.[4][5] In 1936, L'Oreal released its first sunscreen product, formulated by French chemist Eugène Schueller.[140]
Early adopters of sunscreen were the US military. In 1944, as the hazards of sun overexposure became apparent to soldiers stationed in the Pacific tropics at the height of World War II,[25][140][141][142] Benjamin Green, an airman and later a pharmacist produced Red Vet Pet (for red veterinary petrolatum) for the US military. Sales boomed when Coppertone improved and commercialized the substance under the Coppertone girl and Bain de Soleil branding in the early 1950s. In 1946, Austrian chemist Franz Greiter introduced a product, called Gletscher Crème (Glacier Cream), subsequently became the basis for the company Piz Buin, named in honor of the mountain where Greiter allegedly received the sunburn.[143][144][145]
In 1974, Greiter adapted earlier calculations from Friedrich Ellinger and Rudolf Schulze and introduced the "sun protection factor" (SPF), which has become the global standard for measuring UVB protection.[25][146] It has been estimated that Gletscher Crème had an SPF of 2.
Water-resistant sunscreens were introduced in 1977,[140] and recent development efforts have focused on overcoming later concerns by making sunscreen protection both longer-lasting and broader-spectrum, as well as more appealing to use.[25]
Research
New products are in development such as sunscreens based on bioadhesive nanoparticles. These function by encapsulating commercially used UV filters, while being not only adherent to the skin but also non-penetrant. This strategy inhibits primary UV-induced damage as well as secondary free radicals. Additionally, UV rays can pass through glass windows. And because of this, it's wise to wear sunscreen inside your home, as well as inside your car.[147]
Also UV filters based on sinapate esters are under study.[148]
Notes
- ↑ "Preventing melanoma". Cancer Research UK. Archived from the original on May 22, 2008. Retrieved September 22, 2009.
- 1 2 Rigel, Darrell S.; Weiss, Robert A.; Lim, Henry W.; Dover, Jeffrey S. (January 30, 2004). Photoaging. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8247-5209-5.
- 1 2 Rigel, Darrell S.; Weiss, Robert A.; Lim, Henry W.; Dover, Jeffrey S. (January 30, 2004). Photoaging. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8247-5209-5.
- 1 2 "7 Wonders of South Australia winners: Innovations - ABC (none) - Australian Broadcasting Corporation". www.abc.net.au. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- 1 2 "History Of Hamilton". Hamilton. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ↑ Aldahan, Adam S.; Shah, Vidhi V.; Mlacker, Stephanie; Nouri, Keyvan (December 1, 2015). "The History of Sunscreen". JAMA Dermatology. 151 (12): 1316. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2015.3011. PMID 26650657.
- 1 2 Alain Ko, Stephen (September 1, 2016). ""Physical" vs. "chemical" sunscreens and other sunscreen myths". KindofStephen. Retrieved January 9, 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - 1 2 Cole, Curtis; Shyr, Thomas; Ou-Yang, Hao (January 2016). "Metal oxide sunscreens protect skin by absorption, not by reflection or scattering". Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine. 32 (1): 5–10. doi:10.1111/phpp.12214. ISSN 1600-0781. PMID 26431814. S2CID 20695063.
- ↑ Wong, Michelle (March 30, 2018). "Chemical vs Physical Sunscreens: The Science (with video)". Lab Muffin Beauty Science. Retrieved January 9, 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ "Skin Cancer - Skin Cancer Facts - Common Skin Cancer Types". www.cancer.org. Archived from the original on April 10, 2008.
- ↑ Sunscreens and Photoprotection at eMedicine
- ↑ Poon, Terence S.C.; Barnetson, Ross StC.; Halliday, Gary M. (July 2003). "Prevention of Immunosuppression by Sunscreens in Humans Is Unrelated to Protection from Erythema and Dependent on Protection from Ultraviolet A in the Face of Constant Ultraviolet B Protection". Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 121 (1): 184–190. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12317.x. PMID 12839580.
- ↑ Phytophotodermatitis at eMedicine
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Questions and Answers: FDA announces new requirements for over-the-counter (OTC) sunscreen products marketed in the U.S." Food and Drug Administration. June 23, 2011. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ↑ Gibson LE. "Is sunscreen from last year still good? When does sunscreen expire?". Mayo Clinic.
- ↑ Kanavy HE, Gerstenblith MR (December 2011). "Ultraviolet radiation and melanoma". Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 30 (4): 222–8. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2011.08.003. PMID 22123420.
- ↑ World Cancer Report 2014. World Health Organization. 2014. pp. Chapter 5.14. ISBN 978-9283204299.
