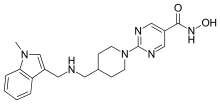
Quisinostat
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | JNJ-26481585 |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | oral[1] |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H26N6O2 |
| Molar mass | 394.479 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Quisinostat (USAN;[2] development code JNJ-26481585) is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of cancer. It is a "second generation" histone deacetylase inhibitor with antineoplastic activity.[3][4][5] It is highly potent against class I and II HDACs.[6]
It was developed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals and licensed to NewVac LLC.[7]
Preclinical studies show that quisinostat amplifies HDAC-repressed expression of E-cadherin, leading to a reversal of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in tumor cells.[7] Results of a phase I trials in patients with multiple myeloma in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone were published in 2016.[8]
References
- ↑ "NCI Drug Dictionary". National Cancer Institute. 2 February 2011.
- ↑ "Quisinostat" (PDF). American Medical Association.
- ↑ Tong WG, Wei Y, Stevenson W, Kuang SQ, Fang Z, Zhang M, et al. (February 2010). "Preclinical antileukemia activity of JNJ-26481585, a potent second-generation histone deacetylase inhibitor". Leukemia Research. 34 (2): 221–8. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2009.07.024. PMID 19682743.
- ↑ Stühmer T, Arts J, Chatterjee M, Borawski J, Wolff A, King P, et al. (May 2010). "Preclinical anti-myeloma activity of the novel HDAC-inhibitor JNJ-26481585". British Journal of Haematology. 149 (4): 529–36. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08126.x. PMID 20331455. S2CID 42077659.
- ↑ "Quisinostat". NCI Drug Dictionary. National Cancer Institute.
- ↑ Carol H, Gorlick R, Kolb EA, Morton CL, Manesh DM, Keir ST, et al. (February 2014). "Initial testing (stage 1) of the histone deacetylase inhibitor, quisinostat (JNJ-26481585), by the Pediatric Preclinical Testing Program". Pediatric Blood & Cancer. 61 (2): 245–52. doi:10.1002/pbc.24724. PMC 4225045. PMID 24038993.
- 1 2 LLC, NewVac. "NewVac Reports Primary Endpoint Met in Phase II Clinical Trial of Quisinostat in Combination with Paclitaxel and Carboplatin in Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer". www.prnewswire.com.
- ↑ Moreau P, Facon T, Touzeau C, Benboubker L, Delain M, Badamo-Dotzis J, et al. (July 2016). "Quisinostat, bortezomib, and dexamethasone combination therapy for relapsed multiple myeloma". Leukemia & Lymphoma. 57 (7): 1546–59. doi:10.3109/10428194.2015.1117611. PMID 26758913. S2CID 42026457.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.