Superficial fibular nerve
| Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve | |
|---|---|
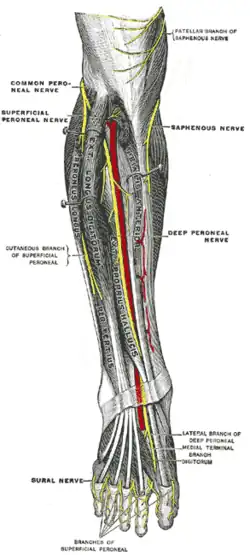 Deep nerves of the front of the leg. | |
| Details | |
| From | Common peroneal nerve |
| To | Medial dorsal cutaneous nerve, intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus fibularis superficialis, nervus peroneus superficialis |
| TA98 | A14.2.07.050 |
| TA2 | 6574 |
| FMA | 44699 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The superficial fibular nerve (also known as superficial peroneal nerve) innervates the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles and the skin over the antero-lateral aspect of the leg along with the greater part of the dorsum of the foot (with the exception of the first web space, which is innervated by the deep fibular nerve).
Structure
Lateral side of the leg
The superficial fibular nerve is the main nerve of the lateral compartment of the leg. It begins at the lateral side of the neck of fibula, and runs through the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles. In the middle third of the leg, it descends between the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis, and then reaches the anterior border of the fibularis brevis to enter the groove between the fibularis brevis and the extensor digitorum longus under the deep fascia of leg. It becomes superficial at the junction of upper two-thirds and lower one-thirds of the leg by piercing the deep fascia. The superficial fibular nerve gives off several branches in the leg.[1]
- Muscular branches to fibularis longus and fibularis brevis[1]
- Cutaneous branches supply the skin over the lower one-third of the lateral side of the leg and greater part of the dorsum of the foot except for areas that are supplied by the saphenous nerve (medial side of the leg), the sural nerve (lateral side of the foot), the deep fibular nerve (first webbed space of the dorsum of the foot), the medial, and the lateral plantar nerves (plantar surface of the foot).[1]
Foot
At the junction between the upper two-thirds and lower one-thirds of the leg, the superficial fibular nerve is divided into medial dorsal cutaneous nerve (medial branch) and intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve (lateral branch).[1]
- The medial branch crosses the ankle and divides into two dorsal digital nerves—one for the medial side of the big toe, and the other for the adjoining sides of the second and third toes.[1]
- The lateral branch divides into two dorsal digital nerves for the adjoining sides of the third and fourth toes and the fourth and fifth toes.[1]
- Communicating branches: The medial branch communicates with saphenous nerve and the deep fibular nerve, while the lateral branch communicates with the sural nerve.[1]
Clinical significance
Injury to the nerve can result in an inability to evert the foot and loss of sensation over the dorsum of the foot (with the exception of the first web space between the great toe and the second toe, where the deep fibular nerve innervates).
Additional images
 Cutaneous nerves of the right lower extremity. Front and posterior views.
Cutaneous nerves of the right lower extremity. Front and posterior views.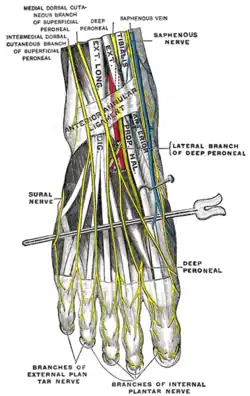 Nerves of the dorsum of the foot.
Nerves of the dorsum of the foot.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Krishna, Garg (2010). "Front, lateral, and medial sides of leg and dorsum of foot (Chapter 8)". BD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy (Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical) Volume 2 - Lower limb, abdomen, and pelvis (Fifth ed.). India: CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd. p. 109,110. ISBN 978-81-239-1864-8.
External links
- Anatomy photo:15:st-0505 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Leg - Nerves"