- ↑ Azoury SC, Lange JR (October 2014). "Epidemiology, risk factors, prevention, and early detection of melanoma". The Surgical Clinics of North America. 94 (5): 945–62, vii. doi:10.1016/j.suc.2014.07.013. PMID 25245960.
- ↑ Burnett ME, Wang SQ (April 2011). "Current sunscreen controversies: a critical review". Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine. 27 (2): 58–67. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0781.2011.00557.x. PMID 21392107. S2CID 29173997.
- ↑ Kütting B, Drexler H (December 2010). "UV-induced skin cancer at workplace and evidence-based prevention". International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health. 83 (8): 843–54. doi:10.1007/s00420-010-0532-4. PMID 20414668. S2CID 40870536.
- 1 2 Hughes MC, Williams GM, Baker P, Green AC (June 2013). "Sunscreen and prevention of skin aging: a randomized trial". Annals of Internal Medicine. 158 (11): 781–90. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-158-11-201306040-00002. PMID 23732711. S2CID 12250745.
- ↑ Randhawa, Manpreet; Wang, Steven; Leyden, James J.; Cula, Gabriela O.; Pagnoni, Alessandra; Southall, Michael D. (December 2016). "Daily Use of a Facial Broad Spectrum Sunscreen Over One-Year Significantly Improves Clinical Evaluation of Photoaging". Dermatologic Surgery. 42 (12): 1354–1361. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000000879. PMID 27749441. S2CID 37092409.
- ↑ Dresbach SH, Brown W (2008). "Ultraviolet Radiation" (PDF). Ohioline Fact Sheet Series. Ohio State University Extension. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 12, 2008.
- ↑ Australian Government: Therapeutic Goods Administration (July 2009). "A review of the scientific literature on the safety of nanoparticulate titanium dioxide or zinc oxide in sunscreens" (PDF). Archived from the original on April 6, 2011. Retrieved June 15, 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - 1 2 3 4 Lim HW. "Quantum Leaps: New, Improved Sunscreens Have Arrived". The Skin Cancer Foundation. Archived from the original on April 14, 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ "Sunscreen allergy | DermNet NZ". www.dermnetnz.org. Retrieved September 17, 2019.
- ↑ Pfotenhauer, Kim M.; Shubrook, Jay H. (May 1, 2017). "Vitamin D Deficiency, Its Role in Health and Disease, and Current Supplementation Recommendations". Journal of Osteopathic Medicine. 117 (5): 301–305. doi:10.7556/jaoa.2017.055. ISSN 2702-3648. PMID 28459478. S2CID 19068865.
- ↑ "Sunscreen may cause vitamin D deficiency, says study". www.medicalnewstoday.com. May 3, 2017. Retrieved October 27, 2021.
- ↑ Norval M, Wulf HC (October 2009). "Does chronic sunscreen use reduce vitamin D production to insufficient levels?". The British Journal of Dermatology. 161 (4): 732–6. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09332.x. PMID 19663879. S2CID 12276606.
- ↑ Holick MF (December 2004). "Sunlight and vitamin D for bone health and prevention of autoimmune diseases, cancers, and cardiovascular disease". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 80 (6 Suppl): 1678S–88S. doi:10.1093/ajcn/80.6.1678S. PMID 15585788.
- ↑ Sayre RM, Dowdy JC (2007). "Darkness at noon: sunscreens and vitamin D3". Photochemistry and Photobiology. 83 (2): 459–63. doi:10.1562/2006-06-29-RC-956. PMID 17115796. S2CID 23767593.
- ↑ "Vitamin D". nhs.uk. October 23, 2017. Retrieved February 17, 2022.
- ↑ Holick MF (February 2002). "Vitamin D: the underappreciated D-lightful hormone that is important for skeletal and cellular health". Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Obesity. 9 (1): 87–98. doi:10.1097/00060793-200202000-00011. S2CID 87725403.
- ↑ Holick MF (September 2002). "Sunlight and vitamin D: both good for cardiovascular health". Journal of General Internal Medicine. 17 (9): 733–5. doi:10.1046/j.1525-1497.2002.20731.x. PMC 1495109. PMID 12220371.
- ↑ Holick MF (July 2007). "Vitamin D deficiency". The New England Journal of Medicine. 357 (3): 266–81. doi:10.1056/NEJMra070553. PMID 17634462.
- ↑ "Are Vitamin D Levels Jeopardized by Sunscreen?". GEN - Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology News. May 10, 2019. Retrieved May 18, 2019.
- ↑ Young, A.R.; Narbutt, J.; Harrison, G.I.; Lawrence, K.P.; Bell, M.; O'Connor, C.; Olsen, P.; Grys, K.; Baczynska, K.A.; Rogowski‐Tylman, M.; Wulf, H.C.; Lesiak, A.; Philipsen, P.A. (November 2019). "Optimal sunscreen use, during a sun holiday with a very high ultraviolet index, allows vitamin D synthesis without sunburn". British Journal of Dermatology. 181 (5): 1052–1062. doi:10.1111/bjd.17888. PMC 6899952. PMID 31069787. S2CID 148570356.
- ↑ "Sunscreen: The comprehensive guide to sunscreen in Australia". Surf Nation. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ↑ "Sunscreen FAQs". American Academy of Dermatology. Archived from the original on July 21, 2014. Retrieved July 22, 2014.
- ↑ Stege H, Budde M, Grether-Beck S, Richard A, Rougier A, Ruzicka T, Krutmann J (2002). "Sunscreens with high SPF values are not equivalent in protection from UVA induced polymorphous light eruption". European Journal of Dermatology. 12 (4): IV–VI. PMID 12118426.
- ↑ Haywood R, Wardman P, Sanders R, Linge C (October 2003). "Sunscreens inadequately protect against ultraviolet-A-induced free radicals in skin: implications for skin aging and melanoma?". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 121 (4): 862–8. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12498.x. PMID 14632206.
- ↑ Moyal DD, Fourtanier AM (May 2008). "Broad-spectrum sunscreens provide better protection from solar ultraviolet-simulated radiation and natural sunlight-induced immunosuppression in human beings". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 58 (5 Suppl 2): S149-54. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.04.035. PMID 18410801.
- ↑ Berneburg M, Plettenberg H, Medve-König K, Pfahlberg A, Gers-Barlag H, Gefeller O, Krutmann J (May 2004). "Induction of the photoaging-associated mitochondrial common deletion in vivo in normal human skin". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 122 (5): 1277–83. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22502.x. PMID 15140232.
- ↑ "Sunscreen makers sued for misleading claims". Associated Press. April 24, 2006. Retrieved January 5, 2015.
- ↑ Pinnell SR, Fairhurst D, Gillies R, Mitchnick MA, Kollias N (April 2000). "Microfine zinc oxide is a superior sunscreen ingredient to microfine titanium dioxide". Dermatologic Surgery. 26 (4): 309–14. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2000.99237.x. PMID 10759815. S2CID 39864876.
- ↑ "Commission Recommendation of 22 September 2006 on the efficacy of sunscreen products and the claims made relating thereto". Official Journal of the European Union. September 22, 2006. Retrieved September 25, 2009.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ "UV Resource Guide - Sunscreens". Arpansa. December 20, 2008. Archived from the original on November 19, 2009. Retrieved September 25, 2009.
- ↑ "SPF50+ Sunscreen". February 1, 2013. Retrieved February 6, 2014.
- 1 2 "Questions and Answers on the 2007 Sunscreen Proposed Rule". Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on September 21, 2008.
- ↑ Department of Health and Human Services: Food and Drug Administration (June 17, 2011). "Revised Effectiveness Determination; Sunscreen Drug Products for Over-the-Counter Human Use" (PDF). Federal Register. 76 (117): 35672–35678. Retrieved November 21, 2013.
- ↑ Research, Center for Drug Evaluation and (April 23, 2019). "Status of OTC Rulemakings - Rulemaking History for OTC Sunscreen Drug Products". FDA.
- 1 2 "Sunscreen Takes Some Heat: New Dangers, New Rules". June 16, 2011. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ↑ "The Burning Facts" (PDF). 2006. Retrieved December 1, 2017.
- ↑ Moyal D (June 2008). "How to measure UVA protection afforded by sunscreen products". Expert Review of Dermatology. 3 (3): 307–13. doi:10.1586/17469872.3.3.307.
- ↑ "What to Know About Sunscreen Before Buying It". Consumer Reports. May 2014. Retrieved December 20, 2014.
- 1 2 Faurschou A, Wulf HC (April 2007). "The relation between sun protection factor and amount of suncreen applied in vivo". The British Journal of Dermatology. 156 (4): 716–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07684.x. PMID 17493070. S2CID 22599824.
- ↑ "www.colipa.com". June 9, 2008. Archived from the original on June 9, 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ↑ "www.cosmeticseurope.eu". Archived from the original on August 26, 2014.
- 1 2 "Nanotechnology Information Center: Properties, Applications, Research, and Safety Guidelines". American Elements.
- ↑ Schroeder P, Krutmann J (April 2010). "What is needed for a sunscreen to provide complete protection". Skin Therapy Letter. 15 (4): 4–5. PMID 20361168.
- 1 2 Barolet D, Christiaens F, Hamblin MR (February 2016). "Infrared and skin: Friend or foe". Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology. 155: 78–85. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.12.014. PMC 4745411. PMID 26745730.
- 1 2 Kavanaugh EE (September 11, 1998). "Re: Tentative Final Monograph for OTC Sunscreen" (PDF). Cosmetic, Toiletry, and Fragrance Association. Retrieved September 25, 2009.
- ↑ Chatelain E, Gabard B (September 2001). "Photostabilization of butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane (Avobenzone) and ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate by bis-ethylhexyloxyphenol methoxyphenyl triazine (Tinosorb S), a new UV broadband filter". Photochemistry and Photobiology. 74 (3): 401–6. doi:10.1562/0031-8655(2001)074<0401:POBMAA>2.0.CO;2. PMID 11594052.
- ↑ "Parsol 340 – Octocrylene". DSM. Archived from the original on August 3, 2009. Retrieved June 22, 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ Burke KE. "Does sunscreen become ineffective with age?". The Skin Cancer Foundation. Retrieved July 31, 2014.
- ↑ Flindt-Hansen H, Thune P, Larsen TE (1990). "The inhibiting effect of PABA on photocarcinogenesis". Archives of Dermatological Research. 282 (1): 38–41. doi:10.1007/BF00505643. PMID 2317082. S2CID 7535511.
- ↑ Flindt-Hansen H, Thune P, Eeg-Larsen T (1990). "The effect of short-term application of PABA on photocarcinogenesis". Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 70 (1): 72–5. doi:10.2340/00015555707275 (inactive October 31, 2021). PMID 1967881.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of October 2021 (link) - ↑ Osgood PJ, Moss SH, Davies DJ (December 1982). "The sensitization of near-ultraviolet radiation killing of mammalian cells by the sunscreen agent para-aminobenzoic acid". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 79 (6): 354–7. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12529409. PMID 6982950.
- ↑ Mosley CN, Wang L, Gilley S, Wang S, Yu H (June 2007). "Light-induced cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of a sunscreen agent, 2-phenylbenzimidazole in Salmonella typhimurium TA 102 and HaCaT keratinocytes". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 4 (2): 126–31. doi:10.3390/ijerph2007040006. PMC 3728577. PMID 17617675.
- ↑ Hanson KM, Gratton E, Bardeen CJ (October 2006). "Sunscreen enhancement of UV-induced reactive oxygen species in the skin". Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 41 (8): 1205–12. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.06.011. PMID 17015167.
- ↑ Hawaii is about to ban your favorite sunscreen to protect its coral reefs
- 1 2 Lautenschlager S, Wulf HC, Pittelkow MR (August 2007). "Photoprotection". Lancet. 370 (9586): 528–37. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60638-2. PMID 17693182. S2CID 208794122.
- ↑ Benech-Kieffer F, Meuling WJ, Leclerc C, Roza L, Leclaire J, Nohynek G (November–December 2003). "Percutaneous absorption of Mexoryl SX in human volunteers: comparison with in vitro data". Skin Pharmacology and Applied Skin Physiology. 16 (6): 343–55. doi:10.1159/000072929. PMID 14528058. S2CID 32449642.
- ↑ Fourtanier A (October 1996). "Mexoryl SX protects against solar-simulated UVR-induced photocarcinogenesis in mice". Photochemistry and Photobiology. 64 (4): 688–93. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.1996.tb03125.x. PMID 8863475. S2CID 96058554.
- ↑ "Amending Annex VI to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council on cosmetic products". eur-lex.europa.eu. April 21, 2016. Retrieved March 22, 2017.
- ↑ "Regulation No. 1223/2009 on cosmetic products". Official Journal of the European Union. December 22, 2009. Retrieved May 26, 2015.
- ↑ Australian Government: Therapeutic Goods Administration (November 2012). "Australian Regulatory Guidelines for Sunscreens". Retrieved June 21, 2015.
- ↑ "Uvinul Grades" (PDF). Retrieved September 25, 2009.
- ↑ Kapes B (July 2005). "Docs rally for better sun protection — Advances still unavailable in United States". Dermatology Times. 26 (7): 100. Retrieved July 23, 2014.
- ↑ "Sunscreen Innovation Act". United States Congress. November 26, 2014. Retrieved January 5, 2015.
- ↑ Sifferlin A (July 16, 2014). "We're One Step Closer to Better Sunscreen". Time. Retrieved August 1, 2014.
- ↑ Administration, Australian Government Department of Health Therapeutic Goods (August 30, 2019). "Australian Regulatory Guidelines for Sunscreens (ARGS)". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ↑ Center, Timothy Gao, PhD, Jung-Mei Tien and Yoon-Hee Choi, Croda Inc , North American Technical (June 24, 2009). "Sunscreen Formulas With Multilayer Lamella Structure". Cosmetics & Toiletries. Retrieved August 13, 2021.
- 1 2 Wu, Y.; Matsui, M. S.; Chen, J. Z. S.; Jin, X.; Shu, C.-M.; Jin, G.-Y.; Dong, G.-H.; Wang, Y.-K.; Gao, X.-H.; Chen, H.-D.; Li, Y.-H. (March 2011). "Antioxidants add protection to a broad-spectrum sunscreen: Antioxidants add protection to a broad-spectrum sunscreen". Clinical and Experimental Dermatology. 36 (2): 178–187. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2010.03916.x. PMID 20804506. S2CID 25145335.
- ↑ Dahabra, Layan; Broadberry, Grace; Le Gresley, Adam; Najlah, Mohammad; Khoder, Mouhamad (March 18, 2021). "Sunscreens Containing Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Enhanced Efficiency: A Strategy for Skin Cancer Prevention". Molecules. 26 (6): 1698. doi:10.3390/molecules26061698. PMC 8003006. PMID 33803643.
- 1 2 Darr, D; Dunston, S; Faust, H; Pinnell, S (July 1996). "Effectiveness of antioxidants (vitamin C and E) with and without sunscreens as topical photoprotectants". Acta Dermato-venereologica. 76 (4): 264–8. doi:10.2340/0001555576264268 (inactive October 31, 2021). PMID 8869680.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of October 2021 (link) - 1 2 3 4 5 Lim, Henry W.; Arellano-Mendoza, Maria-Ivonne; Stengel, Fernando (March 2017). "Current challenges in photoprotection". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 76 (3): S91–S99. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.09.040. PMID 28038886.
- ↑ Yang, Jing; Wiley, Cody J.; Godwin, Donald A.; Felton, Linda A. (June 2008). "Influence of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on transdermal penetration and photostability of avobenzone". European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. 69 (2): 605–612. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2007.12.015. PMID 18226883.
- ↑ Shokri, J.; Hasanzadeh, D.; Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Dizadji-Ilkhchi, M.; Adibkia, K. (July 10, 2013). "The Effect of Beta-Cyclodextrin on Percutaneous Absorption of Commonly Used Eusolex® Sunscreens". Drug Research. 63 (11): 591–596. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1349089. PMID 23842944.
- ↑ Dahabra, Layan; Broadberry, Grace; Le Gresley, Adam; Najlah, Mohammad; Khoder, Mouhamad (2021). "Sunscreens Containing Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Enhanced Efficiency: A Strategy for Skin Cancer Prevention". Molecules. 26 (6): 1698. doi:10.3390/molecules26061698. PMC 8003006. PMID 33803643.
- ↑ Schaefer, Katie (July 3, 2012). "Polycrylene for Photostabilization and Water Resistance". Cosmetics & Toiletries. Retrieved July 27, 2021.
- ↑ cosmeticsdesign.com. "Hallstar develops photostabilizer for sun care products". cosmeticsdesign.com. Retrieved July 27, 2021.
- ↑ Lademann, J.; Meinke, M. C.; Schanzer, S.; Albrecht, S.; Zastrow, L. (May 2017). "Neue Aspekte bei der Entwicklung von Sonnenschutzmitteln" [New aspects in the development of sunscreening agents]. Der Hautarzt (in German). 68 (5): 349–353. doi:10.1007/s00105-017-3965-9. PMID 28280909.
- ↑ Krutmann, J.; Berneburg, M. (January 2021). "Lichtalterung (Photoaging) der Haut: Was gibt es Neues?" [Sun-damaged skin (photoaging): what is new?]. Der Hautarzt (in German). 72 (1): 2–5. doi:10.1007/s00105-020-04747-4. PMID 33346860.
- 1 2 Souza, Carla; Maia Campos, Patrícia; Schanzer, Sabine; Albrecht, Stephanie; Lohan, Silke B.; Lademann, Jürgen; Darvin, Maxim E.; Meinke, Martina C. (2017). "Radical-Scavenging Activity of a Sunscreen Enriched by Antioxidants Providing Protection in the Whole Solar Spectral Range". Skin Pharmacology and Physiology. 30 (2): 81–89. doi:10.1159/000458158. PMID 28319939. S2CID 6252032.
- ↑ Michalski, Basia; Olasz, Edit (July 2020). "What You Didn't Know About the Sun: Infrared Radiation and Its Role in Photoaging". Plastic Surgical Nursing. 40 (3): 166–168. doi:10.1097/PSN.0000000000000334. PMID 32852443. S2CID 221347292.
- 1 2 3 Piras, Emanuele (May 2, 2018). "Synergy of mica and inorganic UV filters maximizes Blue Light Protection as first defense line" (PDF). The International Federation of Societies of Cosmetic Chemists. Germany: Merck.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ Zastrow, L.; Groth, N.; Klein, F.; Kockott, D.; Lademann, J.; Ferrero, L. (April 2009). "UV, sichtbares Licht, Infrarot: Welche Wellenlängen produzieren oxidativen Stress in menschlicher Haut?" [UV, visible and infrared light. Which wavelengths produce oxidative stress in human skin?]. Der Hautarzt (in German). 60 (4): 310–317. doi:10.1007/s00105-008-1628-6. PMID 19319493.
- 1 2 3 4 "Advanced Sun protection with Titanium Dioxides and Functional Fillers" (PDF). Conselho Regional de Química - IV Região. Merck. June 2017. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ "Labeling and Effectiveness Testing: Sunscreen Drug Products for Over-The-Counter Human Use — Small Entity Compliance Guide". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. March 22, 2018. Retrieved July 31, 2021.
{{cite web}}:|first1=missing|last1=(help) - ↑ Kim, Su Ji; Bae, Jiyoun; Lee, Sung Eun; Lee, Jun Bae; Park, Chun Ho; Lim, Doo Hyeon; Park, Myeong Sam; Ha, Jaehyoun (July 23, 2019). "A novel in vivo test method for evaluating the infrared radiation protection provided by sunscreen products". Skin Research and Technology. 25 (6): 890–895. doi:10.1111/srt.12754. PMID 31338921. S2CID 198194413.
- ↑ Dumbuya, Hawasatu; Grimes, Pearl; Lynch, Stephen; Ji, Kalli; Brahmachary, Manisha; Zheng, Qian; Bouez, Charbel; Wangari-Talbot, Janet (July 1, 2020). "Impact of Iron-Oxide Containing Formulations Against Visible Light-Induced Skin Pigmentation in Skin of Color Individuals". Journal of Drugs in Dermatology. 19 (7): 712–717. doi:10.36849/JDD.2020.5032. PMID 32726103. S2CID 220877124.
- ↑ Bernstein, Eric F.; Sarkas, Harry W.; Boland, Patricia (February 2021). "Iron oxides in novel skin care formulations attenuate blue light for enhanced protection against skin damage". Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. 20 (2): 532–537. doi:10.1111/jocd.13803. PMC 7894303. PMID 33210401.
- ↑ Lyons, Alexis B.; Trullas, Carles; Kohli, Indermeet; Hamzavi, Iltefat H.; Lim, Henry W. (May 2021). "Photoprotection beyond ultraviolet radiation: A review of tinted sunscreens". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 84 (5): 1393–1397. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.079. PMID 32335182. S2CID 216556227.
- ↑ "US Patent for Topical emulsions comprising indium tin oxide coated particles Patent (Patent # 10,004,671 issued June 26, 2018) - Justia Patents Search". patents.justia.com. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ↑ Grabenhofer, Rachel (September 28, 2018). "Patent Pick: Lauder Rides the Infrared Wave with Indium Tin Oxide". Cosmetics & Toiletries. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ↑ , Chonan, Takeshi & Kuno, Hiroko, "Fine Particles of Antimony Tin Oxide for Sunscreen, Dispersion Thereof for Sunscreen Material Formation, Sunscreen Material and Transparent Base Material for Sunscreen", issued 2004-01-08
- ↑ Grether-Beck, Susanne; Marini, Alessandra; Jaenicke, Thomas; Krutmann, Jean (January 2015). "Effective Photoprotection of Human Skin against Infrared A Radiation by Topically Applied Antioxidants: Results from a Vehicle Controlled, Double-Blind, Randomized Study". Photochemistry and Photobiology. 91 (1): 248–250. doi:10.1111/php.12375. PMID 25349107. S2CID 206270691.
- ↑ Carlotti, Maria Eugenia; Ugazio, Elena; Gastaldi, Lucia; Sapino, Simona; Vione, Davide; Fenoglio, Ivana; Fubini, Bice (August 2009). "Specific effects of single antioxidants in the lipid peroxidation caused by nano-titania used in sunscreen lotions". Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology. 96 (2): 130–135. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2009.05.001. PMID 19527937.
- ↑ "Skin Cancer Foundation".
- ↑ "How and why we use sunscreen". Cosmetic, Toiletry & Perfumery Association. Archived from the original on September 18, 2016. Retrieved May 11, 2016.
- ↑ Schalka S, dos Reis VM, Cucé LC (August 2009). "The influence of the amount of sunscreen applied and its sun protection factor (SPF): evaluation of two sunscreens including the same ingredients at different concentrations". Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine. 25 (4): 175–80. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0781.2009.00408.x. PMID 19614894. S2CID 38250220.
- ↑ "Press Announcements - Statement from FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, M.D., on new FDA actions to keep consumers safe from the harmful effects of sun exposure, and ensure the long-term safety and benefits of sunscreens". www.fda.gov. Retrieved August 23, 2018.
- ↑ "Palau is first country to ban 'reef toxic' sun cream". BBC News. January 1, 2020.
- ↑ Raffa, Robert B.; Pergolizzi, Joseph V.; Taylor, Robert; Kitzen, Jan M. (February 2019). "Sunscreen bans: Coral reefs and skin cancer". Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics. 44 (1): 134–139. doi:10.1111/jcpt.12778. PMID 30484882. S2CID 53731228.
- ↑ Department of Health and Human Services: Food and Drug Administration (August 25, 1978). "Sunscreen Drug Products for Over-the-Counter Human Use" (PDF). Federal Register. 43 (166): 38206–38269. Retrieved July 30, 2014.
- ↑ Department of Health and Human Services: Food and Drug Administration (June 17, 2011). "Sunscreen Drug Products for Over-the-Counter Human Use; Final Rules and Proposed Rules" (PDF). Federal Register. 76 (117): 35620–35665. Retrieved August 19, 2014.
- ↑ Department of Health and Human Services: Food and Drug Administration (May 11, 2012). "Sunscreen Drug Products for Over-the-Counter Human Use; Delay of Compliance Dates" (PDF). Federal Register. 77 (92): 27591–27593. Retrieved September 27, 2012.
- ↑ "Is Sunscreen Safe?". Eluxe. June 8, 2014. Archived from the original on April 4, 2015.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ LaMotte S (May 21, 2019). "Majority of sunscreens could flunk proposed FDA standards for safety and efficacy, report to say". CNN. Retrieved May 27, 2019.
- ↑ Carrns, Ann (July 17, 2015). "When Using a Health Savings Account, Know What Is Eligible". The New York Times.
- ↑ Kliff, Sarah (December 3, 2014). "From condoms to defibrillators, the best stuff you can buy with leftover FSA dollars". Vox.
- ↑ Sánchez-Quiles, David; Tovar-Sánchez, Antonio (August 19, 2014). "Sunscreens as a Source of Hydrogen Peroxide Production in Coastal Waters". Environmental Science & Technology. 48 (16): 9037–9042. Bibcode:2014EnST...48.9037S. doi:10.1021/es5020696. hdl:10261/103567. PMID 25069004.
- ↑ Danovaro, R.; Corinaldesi, C. (February 1, 2003). "Sunscreen Products Increase Virus Production Through Prophage Induction in Marine Bacterioplankton". Microbial Ecology. 45 (2): 109–118. doi:10.1007/s00248-002-1033-0. PMID 12545312. S2CID 11379801.
- ↑ Danovaro, Roberto; Bongiorni, Lucia; Corinaldesi, Cinzia; Giovannelli, Donato; Damiani, Elisabetta; Astolfi, Paola; Greci, Lucedio; Pusceddu, Antonio (April 2008). "Sunscreens Cause Coral Bleaching by Promoting Viral Infections". Environmental Health Perspectives. 116 (4): 441–447. doi:10.1289/ehp.10966. PMC 2291018. PMID 18414624.
- 1 2 Hughes T (February 4, 2019). "There's insufficient evidence your sunscreen harms coral reefs". The Conversation.
- ↑ Bogle A (November 11, 2015). "No, your sunscreen isn't killing the world's coral reefs". Mashable. Retrieved April 7, 2019.
- ↑ Downs, C. A.; Kramarsky-Winter, Esti; Segal, Roee; Fauth, John; Knutson, Sean; Bronstein, Omri; Ciner, Frederic R.; Jeger, Rina; Lichtenfeld, Yona; Woodley, Cheryl M.; Pennington, Paul; Cadenas, Kelli; Kushmaro, Ariel; Loya, Yossi (February 2016). "Toxicopathological Effects of the Sunscreen UV Filter, Oxybenzone (Benzophenone-3), on Coral Planulae and Cultured Primary Cells and Its Environmental Contamination in Hawaii and the U.S. Virgin Islands". Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 70 (2): 265–288. doi:10.1007/s00244-015-0227-7. PMID 26487337. S2CID 4243494.
- ↑ Beitsch R. "Some Sunscreens May Kill Corals. Should They Be Banned?".
- ↑ Toxicology, Society of Environmental; Chemistry. "Coral decline—is sunscreen a scapegoat?". phys.org. Retrieved October 27, 2021.
- ↑ Sirois, Jay (July 2019). "Examine all available evidence before making decisions on sunscreen ingredient bans". Science of the Total Environment. 674: 211–212. Bibcode:2019ScTEn.674..211S. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.137. PMID 31004897. S2CID 125082651.
- ↑ "Coral: Palau to ban sunscreen products to protect reefs". BBC News. November 1, 2018.
- ↑ "New study measures UV-filters in seawater and corals from Hawaii". University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science. April 1, 2019. Retrieved June 20, 2019.
- ↑ Mitchelmore, Carys L.; He, Ke; Gonsior, Michael; Hain, Ethan; Heyes, Andrew; Clark, Cheryl; Younger, Rick; Schmitt-Kopplin, Philippe; Feerick, Anna; Conway, Annaleise; Blaney, Lee (June 2019). "Occurrence and distribution of UV-filters and other anthropogenic contaminants in coastal surface water, sediment, and coral tissue from Hawaii". Science of the Total Environment. 670: 398–410. Bibcode:2019ScTEn.670..398M. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.034. PMID 30904653. S2CID 85496503.
- ↑ "What is coral bleaching?". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved April 7, 2019.
- ↑ Nadim S (2005). "Sunscreen Evolution". In Shaath N (ed.). Sunscreens : regulations and commercial development (3 ed.). Boca Raton, Fl.: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0824757946.
- ↑ Craddock PT (1998). 2000 Years of Zinc and Brass. British Museum. p. 27. ISBN 978-0-86159-124-4.
- ↑ Tilmantaite B (March 20, 2014). "In Pictures: Nomads of the sea". Al Jazeera. Retrieved December 22, 2014.
- ↑ Ma, Yangmyung; Yoo, Jinah (April 2021). "History of sunscreen: An updated view". Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. 20 (4): 1044–1049. doi:10.1111/jocd.14004. PMID 33583116. S2CID 231928055.
- 1 2 3 Rigel DS (2004). Photoaging. Hoboken: Informa Healthcare. pp. 73–74. ISBN 9780824752095.
- ↑ Wang SQ, Hu JY. "Challenges in Making an Effective Sunscreen". The Skin Cancer Foundation. Retrieved June 12, 2014.
- ↑ Maceachern WN, Jillson OF (January 1964). "A Practical Sunscreen— "Red Vet Pet"". Archives of Dermatology. 89 (1): 147–50. doi:10.1001/archderm.1964.01590250153027. PMID 14070829.
- ↑ Shaath NA, ed. (2005). Sunscreens: Regulations and Commercial Development, Third Edition. Taylor & Francis Group.
- ↑ "Sunscreen: A History". The New York Times. June 23, 2010. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ↑ "Gletscher Crème". 2010-04-22. Piz Buin. Archived from the original on May 12, 2010. Retrieved June 29, 2013.
- ↑ Lim HW, Hönigsmann H, Hawk JL, eds. (2007). Photodermatology. CRC Press. p. 6. ISBN 9781420019964. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ↑ Deng, Yang; Ediriwickrema, Asiri; Yang, Fan; Lewis, Julia; Girardi, Michael; Saltzman, W. Mark (December 2015). "A sunblock based on bioadhesive nanoparticles". Nature Materials. 14 (12): 1278–1285. Bibcode:2015NatMa..14.1278D. doi:10.1038/nmat4422. PMC 4654636. PMID 26413985.
- ↑ Horbury, Michael D.; Holt, Emily L.; Mouterde, Louis M. M.; Balaguer, Patrick; Cebrián, Juan; Blasco, Laurent; Allais, Florent; Stavros, Vasilios G. (December 2019). "Towards symmetry driven and nature inspired UV filter design". Nature Communications. 10 (1): 4748. Bibcode:2019NatCo..10.4748H. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12719-z. PMC 6802189. PMID 31628301. S2CID 204757709.
External links
- Does it work, or not? – illustrated explanation of how UV light is absorbed by chemicals in sunscreen from Wired
- 56% of Americans Rarely or Never Use Sunscreen - A survey conducted about the sunscreen habits of modern Americans.